一篇文章一次性搞定JavaScript 从 ES6 到 ES12的基础框架知识
共 16007字,需浏览 33分钟
·
2022-11-01 20:15

英文 | https://medium.com/@bluetch/javascript-es6-es7-es8-es9-es10-es11-and-es12-519d8be7d48c
class Animal {constructor(name, color) {this.name = name;this.color = color;}// This is a property on the prototype chaintoString() {console.log('name:' + this.name + ', color:' + this.color);}}var animal = new Animal('myDog', 'yellow'); // instantiateanimal.toString(); // name: myDog, color: yellowconsole.log(animal.hasOwnProperty('name')); //trueconsole.log(animal.hasOwnProperty('toString')); // falseconsole.log(animal.__proto__.hasOwnProperty('toString')); // trueclass Cat extends Animal {constructor(action) {// The subclass must call the super function in the constructor, otherwise an error will be reported when new comes out// If the constructor was not written originally, the default constructor with super will be automatically generatedsuper('cat','white');this.action = action;}toString() {console.log(super.toString());}}var cat = new Cat('catch')cat.toString();console.log(cat instanceof Cat); // trueconsole.log(cat instanceof Animal); // true
2. 模块
每个模块都有自己的命名空间以避免冲突,使用导入和导出来导入和导出。
基本上将 .js 文件视为模块。
3.箭头函数
() => {…},是函数的缩写。最重要的是,他可以确保这始终指向自己
不再写 var self = this、var that = this 等等!
const add = (a, b) => { return a + b};const res = add(1, 2); // 3// If the syntax is simple, `{}` and `return` can be omitted. It will look neaterconst minus = (a, b) => a - b;const res1 = minus(3, 1); // 2
4.函数参数默认值
如果函数不传递参数,则使用默认值,更简洁的写法。
function example(height = 50, width = 40) {const newH = height * 10;const newW = width * 10;return newH + newW;}example(); // 900 (50*10 + 40*10)
5. 模板字面量
过去,长字符串的组合是通过 + 号来连接的。
它的可读性很差,使用模板字符串,它更容易阅读。
const firstName = 'Ken';const lastName = 'Huang';// not use template literalconst name = 'Hello, My name is' + firstName + ', ' + lastName;// use template literalconst nameWithLiteralString = `Hello, My name is ${firstName}, ${lastName}`;
6.解构赋值
允许 JavaScript 轻松地从数组和对象中获取内容。
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];const [one, two, three] = arr;console.log(one); // 1console.log(two); // 2console.log(three); // 3// To skip certain valuesconst [first,,,,last] = arr;console.log(first); // 1console.log(last); // 5// Objects can also be destructurized and assignedconst student = {name: 'Ken Huang',age: 38,city: 'Taipei'};const {name, age, city} = student;console.log(name); // "Ken Huang"console.log(age); // "38"console.log(city); // "Taipei"
7.扩展运算符
它是用三点(...)表示,Array是可以扩展的,如果是Object,会按照key-value进行扩展。
const stuendts = ['Angel', 'Ryan'];const people = ['Sara', ...stuendts, 'Kelly', 'Eason'];conslog.log(people); // ["Sara", "Angel", "Ryan", "Kelly", "Eason"]
8. 对象属性简写
如果构成对象的字段名称与前面段落中的变量相同,则可以省略该值,看起来更流线型。
const name = 'Angel', age = 18, city = 'ChangHwa';// Before ES6, we must write like thisconst customer = {name: name,age: age,city: city} // // {name: 'Angel', age: 18, city: 'ChangHwa'}// After ES6, we can do itconst newCustomer = {name,age,city} // {name: '小明Angel, age: 18, city: 'ChangHwa'}
9. Promise
Promise 是一种异步(非同步)写法的解决方案,比原来的回调写法更加优雅。
早期是开源社区的套件,后来被纳入语言标准。
早期回调 hell……
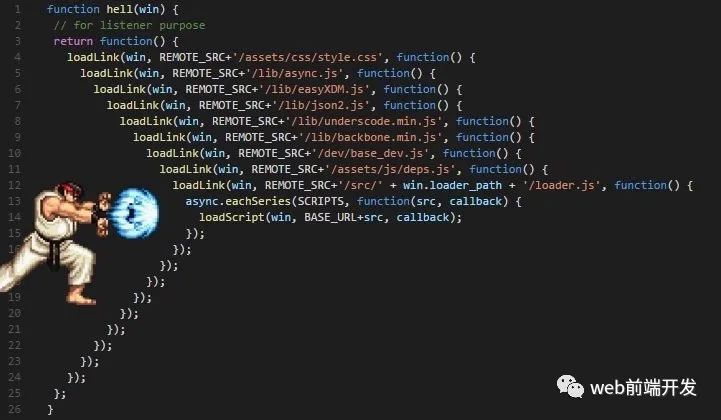
使用 Promise 后,回调 hell 扁平化
const waitSecond = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {setTimeout(resolve, 1000);});waitSecond.then( () => {console.log('hello World after 1 second.');// output this line after 1 secondreturn waitSecond;}).then( () => {console.log('Hell World after 2 sceond.');// output this line after 2second})
并且ES8(ES2017)发布了更完美的async,await,直接让异步写得像同步一样。
缺点是当思路落到复杂的业务逻辑上时,有时会错过await,在运行时发现错误。
10. let, const 替换 var
let:通用变量,可以被覆盖
const:一旦声明,其内容不可修改。因为数组和对象都是指标,所以它们的内容可以增加或减少, 但不改变其指标.
