Linux 多核 SMP 系统的引导
本篇文章基于Linux 2.6.32,x86体系结构
系统的引导和初始化阶段是个特例,因为在这个阶段里系统中只有一个“上下文”,只能由一个处理器来处理。在这个阶段里,也就是在系统刚加电或“总清(reset)”之后,系统中暂时只有一个处理器运行,这个处理器称之为“引导处理器”BP;其余的处理器则处于暂停状态,称为“应用处理器”AP。“引导处理器”完成整个系统的引导和初始化,并创建起多个进程,从而可以由多个处理器同时参与处理时,才启动所有的“应用处理器”,让他们完成自身的初始化以后,投入运行。参考intel手册:
The MP initialization protocol defines two classes of processors: the bootstrap processor (BSP) and the application processors (APs). Following a power-up or RESET of an MP system, system hardware dynamically selects one of the processors on the system bus as the BSP. The remaining processors are designated as APs.
我们在这里关心的是“引导处理器”怎样为各个“应用处理器”做好准备,然后启动其运行的过程。
在初始化阶段,引导处理器先完成自身的初始化,进入保护模式并开启页式存储管理机制,再完成系统特别是内存的初始化,然后从 start_kernel() –> rest_init() –> kernel_init() –> smp_init() 进行SMP系统的初始化。由于此时APs处于暂停状态,所以BP需要通过 smp_init() –> cpu_up() –> native_cpu_up() –> do_boot_cpu() –> wakeup_secondary_cpu_via_init() 发送IPI中断唤醒APs,这样APs就开始了正常的运行过程,拥有和BP一样的地位。详细过程我们后面分析。先来看总体大纲图:
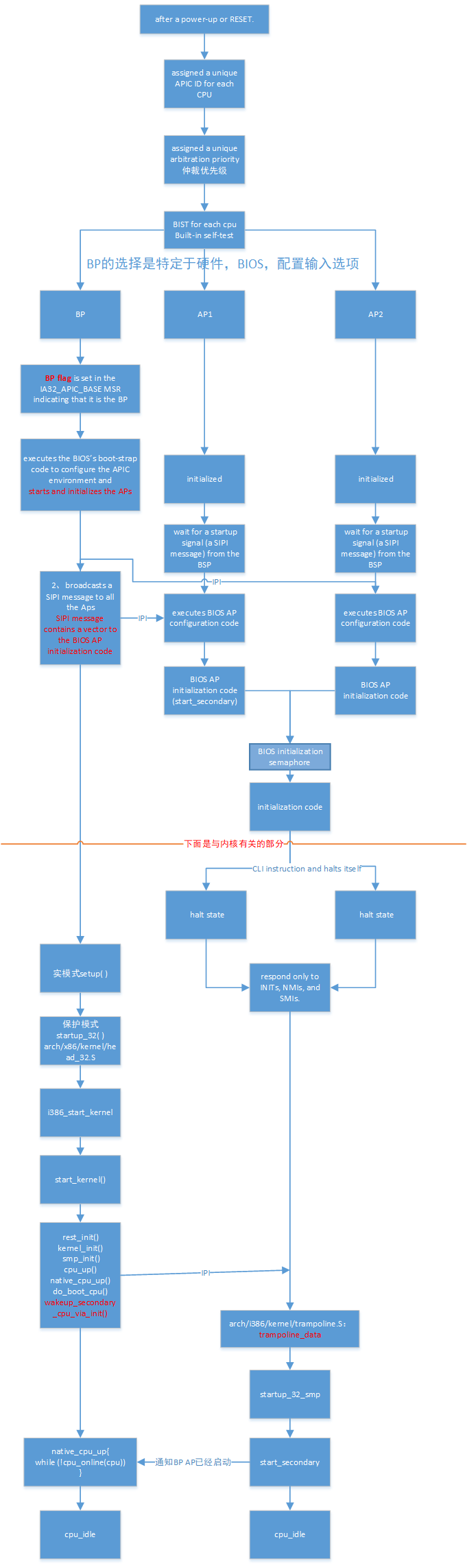
smp_init
smp_init的代码在init/main.c:
/* Called by boot processor to activate the rest. */
static void __init smp_init(void)
{
unsigned int cpu;
/* FIXME: This should be done in userspace --RR */
for_each_present_cpu(cpu) {
if (num_online_cpus() >= setup_max_cpus)
break;
if (!cpu_online(cpu))
cpu_up(cpu);//(1)--------
//cpu_up到最终调用smp_ops.cpu_up(cpu);
//.cpu_up = native_cpu_up是一个回调函数。在arch/x86/kernel/smp.c注册
}
/* Any cleanup work */
printk(KERN_INFO "Brought up %ld CPUs\n", (long)num_online_cpus());
}
native_cpu_up的注册:
struct smp_ops smp_ops = {
……
.smp_cpus_done = native_smp_cpus_done,
.cpu_up = native_cpu_up,
……
}
native_cpu_up
接下来看标号(1)处 native_cpu_up(unsigned int cpu) 。依次启动系统中各个CPU。
int __cpuinit native_cpu_up(unsigned int cpu)
{
......
