一文玩转 EhCache 缓存框架!

Ehcache 介绍
EhCache 从 Hibernate 发展而来,是一个纯Java的进程内缓存框架,具有快速、精干等特点。Ehcache是一种广泛使用的开源Java分布式缓存。主要面向通用缓存,Java EE和轻量级容器。它具有内存和磁盘存储,缓存加载器,缓存扩展,缓存异常处理程序,一个gzip缓存servlet过滤器,支持REST和SOAP api等特点。
主要特性:
快速,简单 多种缓存策略 缓存数据有两级:内存和磁盘,因此无需担心容量问题 缓存数据会在虚拟机重启的过程中写入磁盘 可以通过RMI、可插入API等方式进行分布式缓存 具有缓存和缓存管理器的侦听接口 支持多缓存管理器实例,以及一个实例的多个缓存区域 提供Hibernate的缓存实现
Show me the code
在 pom.xml 文件中添加 Ehcache 依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.sf.ehcache</groupId>
<artifactId>ehcache</artifactId>
</dependency>
不需要配置version,SpringBoot的根pom已经对版本号做了统一声明!
配置文件:
在配置文件 application.yaml 中配置 ehcache 的相关参数,具体内容如下:
spring:
application:
name: spring-boot-bulking-ehcache
cache:
type: ehcache
ehcache:
config: classpath:/ehcache.xml
spring.cache.type 声明spring框架使用哪一种类型的缓存,因为spring框架提供了多种缓存可供选择。
添加 Ehcache 配置:
在src/main/resources 目录下,创建配置文件ehcache.xml ,内容如下:
<ehcache name="test">
<diskStore path="java.io.tmpdir"/>
<defaultCache
maxEntriesLocalHeap="1000"
eternal="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="300"
timeToLiveSeconds="600"
overflowToDisk="true"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU">
</defaultCache>
<cache name="userCache"
maxEntriesLocalHeap="200"
eternal="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="300"
timeToLiveSeconds="600"
overflowToDisk="true">
</cache>
</ehcache>
参数含义:
diskStore:磁盘缓存位置 name:缓存名称 maxElementsInMemory:内存中最大缓存对象数 maxElementsOnDisk:硬盘中最大缓存对象数,若是0表示无穷大 eternal:true表示对象永不过期,此时会忽略timeToIdleSeconds和timeToLiveSeconds属性,默认为false timeToIdleSeconds:设定允许对象处于空闲状态的最长时间,以秒为单位。当对象自从最近一次被访问后,如果处于空闲状态的时间超过了timeToIdleSeconds属性值,这个对象就会过期,EHCache将把它从缓存中清空。只有当eternal属性为false,该属性才有效。如果该属性值为0,则表示对象可以无限期地处于空闲状态 timeToLiveSeconds:设定对象允许存在于缓存中的最长时间,以秒为单位。当对象自从被存放到缓存中后,如果处于缓存中的时间超过了 timeToLiveSeconds属性值,这个对象就会过期,EHCache将把它从缓存中清除。只有当eternal属性为false,该属性才有效。如果该属性值为0,则表示对象可以无限期地存在于缓存中。timeToLiveSeconds必须大于timeToIdleSeconds属性,才有意义 overflowToDisk:当内存中对象数量达到maxElementsInMemory时,Ehcache将会对象写到磁盘中。 diskSpoolBufferSizeMB:磁盘缓存区大小,默认为30MB。每个Cache都应该有自己的一个缓存区。 diskPersistent:是否缓存虚拟机重启期数据。 diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds:磁盘失效线程运行时间间隔,默认是120秒。 memoryStoreEvictionPolicy:当达到maxElementsInMemory限制时,Ehcache将会根据指定的策略去清理内存。默认策略是LRU(最近最少使用)。你可以设置为FIFO(先进先出)或是LFU(较少使用)。 clearOnFlush:内存数量最大时是否清除。
开启缓存:
入口启动类添加注解 @EnableCaching
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = {DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class,
DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration.class})
@EnableCaching // 开启缓存,Spring Boot 会自动配置缓存的 CacheManager
public class StartApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(StartApplication.class, args);
}
}
缓存业务使用:
@Component
@CacheConfig(cacheNames = "userCache")
public class UserService {
@Cacheable(key = "#id")
public User getUserById(Long id) {
System.out.println("缓存中无值");
User user = User.builder().id(id).userName("雪糕(" + id + ")").age(18).address("杭州").build();
return user;
}
@CachePut(key = "#user.id")
public User updateUser(User user) {
user.setUserName("雪糕(new name)");
return user;
}
@CacheEvict(key = "#id")
public void deleteById(Long id) {
System.out.println("db 删除数据,id=" + id);
}
}
@CacheConfig 作用于类上,用来描述该类中所有方法使用的缓存名称。当然也可以不使用该注解,直接在具体方法上的缓存注解里配置名称 @Cacheable 用于查询方法上,表示将一个方法的返回值缓存起来。默认情况下,缓存的 key 就是方法的参数,缓存的 value 就是方法的返回值 @CachePut 更新操作,当数据库中的数据更新后,缓存中的数据也要跟着更新,使用该注解,可以将方法的返回值自动更新到已经存在的 key 上 @CacheEvict 删除操作,当数据库中的数据删除后,相关的缓存数据也要自动清除。
除了采用 @Cacheable 、@CachePut 等方法注解解耦式操作缓存外,我们也可以使用 CacheManager显示方式手动来操作缓存。
CacheManager
Spring定义了CacheManager和Cache接口统一不同的缓存技术。其中CacheManager是Spring提供的各种缓存技术的抽象接口,而Cache接口包含缓存的读、写、删等各种操作。
针对不同的缓存技术,需要实现不同的CacheManager,Spring预先定义了主流缓存框架的cacheManger实现类
| CacheManager | 描述 |
|---|---|
| SimpleCacheManager | 使用简单的Collection来存储缓存,主要用于测试 |
| ConcurrentMapCacheManager | 使用ConcurrentMap作为缓存技术(默认) |
| NoOpCacheManager | 测试用 |
| EhCacheCacheManager | 使用EhCache作为缓存技术,以前在hibernate的时候经常用 |
| GuavaCacheManager | 使用google guava的GuavaCache作为缓存技术 |
| HazelcastCacheManager | 使用Hazelcast作为缓存技术 |
| JCacheCacheManager | 使用JCache标准的实现作为缓存技术,如Apache Commons JCS |
| RedisCacheManager | 使用Redis作为缓存技术 |
| CaffeineCacheManager | 使用Caffeine作为缓存技术 |
Spring Boot 为我们预留接口扩展,方便我们自动配置 EhCache、Redis、Guava、ConcurrentMap等缓存,默认使用ConcurrentMapCacheManager。Spring Boot的
application.yaml配置文件,使用spring.cache前缀属性进行配置。
本文我们使用 EhCache 缓存,代码示例如下:
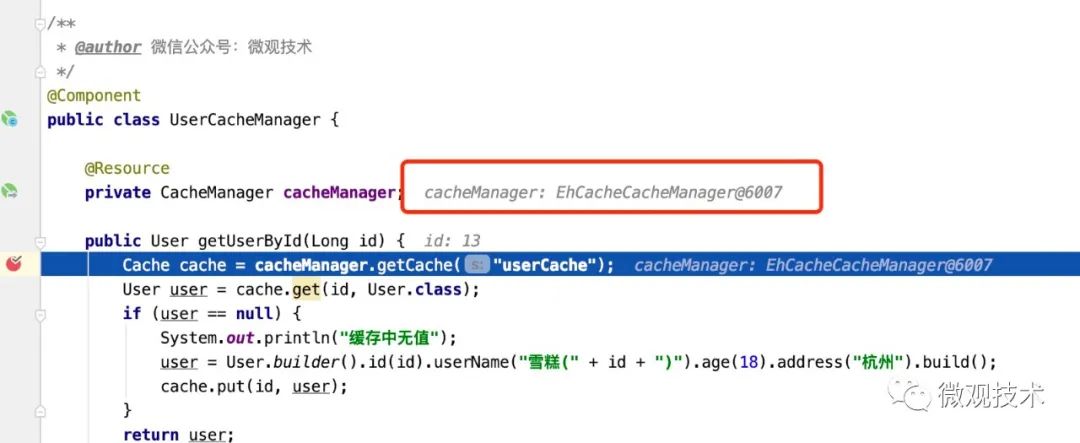
@Component
public class UserCacheManager {
@Resource
private CacheManager cacheManager;
public User getUserById(Long id) {
Cache cache = cacheManager.getCache("userCache");
User user = cache.get(id, User.class);
if (user == null) {
System.out.println("缓存中无值");
user = User.builder().id(id).userName("雪糕(" + id + ")").age(18).address("杭州").build();
cache.put(id, user);
}
return user;
}
public User updateUser(User user) {
user.setUserName("雪糕(new name)");
Cache cache = cacheManager.getCache("userCache");
cache.put(user.getId(), user);
return user;
}
public void deleteById(Long id) {
Cache cache = cacheManager.getCache("userCache");
cache.evict(id);
System.out.println("db 删除数据,id=" + id);
}
}
演示代码地址
https://github.com/aalansehaiyang/spring-boot-bulking
模块:spring-boot-bulking-ehcache

往期推荐

Spring为什么建议构造器注入?

超级详细的Spring Boot 注解总结

Spring中的重试功能!嗯,有点东西
