CentOS 7 系统优化脚本
在公众号后台回复:JGNB,可获取杰哥原创的 PDF 手册。
一、介绍
作为一名运维,经常会部署各种用途的操作系统,但在这些工作中,我们会发现很多工作其实是重复性的劳动,操作的内容也是大同小异,基于这类情况,我们可以把相同的操作做成统一执行的脚本,不同的东西作为变量手动输入。节约下来的时间不就可以做更多有意义的事情吗?
最近在粉丝有推荐下发现一款比较好用的shell源码,也基于此改编了一下,分享给大家。
二、菜单
主菜单:
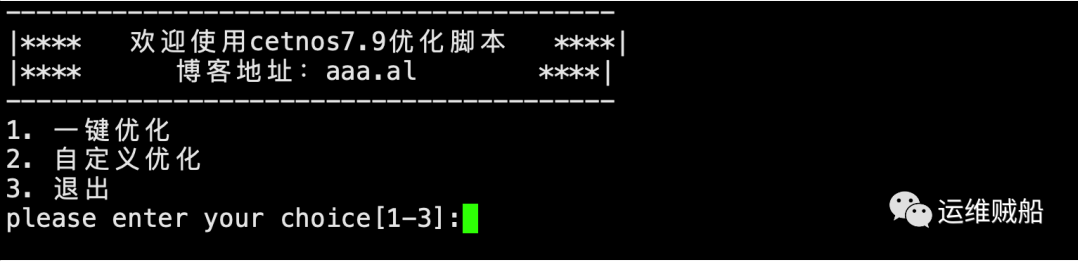
二级菜单:
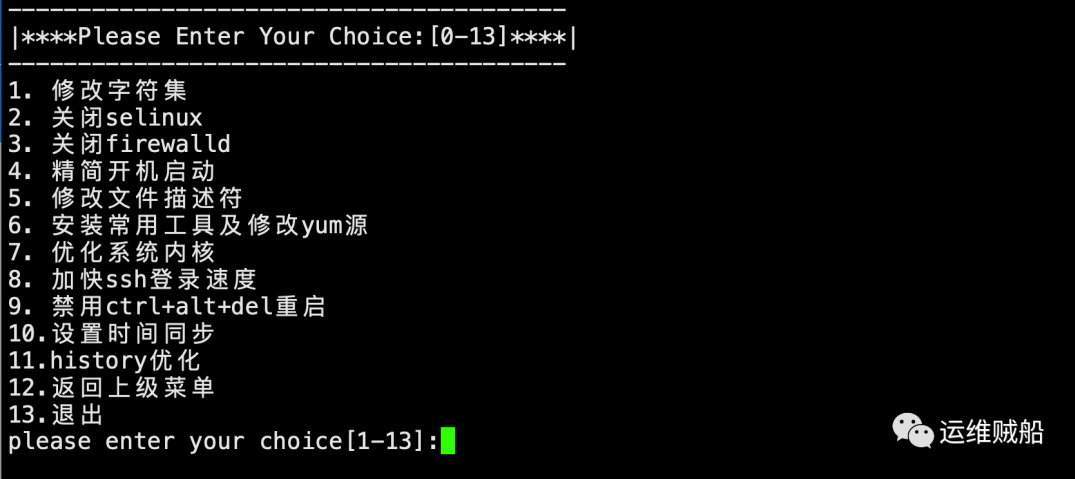
主要实现系统的各类优化,比如常用的修改字符集、关闭selinux、关闭防火墙、安装常用工具和加快ssh登录等功能。
三、源码
#!/bin/sh
. /etc/rc.d/init.d/functions
export LANG=zh_CN.UTF-8
#一级菜单
menu1()
{
clear
cat <<eof
----------------------------------------
|**** 欢迎使用cetnos7.9优化脚本 ****|
|**** 博客地址: aaa.al ****|
----------------------------------------
1. 一键优化
2. 自定义优化
3. 退出
EOF
read -p "please enter your choice[1-3]:" num1
}
#二级菜单
menu2()
{
clear
cat <<eof
----------------------------------------
|****Please Enter Your Choice:[0-13]****|
----------------------------------------
1. 修改字符集
2. 关闭selinux
3. 关闭firewalld
4. 精简开机启动
5. 修改文件描述符
6. 安装常用工具及修改yum源
7. 优化系统内核
8. 加快ssh登录速度
9. 禁用ctrl+alt+del重启
10.设置时间同步
11.history优化
12.返回上级菜单
13.退出
EOF
read -p "please enter your choice[1-13]:" num2
}
#1.修改字符集
localeset()
{
echo "========================修改字符集========================="
cat > /etc/locale.conf <<eof
LANG="zh_CN.UTF-8"
#LANG="en_US.UTF-8"
SYSFONT="latarcyrheb-sun16"
EOF
source /etc/locale.conf
echo "#cat /etc/locale.conf"
cat /etc/locale.conf
action "完成修改字符集" /bin/true
echo "==========================================================="
sleep 2
}
#2.关闭selinux
selinuxset()
{
selinux_status=`grep "SELINUX=disabled" /etc/sysconfig/selinux | wc -l`
echo "========================禁用SELINUX========================"
if [ $selinux_status -eq 0 ];then
sed -i "s#SELINUX=enforcing#SELINUX=disabled#g" /etc/sysconfig/selinux
setenforce 0
echo '#grep SELINUX=disabled /etc/sysconfig/selinux'
grep SELINUX=disabled /etc/sysconfig/selinux
echo '#getenforce'
getenforce
else
echo 'SELINUX已处于关闭状态'
echo '#grep SELINUX=disabled /etc/sysconfig/selinux'
grep SELINUX=disabled /etc/sysconfig/selinux
echo '#getenforce'
getenforce