mtrr_save_state();
per_cpu(cpu_state, cpu) = CPU_UP_PREPARE;//设置对应CPU的状态
err = do_boot_cpu(apicid, cpu); //唤醒AP------------
......
while (!cpu_online(cpu)) {//在这里不停的一直等。确认前一个AP唤醒后,再唤醒下一个AP
cpu_relax();
......
}
return 0;
}
1、do_boot_cpu
发送IPI中断唤醒APs,并且在IPI中断中,带有AP唤醒后要执行的代码地址(实际上只是一个vector,AP会把这个vector«12作为要执行的代码地址)。
static int __cpuinit do_boot_cpu(int apicid, int cpu)
{
unsigned long boot_error = 0;
unsigned long start_ip;
int timeout;
struct create_idle c_idle = {
.cpu = cpu,
.done = COMPLETION_INITIALIZER_ONSTACK(c_idle.done),
};
/*
* 完成c_idle.work.func = do_fork_idle
*/
INIT_WORK(&c_idle.work, do_fork_idle);
......
if (!keventd_up() || current_is_keventd())
/* 执行do_fork_idle:将init进程使用copy_process复制,并且调用init_idle函数,设置可以运行
* 的CPU。fork出一个idel线程,地址空间还是沿用init进程地址空间。
*/
c_idle.work.func(&c_idle.work);
else {
......
}
set_idle_for_cpu(cpu, c_idle.idle);
do_rest:
per_cpu(current_task, cpu) = c_idle.idle;
......
/* AP的GDT已经在start_kernel()-->setup_per_cpu_areas()初始化完成,这里只是保存它的基地址
* 到early_gdt_descr,等后面唤醒时,AP自己设置到GDTR。见startup_32_smp末尾
*/
early_gdt_descr.address = (unsigned long)get_cpu_gdt_table(cpu);
//AP初始化完成后,就运行start_secondary函数,见startup_32_smp末尾
initial_code = (unsigned long)start_secondary;
//为AP设定好执行start_secondary时将要使用的stack,见startup_32_smp末尾
stack_start.sp = (void *) c_idle.idle->thread.sp;
//real-mode code that AP runs after BSP kicks it(嘻嘻)
/* 复制trampoline_data到trampoline_end之间的代码(在arch/i386/kernel/trampoline.S中)到
* trampoline_base处。这里复制到trampoline_base的代码是等下AP唤醒后要执行的代码。所以得通过IPI
* 的方式告诉AP,trampoline_base对应物理页所在位置。
* trampoline_base是之前在start_kernel()-->setup_arch()-->smp_alloc_memory():
* trampoline_base = (void *) alloc_bootmem_low_pages(PAGE_SIZE)
* 处申请的页。这里为什么要在低端内存去分配trampoline_base?还记得之前说的 IPI传递给AP只是传递
* 了一个vector,这个vector只有8位大小,AP自己再<<12,所以AP总共只能寻址1M的物理地址空间。因为
* AP在唤醒后是处于实模式的。
*
* 所以底下调用virt_to_phys,获取trampoline_base对应物理页的地址start_eip,start_eip是4K对其
* 的,所以start_eip是形如0xSS000,等下通过IPI发送给AP的是0xSS
*/
start_ip = setup_trampoline(){
memcpy(trampoline_base, trampoline_data,
trampoline_end - trampoline_data);
return virt_to_phys(trampoline_base);
}
......
/*
* Kick the secondary CPU. Use the method in the APIC driver
* if it's defined - or use an INIT boot APIC message otherwise:
*/
if (apic->wakeup_secondary_cpu)
boot_error = apic->wakeup_secondary_cpu(apicid, start_ip);
else
/* 这里是重点拉,发送IPI中断。
* 在这个函数中通过操作APIC_ICR寄存器,BSP向目标AP发送IPI消息,触发目标AP从start_eip地址处,
* 实模式开始运行。
*/
boot_error = wakeup_secondary_cpu_via_init(apicid, start_ip);
if (!boot_error) {
/*
* allow APs to start initializing.
*/
pr_debug("Before Callout %d.\n", cpu);
cpumask_set_cpu(cpu, cpu_callout_mask);
pr_debug("After Callout %d.\n", cpu);
/*
* Wait 5s total for a response
*/
for (timeout = 0; timeout < 50000; timeout++) {
/* AP唤醒后会进入start_secondary()-->smp_callin() 设置对应的cpu_callin_mask
* 所以这里只要检测到cpu_callin_mask被设置了,代表AP激活成功
*/
if (cpumask_test_cpu(cpu, cpu_callin_mask))
break; /* It has booted */
udelay(100);
/*
* Allow other tasks to run while we wait for the
* AP to come online. This also gives a chance
* for the MTRR work(triggered by the AP coming online)
* to be completed in the stop machine context.
*/
schedule();
}
if (cpumask_test_cpu(cpu, cpu_callin_mask)) {
/* Signal AP that it may continue to boot */
cpumask_set_cpu(cpu, cpu_may_complete_boot_mask);
pr_debug("CPU%d: has booted.\n", cpu);//提示对应的AP激活成功
} else {
boot_error = 1;
......可能出了什么问题
}
}
......
return boot_error;
}
2、wakeup_secondary_cpu_via_init发送IPI
发送IPI中断,至于为什么这里apic_icr_write可以发送vector到AP,请参考intel文档。
wakeup_secondary_cpu_via_init(int phys_apicid, unsigned long start_eip)
{
......
/*
* STARTUP IPI
*/
/* Target chip */
/* Boot on the stack */
/* Kick the second */
apic_icr_write(APIC_DM_STARTUP | (start_eip >> 12),
phys_apicid);
......
}
AP接收到IPI,就开始激活执行了。
3、trampoline.S 这段代码就是前面do_boot_cpu()—>setup_trampoline()拷贝到trampoline_base的代码:
ENTRY(trampoline_data)
r_base = .
wbinvd // Needed for NUMA-Q should be harmless for others
mov %cs, %ax // Code and data in the same place
mov %ax, %ds
cli // We should be safe anyway
/* 这个是设置标识,以便BP知道AP运行到这里了。当前处于实模式,DS段寄存器指向前面的r_base处,此处往
* r_base处写入0xA5A5A5A5。BP可以
* 通过虚拟地址trampoline_base寻址到r_base来查看是否设置$0xA5A5A5A5,以此来检测AP激活是否成功
*/
movl $0xA5A5A5A5, trampoline_data - r_base // write marker for master knows we're running
/* GDT tables in non default location kernel can be beyond 16MB and
* lgdt will not be able to load the address as in real mode default
* operand size is 16bit. Use lgdtl instead to force operand size
* to 32 bit.
*/
/* 设置临时idt和gdt,方便后面开启保护模式
* 至于为什么这里要减r_base,因为此时的DS段寄存器已经指向r_base
* boot_idt_descr - r_base + DS段寄存器<<4 = boot_idt_descr
*/
lidtl boot_idt_descr - r_base # load idt with 0, 0
lgdtl boot_gdt_descr - r_base # load gdt with whatever is appropriate
xor %ax, %ax
inc %ax // protected mode (PE) bit
lmsw %ax // into protected mode 将%ax加载到CR0,进入保护模式
// flush prefetch and jump to startup_32_smp in arch/i386/kernel/head.S
/* 长跳转至startup_32_smp。此时的__BOOT_CS为0x10,对应GDT的描述符base为0,然后没有开启分页,直接
* 访问startup_32_smp物理地址
*/
ljmpl $__BOOT_CS, $(startup_32_smp-__PAGE_OFFSET)
boot_gdt_descr:
.word __BOOT_DS + 7 // gdt limit
.long boot_gdt - __PAGE_OFFSET // gdt base
/* 由于编译时boot_gdt是加上了__PAGE_OFFSET,而当前还没有开启页表,所以boot_gdt - __PAGE_OFFSET
* 后作为物理地址直接使用。
*/
boot_idt_descr:
.word 0 // idt limit = 0
.long 0 // idt base = 0L
.globl trampoline_end
trampoline_end:
// -------------------------------------boot_gdt来自于arch/x86/kernel/head_32.S
ENTRY(boot_gdt)
.fill GDT_ENTRY_BOOT_CS,8,0 /* GDT_ENTRY_BOOT_CS为2,这里有两项 */
.quad 0x00cf9a000000ffff /* kernel 4GB code at 0x00000000 */
.quad 0x00cf92000000ffff /* kernel 4GB data at 0x00000000 */
在这段代码中,设置标识,以便BSP知道该AP已经运行到这段代码,加载GDT和LDT表基址。然后启动保护模式,更新CS段寄存器,跳转到startup_32_smp 处。
4、startup_32_smp
ENTRY(startup_32_smp)
cld
/* 前面长跳转已经设置好CS,这里设置其他段寄存器。__BOOT_DS为0x18,使用GDT第4项,base全为0。也就是说
* 从现在开始,只需要关注EIP
*/
movl $(__BOOT_DS),%eax
movl %eax,%ds
movl %eax,%es
movl %eax,%fs
movl %eax,%gs
......
