【深度学习】利用OpenCV+ConvNets检测几何图形

人工智能领域中增长最快的子领域之一是自然语言处理(NLP),它处理计算机与人类(自然)语言之间的交互,特别是如何编程计算机以处理和理解大量自然语言数据。
自然语言处理通常涉及语音识别、自然语言理解和自然语言生成等。其中,命名实体识别(NER)等信息提取问题正迅速成为NLP的基础应用之一。在这篇文章中,我们将分享一个解决执行NER时出现的最棘手问题之一的解决方案。

深度学习的最新发展导致了可用于实体提取和其他NLP相关任务的复杂技术的迅速发展。通常,企业级OCR软件(ABBY、ADLIB等)用于将大量非结构化和基于图像的文档转换为完全可搜索的PDF和PDF/A,人们可以使用最先进的算法(BERT、ELMo等)创建高度上下文化的语言模型来推断提取的信息并实现NLP目标。
但实际上,并非所有文档都仅由基于语言的数据组成。文档可以具有许多其他非语言元素,例如单选按钮、签名块或某些其他几何形状,这些元素可能包含有用的信息,但无法通过OCR或上述任何算法轻松处理。因此,需要设计一个专门的解决方案来识别和处理这些元素。

步骤1:将文档(PDF等)转换为图像文件。编写一个基于OpenCV API的启发式代码来提取所有可能的图像片段,此代码应针对覆盖率而不是准确性进行优化。
步骤2:相应地标记步骤1中提取的图像。创建一个基于CNN的深度学习网络,并根据标记的图像对其进行培训,这一步将保证准确性。
步骤3:创建一个Sklearn pipeline,集成上述两个步骤,以便在接收文档时,提取所有潜在图像,然后使用经过训练的CNN模型预测所需形状的图像。
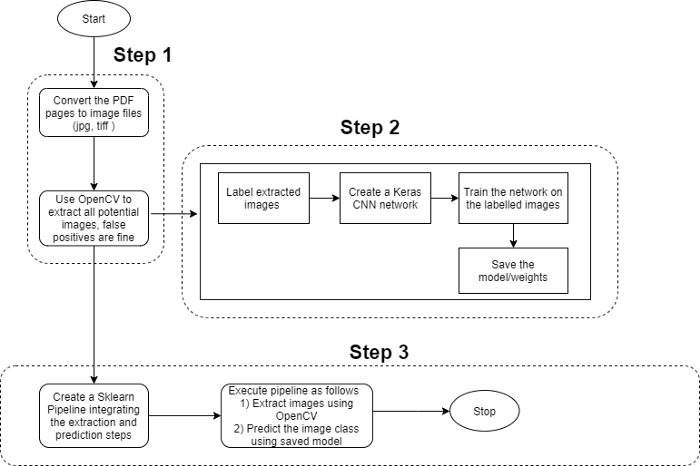
需要注意的是,OpenCV代码尽可能多的识别所需形状的图像段。本质上,我们需要有一个宽的检测范围,不必担心误报,它们将由后续的ConvNet模型处理。之所以选择CNN进行图像分类,是因为它易于建模和快速建模,但只要性能和精度在可接受的范围内,就可以使用任何其他选择的算法。Pipelining 在构造ML代码中起着关键作用,它有助于简化工作流程和强制执行步骤的顺序。
第1步:OpenCV
此代码具有双重用途:
1)创建训练/测试数据
2)在集成到管道中时提取图像段
提取代码目前可以检测2种类型(单选按钮和复选框),但通过在ShapeFinder类下添加新方法,可以轻松支持其他对象,下面是用于识别正方形/矩形(也称为复选框)的代码片段。
#detect checkbox/squaredef extract_quads(self,image_arr,name_arr):if len(image_arr) > 0:for index,original_image in enumerate(image_arr):#to store extracted imagesextracted_quad = []image = original_image.copy()#grayscale only if its not alreadyif len(image.shape) > 2:gray = cv2.cvtColor(image.copy(), cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)else:gray = image.copy()#image preprocessing for quadrilateralsimg_dilate = self.do_quad_imageprocessing(gray,self.blocksize,self.thresh_const,self.kernelsize)if len(img_dilate) > 0:try:#detect contourscnts = cv2.findContours(img_dilate.copy(), cv2.RETR_LIST, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)cnts = imutils.grab_contours(cnts)#loop through detected contoursfor c in cnts:peri = cv2.arcLength(c, True)approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(c, (self.epsilon)* peri, True)#bounding rec cordinates(x, y, w, h) = cv2.boundingRect(approx)#get the aspect ratioaspectratio = float(w/h)area = cv2.contourArea(c)if area < self.rec_max_area and area > self.rec_min_area and (aspectratio >= self.aspect_ratio[0] and aspectratio <= self.aspect_ratio[1]):#check if there are 4 corners in the polygonif len(approx) == 4:cv2.drawContours(original_image,[c], 0, (0,255,0), 2)roi = original_image[y:y+h, x:x+w]extracted_quad.append(roi)except Exception as e:print('The following exception occured during quad shape detection: ',e)self.extracted_img_data.append([original_image,extracted_quad,name_arr[index]])else:print('No image is found during the extraction process')
使用pdf2image将pdf转换为图像:
