探究 | Elasticsearch Painless 脚本 ctx、doc、_source 的区别是什么?
1、实战问题
星主,请教一下,我在painless中使用doc的形式访问字段,如if(doc['xxx'].value ...)报错了,是painless中不允许使用doc吗?
我看官方示例和您之前的博客都是用ctx,请问 ctx 和 doc, params,params._source之间有什么区别吗? 我知道doc直接从内存获取,params从磁盘获取,但是对于上述4个的区别不是很了解,也没有查询到相关的资料......
——来自《死磕Elasticsearch 知识星球》
上述问题不止一次被问到,我自己在使用 painless 脚本的时候,也会遇到上述困惑。
今天,我们把这几种的区别梳理清楚。
2、关于 Elasticsearch painless 脚本
如果对 painless “无痛”脚本不了解的,推荐阅读:
3、 从应用层面解读:ctx、doc、_source 的区别?
3.1 场景1:ingest 管道预处理脚本使用 ctx
PUT _ingest/pipeline/check_url
{
"processors": [
{
"set": {
"if": """ctx.href.url!=null && ctx.href.url.startsWith("http")""",
"field": "href.insecure",
"value": true
}
}
]
}
POST test/_doc/1?pipeline=check_url
{
"href": {
"url": "http://www.elastic.co/"
}
}
POST test/_search
上面的脚本通过 ingest painless 脚本实现了判定:
ctx.href.url 如果非空且 ctx.href.url 以 http 开头,则:href.insecure 设置为:true。
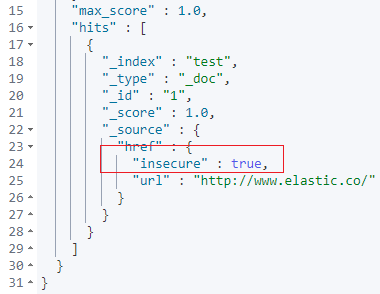
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/painless/7.15/painless-ingest-processor-context.html
3.2 场景 2:update/update_by_query 脚本使用 ctx._source
POST test/_doc/2
{
"tags": "green"
}
GET test/_doc/2
POST test/_update/2
{
"script": {
"source": "if (ctx._source.tags.contains(params.tag)) { ctx.op = 'delete' } else { ctx.op = 'none' }",
"lang": "painless",
"params": {
"tag": "green"
}
}
}
GET test/_doc/2
如果标签字段:tags 包含:“green”,则 执行删除操作;否则保持现状。
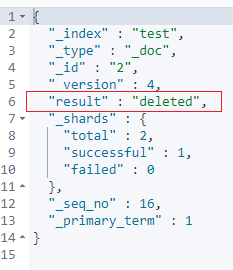
官方文档地址:
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/painless/7.15/painless-update-context.html
3.3 场景3:reindex 脚本使用 ctx._source
POST test-04/_doc/1
{
"foo": "bar",
"views": 1
}
POST _reindex
{
"source": {
"index": "test-04"
},
"dest": {
"index": "test-new-04"
},
"script": {
"source": "if (ctx._source.foo == 'bar') {ctx._source.views++; ctx._source.remove('foo')}",
"lang": "painless"
}
}
GET test-new-04/_search
如上 reindex 脚本解读如下:
如果源索引:test-04 字段 foo 内容=‘bar’,则 reindex 后删除 ‘foo’ 字段 且 views 取值加 1 。

3.4 场景4:search 脚本使用 doc['XXX']
DELETE test_03
PUT test_03
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"views": {
"type": "integer"
}
}
}
}
POST test_03/_doc/1
{
"views": 30
}
GET test_03/_search
{
"script_fields": {
"rnd_views": {
"script": {
"lang": "painless",
"source": """
java.util.Random rnd = new Random();
doc['views'].value+rnd.nextInt(1000);
"""
}
}
},
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
对观看数 views 在检索的时候加了随机值。
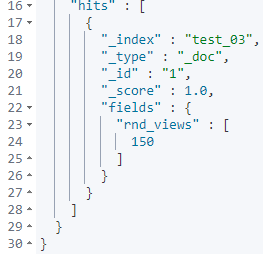
官方文档:
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/painless/7.15/painless-field-context.html
3.5 应用层面小结
从上面的应用层面,我们能看出区别:
ingest 场景,使用:ctx.XXX;
update / update / update_by_query / reindex 场景,使用:ctx._source;
search和聚合场景,使用:doc['value']。
当然,Elasticsearch 远不止上面这些场景,更多推荐阅读:

4、那遇到复杂的脚本处理咋办呢?
4.1 获取字符串中的子串
举例如下:求字符串中的某子串,java 语法中的 substring 还能用吗?
如果使用:ingest processor 预处理方式,怎么查官方是否支持,我相信是大家关注的问题。
因为:支不支持可以试,但试是穷举的方式,时间复杂度为 O(n);
能查看官方明确说支持,是最快的方式,时间复杂度为O(1)。
对于我们程序员来说,怎么快,我们就怎么来。
来吧,一步步走一遍,其他复杂例子原理同。
4.1.1 第一步,找 shard API。
细节 API 入口文档。
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/painless/master/painless-api-reference-shared.html
4.1.2 第二步,找到 string
如上是 7.13 版本截图,早期版本如:7.2 版本还有 string类, 7.13 已没有。
4.1.3 第三步:找 substring

4.1.4 第四步:找 java API
这就到了 oracle 官网了。
 实践一把:
实践一把:
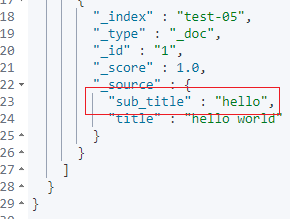
POST test-05/_doc/1
{
"title": "hello world"
}
PUT _ingest/pipeline/substring_pipeline
{
"processors": [
{
"script": {
"lang": "painless",
"source": """
ctx.sub_title = ctx.title.substring(0,5);
"""
}
}
]
}
POST test-05/_update_by_query?pipeline=substring_pipeline
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
POST test-05/_search
核心步骤再结合上面的截图解释一下:
-步骤1:确认 string 类型支持取子串;
-步骤2:找到取子串的语法:substring;
-步骤3:通过 ingest 预处理方式实现取子串,借助 ctx 组合 substring 实现。
4.2 获取日期格式的年份
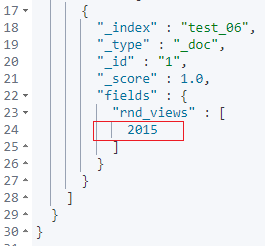
POST test_06/_bulk
{"index":{"_id":1}}
{"m_type":1,"create_time":"2015-01-01T12:10:30Z","update_time":"2021-07-01T12:10:30Z"}
GET test_06/_mapping
GET test_06/_search
{
"script_fields": {
"rnd_views": {
"script": {
"lang": "painless",
"source": """
doc['create_time'].value.getYear()
"""
}
}
},
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
5、小结
Painless 脚本在数据预处理、更新、reindex、获取字段方面应用广泛。
因业务场景的不同,脚本使用方式也会有不同。大家使用过程中要根据使用方式的不同,来决定ctx、doc、_source 的选型。
希望本文对你的脚本实战选型有所帮助,也欢迎留言交流你的脚本使用心得......
推荐
更短时间更快习得更多干货!
已带领72位球友通过 Elastic 官方认证!
可能是中国学习氛围最好的 Elastic 圈子!
文字教程、视频教程、打卡氛围一应俱全。
全球近 1500+ 球友等你 >>