/*
* Enable paging
*/
/* 还记得前面fork的idel线程吗?这里使用和init进程同样的页表,以使后面能够正确的找到idel线程的内核栈和
* 执行函数。
*/
movl $pa(swapper_pg_dir),%eax
movl %eax,%cr3 /* set the page table pointer.. */
movl %cr0,%eax
orl $X86_CR0_PG,%eax
movl %eax,%cr0 /* ..and set paging (PG) bit 开启分页 */
/* CS保持原样,更新EIP,此时的EIP为0xC01000xx线性地址,因为在编译时,符号1:的地址在3g后面*/
ljmp $__BOOT_CS,$1f
1:
/* 更新SS和esp,以使用idel进程的内核栈。还记得在do_boot_cpu():stack_start.sp = (void *)
* c_idle.idle->thread.sp; 后面执行的函数都使用该内核栈
*/
lss stack_start,%esp
/* 把eflags全部置零 */
pushl $0
popfl
call setup_idt
/* 使用BP已经设置好的GDT。见do_boot_cpu()
* early_gdt_descr.address = (unsigned long)get_cpu_gdt_table(cpu)
*/
lgdt early_gdt_descr
lidt idt_descr
/* 由于重新设置了GDT,所以更新CS为__KERNEL_CS GDT第13项 */
ljmp $(__KERNEL_CS),$1f
1: movl $(__KERNEL_DS),%eax // 更新其他所有的段寄存器
movl %eax,%ss
movl $(__USER_DS),%eax
movl %eax,%ds
movl %eax,%es
movl $(__KERNEL_PERCPU), %eax
movl %eax,%fs // set this cpu's percpu,这样AP就能找到自己的cpuid,至于原理
// 请参考 https://frankjkl.github.io/2019/03/09/Linux内核-smp_processor_id/
......
/* 对于BP来讲stack_start为init进程的内核栈,initial_code为i386_start_kernel */
/* 对于AP来讲stack_start为BP设置的idel进程的内核栈,initial_code为start_secondary */
movl (stack_start), %esp
1:
/* 见do_boot_cpu函数
* initial_code = (unsigned long)start_secondary
*/
jmp *(initial_code)
这个函数的主要作用在于开启分页,更新EIP,ESP。重新设置GDT,更新所有的段寄存器,最后跳转到start_secondary执行。
5、start_secondary
此时分页和保护模式都已经开启,且完全进入BP事先为我们fork好的idel线程的上下文。
static void __cpuinit start_secondary(void *unused)
{
......
cpu_init();
preempt_disable();
/* 设定cpu_callin_mask来告诉BP,AP已经启动。BP才能继续运行。
* 参考do_boot_cpu:if (cpumask_test_cpu(cpu, cpu_callin_mask))
*/
smp_callin();
/* otherwise gcc will move up smp_processor_id before the cpu_init */
barrier();
......
//通知BP AP已经启动(BP会在native_cpu_up的while循环里等待)
set_cpu_online(smp_processor_id(), true);
......
//更新AP的状态
per_cpu(cpu_state, smp_processor_id()) = CPU_ONLINE;
......
cpu_idle();
}
本函数主要是通知BP本AP启动完成,然后cpu_idle,参与到任务调度。
总结
整理一下AP启动的整个过程:
wakeup_secondary_cpu_via_init:BP发送IPI中断给AP trampoline.S AP引导代码,为16进制代码,启用保护模式 head.s 为AP创建分页管理 start_secondary 通知BP启动成功。AP参与任务调度。
F&Q:
1、每个AP自己的GDTR在哪里设置的?(每个AP的GDT都已经由BP处理器初始化完成,就等待设置到CPU上)
do_boot_cpu() -> early_gdt_descr.address = (unsigned long)get_cpu_gdt_table(cpu);
startup_32_smp() –> lgdt early_gdt_descr;
2、发送IPI到AP后,CS:IP如何设置的?
CS 为 0x**00(**代表IPI中包含的vector),IP为0,CS:IP就可以引用trampoline.S中的代码
参考:
https://www.bbsmax.com/A/xl56ELa7Jr/ 《Linux内核源代码情景分析》 https://www.tldp.org/HOWTO/Linux-i386-Boot-Code-HOWTO/smpboot.html
原文:
https://frankjkl.github.io/2019/03/10/Linux%E5%86%85%E6%A0%B8-SMP%E7%B3%BB%E7%BB%9F%E7%9A%84%E5%BC%95%E5%AF%BC/