def Img2Pdf(dirname):images = []#get the pdf filefor x in os.listdir(dirname):if (dirname.split('.')[1]) == 'pdf':pdf_filename = ximages_from_path = convert_from_path(os.path.join(dirname),dpi=300, poppler_path = r'C:\Program Files (x86)\poppler-0.68.0_x86\poppler-0.68.0\bin')for image in images_from_path:images.append(np.array(image))return images
第二步:卷积神经网络
由于提取的图像片段将具有相对较小的尺寸,简单的3层CNN将为我们提供帮助,但我们仍然需要加入一些正则化和Adam来优化输出。
网络应针对每种类型的图像样本分别进行训练,以获得更好的精度。如果添加了新的图像形状,可以创建一个新的网络,但现在我们对复选框和单选按钮都使用了相同的网络。它目前只是一个二进制分类,但进一步的分类也可以这样做:
勾选复选框
空复选框
其他
#keras thingsfrom keras.utils import to_categoricalfrom keras import layersfrom keras import modelsfrom keras.regularizers import l2Y_test_orig = to_categorical(Y_test_orig, num_classes=2)Y_train_orig = to_categorical(Y_train_orig, num_classes=2)# 3 layer ConvNetmodel = models.Sequential()model.add(layers.Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu',input_shape=(32,32,1)))model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)))model.add(layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu'))model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)))model.add(layers.Conv2D(128, (3, 3), activation='relu'))model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)))#dense layermodel.add(layers.Flatten())#add the regulizermodel.add(layers.Dense(128, activation='linear', activity_regularizer=l2(0.0003)))model.add(layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'))model.add(layers.Dense(2, activation='sigmoid'))model.summary()from keras.optimizers import Adamopt = Adam(lr=0.001)model.compile(optimizer=opt, loss=keras.losses.categorical_crossentropy, metrics=['accuracy'])ntrain = len(X_train_orig)nval = len(X_test_orig)X_train_orig = X_train_orig.reshape((len(X_train_orig),32,32,1))X_test_orig = X_test_orig.reshape((len(X_test_orig),32,32,1))train_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale = 1./255,rotation_range = 40, width_shift_range = .2,height_shift_range = .2, shear_range = .2, zoom_range = .2, horizontal_flip = True)val_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale = 1./255)train_generator = train_datagen.flow(X_train_orig,Y_train_orig,batch_size=32)val_generator = val_datagen.flow(X_test_orig,Y_test_orig,batch_size = 32)#X_train_orig, X_test_orig, Y_train_orig,Y_test_orighistory = model.fit_generator(train_generator,steps_per_epoch = ntrain/32, epochs = 64, validation_data = val_generator, validation_steps = nval/32 )
第3步中,我们将把所有内容整合在一个Sklearn pipeline中,并通过predict函数将其公开。我们没有介绍的一个重要功能是将复选框或单选按钮与文档中相应的文本相关联。在实际应用中,仅仅检测没有关联的元素是毫无用处的。
GITHUB代码链接:
https://github.com/nebuchadnezzar26/Shape-Detector
往期精彩回顾 本站qq群554839127,加入微信群请扫码:
