Vuex 更好的替代品 Pinia,真香
来自:掘金,作者:凯哥爱吃皮皮虾
链接:https://juejin.cn/post/7068113574043844622
Pinia
pinia 目前已经是 vue 官方正式的状态库。适用于 vue2 和 vue3,本文只描述vue3的写法。

pinia 的优势
相对于以前的 vuex,pinia具有以下优势
-
更简单的写法,代码更清晰简洁,支持 composition api和options api语法 -
更完善的 typescript 支持,无需创建自定义复杂的包装类型来支持 TypeScript,所有内容都是类型化的,并且 API 的设计方式尽可能利用 TS 类型推断 -
非常轻量,只有1kb的大小 -
不需要再注入魔法字符串等进行调用
安装
yarn add pinia
// or
npm install pinia
定义、使用store
创建一个 pinia 并传递给 vue 应用
import { createPinia } from pinia
import { createApp } from vue
import App from ./app.vue
createApp(App).use(createPinia()).mount( #app )
定义store
store的定义是通过 defineStore 这个函数,
它需要一个唯一的名称,该名称可以作为第一个参数传递,也可以用 id 熟悉传递。
import { defineStore } from pinia
export const useMainStore = defineStore( main , {
// other options...
})
import { defineStore } from pinia
export const useMainStore = defineStore({
id: main
// other options...
})
该 id 是必要的,主要是用于 vue devtools
使用store
import { useMainStore } from @/stores/main
export default defineComponent({
setup() {
const store = useMainStore()
return {
store,
}
},
})
上述代码中,useMainStore实例化后的,我们就可以在 store 上访问 state、getters、actions 等(pinia中没有mutations)。
该 store 是一个 reactive 对象,所以不需要 “.value”,也不能对其进行解构使用,否则失去响应性(类似 props)。
storeToRefs
如果一定要对其进行解构使用,可以使用 storeToRefs ,类似 vue3 中的 toRefs
import { storeToRefs } from pinia
export default defineComponent({
setup() {
const store = useMainStore()
const { user, company } = storeToRefs(store)
return {
user,
company
}
},
})
state
定义state
在 pinia 中,定义 state 是在函数中返回 state 初始状态
import { defineStore } from pinia
const useMainStore = defineStore( main , {
state: () => ({
teacherName: 艾伦 ,
userList: [
{ name: 小明 , age: 18 },
{ name: 小李 , age: 15 },
{ name: 小白 , age: 16 },
],
}),
})
export default useMainStore
访问state
可以通过store 实例直接访问
import useMainStore from @/store/main
export default defineComponent({
setup() {
const mainStore = useMainStore()
const teacherName = computed(() => mainStore.teacherName)
const userList = computed(() => mainStore.userList)
return {
teacherName,
userList,
}
},
})
也可以直接修改状态
import useMainStore from @/store/main
export default defineComponent({
setup() {
const mainStore = useMainStore()
function change() {
mainStore.teacherName = 米利
mainStore.userList.push({
name: 小琪 ,
age: 19
})
}
return {
change
}
},
})
虽然可以直接修改,但是出于代码结构来说,全局的状态管理还是不要直接在各个组件处随意修改状态,应放于 action 中统一方法修改(没有mutation了)
重置状态
可以通过调用store 上的方法将状态重置为初始状态
const mainStore = useMainStore()
mainStore.$reset()
$patch
修改state还可以通过使用 $patch 方法
$patch 可以同时修改多个值,举个例子
import useMainStore from @/store/main
export default defineComponent({
setup() {
const mainStore = useMainStore()
mainStore.$patch({
teacherName: 德普 ,
userList: [
{ name: 小明 , age: 18 },
{ name: 小李 , age: 15 },
]
})
return {}
},
})
但是,这种写法的在修改数组时,例如我只想要把 userList 的中第一项"小明"的age 改为 20,也需要传入整个包括所有成员的数组,这无疑增加了书写成本和风险,于是一般都推荐使用以下的传入一个函数的写法
mainStore.$patch((state)=>{
state.teacherName = 德普
state.userList[0].age = 20
})
监听订阅state
通过 store.$subscribe() 的方法,
该方法的第一个参数接受一个回调函数,该函数可以在 state 变化时触发
const subscribe = mainStore.$subscribe((mutation, state) => {
console.log(mutation)
console.log(state)
})
如上所示,该回调函数的两个参数
其中 state 是 mainStore 实例,而 mutation 打印如下
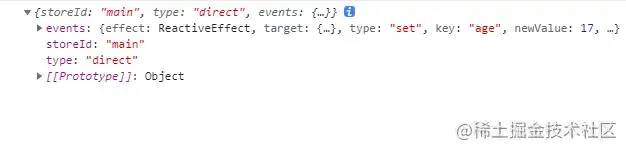
可以发现,打印结果的mutation对象主要包含三个属性
-
events : 是这次state改变的具体数据,包括改变前的值和改变后的值等等数据 -
storeId :是当前store的id -
type:type表示这次变化是通过什么产生的,主要有三个分别是 -
“direct” :通过 action 变化的 -
”patch object“ :通过 $patch 传递对象的方式改变的 -
“patch function” :通过 $patch 传递函数的方式改变的
停止监听
上面代码中,调用mainStore.$subscribe返回的值(即上方示例的 subscribe 变量)可以停止订阅
subscribe()
store.$subscribe() 的方法的第二个参数options对象,是各种配置参数,包括
detached属性,其值是一个布尔值,默认是 false, 正常情况下,当 订阅所在的组件被卸载时,订阅将被停止删除,如果设置detached值为 true 时,即使所在组件被卸载,订阅依然可以生效。
其他属性主要还有 immediate、deep、flush 等等,和 vue3 watch的对应参数效果一样。
getter
定义getter
getter 是 store 中的 state 计算值,以defineStore中的getters属性定义
getters属性的值是一个函数,该函数的第一个参数是 state
const useMainStore = defineStore( main , {
state: () => ({
user: {
name: 小明 ,
age: 7,
},
}),
getters: {
userInfo: (state) => `${state.user.name}今年${state.user.age}岁了`,
// 这里想要正确推断参数 state 的类型,则定义 state 时需要使用箭头函数定义
},
})
上面代码中,getters的值是箭头函数,当getters的值是普通函数时,可以通过 this 访问整个store实例(如下)
但是如果是普通函数,想要通过 this 获取state的值并希望this的类型能正确推断,同时希望函数的返回值类型正确推断,我们需要声明函数的返回类型。
getters: {
userDesc: (state) => `${state.user.name}今年${state.user.age}岁了`,
userBesidesDesc(): string{ // 需注明类型
return `${this.user.age}岁的${this.user.name}` // 可以使用 this 获取值
},
returnUserInfo() {
return this.userDesc // 也可以使用 this 获取其他getters
},
},
访问getter
import useMainStore from @/store/main
export default defineComponent({
setup() {
const mainStore = useMainStore()
const userDesc = computed(() => mainStore.userDesc)
const userBesidesDesc = computed(() => mainStore.userBesidesDesc)
const returnUserInfo = computed(() => mainStore.returnUserInfo)
return {
userDesc,
userBesidesDesc,
returnUserInfo,
}
},
})
action
定义action
action 是 store 中的 方法,支持同步或异步。
action 定义的函数可以是普通函数从而可以通过 this 访问整个store实例,同时该函数可以传入任意参数并返回任何数据
const useMainStore = defineStore( main , {
state: () => ({
count: 0,
}),
actions: {
add() {
this.count++
},
addCountNum(num: number) {
this.count += num
},
},
})
调用action
setup() {
const mainStore = useMainStore()
function mainAction() {
mainStore.addCount()
}
function addCountTwo() {
mainStore.addCountNum(2)
}
return {
mainAction,
addCountTwo
}
},
监听订阅action
通过 store.$onAction(),可以监听action的动作及结果等
该函数可以接收一个回调函数作为参数,回调函数的参数中有五个属性,具体如下
const unsubscribe = mainStore.$onAction(({
name, // action 函数的名称
store, // store 实例,这里是 mainStore
args, // action 函数参数数组
after, // 钩子函数,在action函数执行完成返回或者resolves后执行
onError, // 钩子函数,在action函数报错或者rejects后执行
}) => {})
举个例子,
首先,定义一个store
import { defineStore } from pinia
const useMainStore = defineStore( main , {
state: () => ({
user: {
name: 小明 ,
age: 7,
},
}),
actions: {
subscribeAction(name: string, age: number, manualError?: boolean) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
console.log( subscribeAction函数执行 )
if (manualError) {
reject( 手动报错 )
} else {
this.user.name = name
this.user.age = age
resolve(`${this.user.name}今年${this.user.age}岁了`)
}
})
},
},
})
export default useMainStore
然后在 setup 中使用
import useMainStore from @/store/main
import { ref, defineComponent, computed } from vue
export default defineComponent({
setup() {
const mainStore = useMainStore()
function subscribeNormal() {
mainStore.subscribeAction( 小李 , 18, false)
}
function subscribeError() {
mainStore.subscribeAction( 小白 , 17, true)
}
const unsubscribe = mainStore.$onAction(({
name, // action 函数的名称
store, // store 实例,这里是 mainStore
args, // action 函数参数数组
after, // 钩子函数,在action函数执行完成返回或者resolves后执行
onError, // 钩子函数,在action函数报错或者rejects后执行
}) => {
console.log( action的函数名 , name)
console.log( 参数数组 , args)
console.log( store实例 , store)
after((result) => {
console.log( $onAction after函数 , result)
})
onError(error => {
console.log( 错误捕获 , error)
})
})
return {
subscribeNormal,
subscribeError,
}
},
})
如上,在 setup 中,调用了 subscribeNormal 函数后,页面打印如下
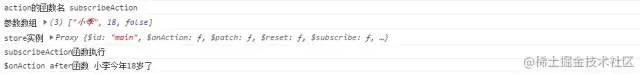
调用了 subscribeError 函数后,页面打印如下
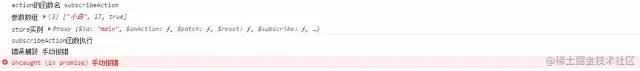
同样,可以通过调用 mainStore.$onAction 返回的值来手动停止订阅,在上面代码的例子中,即是
unsubscribe() // 手动停止订阅
store.$onAction 默认在所在组件卸载时会被自动删除,可以通过传递第二个参数 true,来将action订阅和所在组件分开(即组件卸载时,订阅依然有效)
mainStore.$onAction(callback, true)
store使用位置
在组件中使用时,useStore() 在大多数情况下都可以在调用后开箱即用。
在其他地方使用时,需确保在 pinia 激活使用后( app.use(createPinia()) )才能使用 useStore()
例如在路由守卫中
import { createRouter } from vue-router
import useMainStore from @/store/main
const router = createRouter({
// ...
})
// 报错
const mainStore = useMainStore()
router.beforeEach((to) => {
// 正常使用
const mainStore = useMainStore()
})
在store中也可以访问其他store
import { defineStore } from pinia
import { useUserStore } from ./user
export const useMainStore = defineStore( main , {
getters: {
otherGetter(state) {
const userStore = useUserStore()
return userStore.data + state.data
},
},
actions: {
async fetchUserInfo() {
const userStore = useUserStore()
if (userStore.userInfo) {
...
}
},
},
})
pinia插件
pinia store 支持扩展,通过 pinia 插件我们可以实现以下
-
给 store 添加新属性
-
给 store 添加新选项
-
给 store 添加新方法
-
包装已存在的方法
-
修改甚至删除actions
...
例如可以写一个简单的插件来给所有store添加一个静态属性
import { createPinia } from pinia
const pinia = createPinia()
// 传递一个返回函数
pinia.use(() => ({ env: dev }))
app.use(pinia)
然后,在所有其他的store都可以访问到上面添加的 env 属性
setup() {
const mainStore = useMainStore()
console.log(mainStore.env) // dev
}
插件函数
从上方代码可以发现,pinia 插件是一个函数,这个函数有一个可选参数
import { PiniaPluginContext } from pinia
function myPiniaPlugin(context: PiniaPluginContext) {
console.log(context)
}
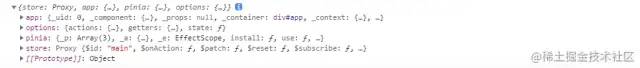
context 打印出来主要有
-
app : 当前应用 Vue.createApp() 创建的 app -
options : defineStore 配置的数据 -
pinia : 当前通过 createPinia() 创建的 pinia 实例 -
store :当前 store 实例
通过 context 我们可以在 store 上设置属性
pinia.use(({ store }) => {
store.env = dev
})
这样,在所有其他的store都可以访问到上面添加的 env 属性
pinia 的 store 是通过 reactive 包装的,可以自动解包它包含的任何 ref 对象
pinia.use(({ store }) => {
store.env = ref( dev )
})
通过上面插件,访问store 的 env 时不需要 .value,就可以直接访问
setup() {
const mainStore = useMainStore()
console.log(mainStore.env) // 不需要加 .value
}
添加外部属性
当需要添加来自其他库或不需要响应式的数据时,应该用 markRaw() 包装传递的对象,例如
markRaw 来自 vue3,可以标记一个对象,使其永远不会转换为 proxy。返回对象本身。
import { markRaw } from vue
import { router } from ./router
import { axios } from axios
pinia.use(({ store }) => {
store.router = markRaw(router)
store.axios = markRaw(axios)
})
在插件内部使用 onAction
pinia.use(({ store }) => {
store.$subscribe(() => {
// react to store changes
})
store.$onAction(() => {
// react to store actions
})
})
新属性的typescript支持
当通过插件添加新属性时,可以扩展 PiniaCustomProperties接口
可以用设置get,set或者简单声明值的类型,以此来安全地写入和读取新加的属性
import pinia
declare module pinia {
export interface PiniaCustomProperties {
set env(value: string | Ref<string>)
get env(): string
// 或者
env: string
}
}
最近很多小伙伴找我要一些程序员必备资料,于是我翻出了压箱底的宝藏,免费分享给大家!
扫描海报二维码免费获取。