fi
action "完成禁用SELINUX" /bin/true
echo "==========================================================="
sleep 2
}
#3.关闭firewalld
firewalldset()
{
echo "=======================禁用firewalld========================"
systemctl stop firewalld.service &> /dev/null
echo '#firewall-cmd --state'
firewall-cmd --state
systemctl disable firewalld.service &> /dev/null
echo '#systemctl list-unit-files | grep firewalld'
systemctl list-unit-files | grep firewalld
action "完成禁用firewalld,生产环境下建议启用!" /bin/true
echo "==========================================================="
sleep 5
}
#4.精简开机启动
chkset()
{
echo "=======================精简开机启动========================"
systemctl disable auditd.service
systemctl disable postfix.service
systemctl disable dbus-org.freedesktop.NetworkManager.service
echo '#systemctl list-unit-files | grep -E "auditd|postfix|dbus-org\.freedesktop\.NetworkManager"'
systemctl list-unit-files | grep -E "auditd|postfix|dbus-org\.freedesktop\.NetworkManager"
action "完成精简开机启动" /bin/true
echo "==========================================================="
sleep 2
}
#5.修改文件描述符
limitset()
{
echo "======================修改文件描述符======================="
echo '* - nofile 65535'>/etc/security/limits.conf
ulimit -SHn 65535
echo "#cat /etc/security/limits.conf"
cat /etc/security/limits.conf
echo "#ulimit -Sn ; ulimit -Hn"
ulimit -Sn ; ulimit -Hn
action "完成修改文件描述符" /bin/true
echo "==========================================================="
sleep 2
}
#6.安装常用工具及修改yum源
yumset()
{
echo "=================安装常用工具及修改yum源==================="
yum install wget -y &> /dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0 ];then
cd /etc/yum.repos.d/
\cp CentOS-Base.repo CentOS-Base.repo.$(date +%F)
ping -c 1 mirrors.aliyun.com &> /dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0 ];then
wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo &> /dev/null
yum clean all &> /dev/null
yum makecache &> /dev/null
else
echo "无法连接网络"
exit $?
fi
else
echo "wget安装失败"
exit $?
fi
yum -y install ntpdate lsof net-tools telnet vim lrzsz tree nmap nc sysstat &> /dev/null
action "完成安装常用工具及修改yum源" /bin/true
echo "==========================================================="
sleep 2
}
#7. 优化系统内核
kernelset()
{
echo "======================优化系统内核========================="
chk_nf=`cat /etc/sysctl.conf | grep conntrack |wc -l`
if [ $chk_nf -eq 0 ];then
cat >>/etc/sysctl.conf<<eof
net.ipv4.tcp_fin_timeout = 2
net.ipv4.tcp_tw_reuse = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_tw_recycle = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_time = 600
net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 4000 65000
net.ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlog = 16384
net.ipv4.tcp_max_tw_buckets = 36000
net.ipv4.route.gc_timeout = 100
net.ipv4.tcp_syn_retries = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_synack_retries = 0
net.core.somaxconn = 16384
net.core.netdev_max_backlog = 16384
net.ipv4.tcp_max_orphans = 16384
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_max = 25000000
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_established = 180
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_time_wait = 120
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_close_wait = 60
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_fin_wait = 120
EOF
sysctl -p
else
echo "优化项已存在。"
fi
action "内核调优完成" /bin/true
echo "==========================================================="
sleep 2
}
#8.加快ssh登录速度
sshset()
{
echo "======================加快ssh登录速度======================"
sed -i 's#^GSSAPIAuthentication yes$#GSSAPIAuthentication no#g' /etc/ssh/sshd_config
sed -i 's/#UseDNS yes/UseDNS no/g' /etc/ssh/sshd_config
systemctl restart sshd.service
echo "#grep GSSAPIAuthentication /etc/ssh/sshd_config"
grep GSSAPIAuthentication /etc/ssh/sshd_config
echo "#grep UseDNS /etc/ssh/sshd_config"
grep UseDNS /etc/ssh/sshd_config
action "完成加快ssh登录速度" /bin/true
echo "==========================================================="
sleep 2
}
#9. 禁用ctrl+alt+del重启
restartset()
{
echo "===================禁用ctrl+alt+del重启===================="
rm -rf /usr/lib/systemd/system/ctrl-alt-del.target
action "完成禁用ctrl+alt+del重启" /bin/true
echo "==========================================================="
sleep 2
}
#10. 设置时间同步
ntpdateset()
{
echo "=======================设置时间同步========================"
yum -y install ntpdate &> /dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0 ];then
/usr/sbin/ntpdate time.windows.com
echo "*/5 * * * * /usr/sbin/ntpdate ntp.aliyun.com &>/dev/null" >> /var/spool/cron/root
else
echo "ntpdate安装失败"
exit $?
fi
action "完成设置时间同步" /bin/true
echo "==========================================================="
sleep 2
}
#11. history优化
historyset()
{
echo "========================history优化========================"
chk_his=`cat /etc/profile | grep HISTTIMEFORMAT |wc -l`
if [ $chk_his -eq 0 ];then
cat >> /etc/profile <<'EOF'
#设置history格式
export HISTTIMEFORMAT="[%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S] [`whoami`] [`who am i|awk '{print $NF}'|sed -r 's#[()]##g'`]: "
#记录shell执行的每一条命令
export PROMPT_COMMAND='\
if [ -z "$OLD_PWD" ];then
export OLD_PWD=$PWD;
fi;
if [ ! -z "$LAST_CMD" ] && [ "$(history 1)" != "$LAST_CMD" ]; then
logger -t `whoami`_shell_dir "[$OLD_PWD]$(history 1)";
fi;
export LAST_CMD="$(history 1)";
export OLD_PWD=$PWD;'
EOF
source /etc/profile
else
echo "优化项已存在。"
fi
action "完成history优化" /bin/true
echo "==========================================================="
sleep 2
}
#控制函数
main()
{
menu1
case $num1 in
1)
localeset
selinuxset
firewalldset
chkset
limitset
yumset
kernelset
sshset
restartset
ntpdateset
historyset
;;
2)
menu2
case $num2 in
1)
localeset
;;
2)
selinuxset
;;
3)
firewalldset
;;
4)
chkset
;;
5)
limitset
;;
6)
yumset
;;
7)
kernelset
;;
8)
sshset
;;
9)
restartset
;;
10)
ntpdateset
;;
11)
historyset
;;
12)
main
;;
13)
exit
;;
*)
echo 'Please select a number from [1-13].'
;;
esac
;;
3)
exit
;;
*)
echo 'Err:Please select a number from [1-3].'
sleep 3
main
;;
esac
}
main $*
将其保存为init.sh,然后赋予执行权限后执行即可。
chmod +x init.sh && ./init.sh
如果这样来回地复制粘贴很麻烦,也可以通过我的一键命令执行,同样能达到上面的效果:
bash -c "$(curl -L s.aaa.al/init.sh)"
最后,如果大家有想实现的功能,也可以在原有脚本的基础上进行修改实现。
推荐阅读:
超硬核!11 个非常实用的 Python 和 Shell 拿来就用脚本实例!

评论