早期,JavaScript的var作用域是全局的。
也就是说,变量是在使用后声明的,执行的时候会自动提到顶层,后面会赋值。
更容易受到污染。
console.log(a); // undefinedvar a = 10;
使用 let 或 const
console.log(a); // ReferenceError: Cannot access 'a' before initializationlet a = 10;
三、ES7 (ES2016)
1.Array.prototype.includes()
用于判断数组是否包含指定值,如果是,则返回true;否则,返回假。
和之前indexOf的用法一样,可以认为是返回一个布尔值,语义上更加清晰。
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];// Check if there is the number 3 in the arrayarr.include(3); // trueif (arr.include(3)) { ... }// ... Equivalent to the previous writing of indexOfarr.indexOf(3); // 2 (return its array position)// If you want to write it in the if, you must add `> -1`, which is not as clear as the include in ES7 in terms of semanticsif (arr.indexOf(3) > -1) { ... }
2. 幂运算符
console.log(2**10); // 1024// equal toconsole.log(Math.pow(2, 10)); // 1024
四、ES8 (ES2017)
1.async, await
异步函数是使用 async 关键字声明的函数,并且允许在其中使用 await 关键字。async 和 await 关键字使异步的、基于 Promise 的行为能够以更简洁的方式编写,避免了显式配置 Promise 链的需要。
async test() {try {const result = await otherAsyncFunction();console.log(result); // output result} catch(e) {console.log(e); // Can catch errors if otherAsyncFunction() throws an error}}
2. Object.values()
返回对象自身属性的所有值,不包括继承的值。
const exampleObj = {a: 1, b: 2, c: 3, d:4};console.log(Object.value(exampleObj)); // [1, 2, 3, 4];// To do the same thing before, use the following notation. much verboseconst values = Object.keys(exampleObj).map(key => exampleObj[key]);
3. Object.entries()
返回可枚举键,即传入对象本身的值。
const exampleObj = {a: 1, b: 2, c: 3, d:4};console.log(Object.entries(exampleObj)); // [["a", 1], ["b", 2], ["c", 3], ["d", 4]];// Usually used with forfor (const [key, value] of Object.entries(exampleObj)) {console.log(`key: ${key}, value: ${value}`);}// key: a, value: 1// key: b, value: 2// key: c, value: 3// key: d, value: 4
4. 字符串 padStart() & padEnd()
你可以在字符串的开头或结尾添加其他内容,并将其填充到指定的长度。
过去,这些功能通常是通过通用的辅助工具包(如 lodash)引入的,并将它们放在一起。
本机语法现在直接提供:
String.padStart(fillingLength, FillingContent);// 如果要填充的内容过多,超过了“填充长度”,会从最左边填充到长度上限,超出的部分会被截断
最常用的情况应该是金额,填写指定长度,不足加0。
// padStart'100'.padStart(5, 0); // 00100// If the content to be padded exceeds the "padding length". Then fill in from the left to the upper limit of the length'100'.padStart(5, '987'); // 98100// padEnd'100'.padEnd(5, 9); // 10099// If the content to be padded exceeds the "padding length". Then fill in from the right to the upper limit of the length'100'.padStart(5, '987'); // 10098
5.尾随逗号
允许在函数参数列表末尾使用逗号
["foo",+ "baz","bar",- "baz",]
6. Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors()
获取你自己的描述符,一般的开发业务需求通常不会用到。
const exampleObj = {a: 1, b: 2, c: 3, d:4};Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(exampleObj);// {a: {…}, b: {…}, c: {…}, d: {…}}// a: {value: 1, writable: true, enumerable: true, configurable: true}// b: {value: 2, writable: true, enumerable: true, configurable: true}// c: {value: 3, writable: true, enumerable: true, configurable: true}// d: {value: 4, writable: true, enumerable: true, configurable: true}// __proto__: Object
7. 共享数组缓冲区
SharedArrayBuffer 是一个固定长度的原始二进制数据缓冲区,类似于 ArrayBuffer。
可用于在共享内存上创建数据。与 ArrayBuffer 不同,SharedArrayBuffer 不能分离。
/*** @param length size,unit byte* @returns {SharedArrayBuffer} the default value is 0。*/const sab = new SharedArrayBuffer(length);
8. Atomics object
Atomics 对象,它提供了一组静态方法来对 SharedArrayBuffer 执行原子操作。
原子的所有属性和函数都是静态的,就像数学一样,出不来新的。
如果一个多线程同时在同一个位置读写数据,原子操作保证了正在操作的数据如预期的那样:即在上一个子操作结束后执行下一个,操作不中断。
可以说是针对Node.Js中多线程Server的开发而加强的功能,在前端开发中使用的机会相当低。
chrome 已经提供了支持
五、ES9 (ES2018)
1.循环等待
在异步函数中,有时需要在同步 for 循环中使用异步(非同步)函数。
async function process(array) {for (const i of array) {await doSomething(i);}}async function process(array) {array.forEach(async i => {await doSomething(i);});}
上面的代码不会像预期的那样输出期望的结果。
for循环本身还是同步的,会在循环中的异步函数完成之前执行整个for循环,然后将里面的异步函数逐一执行。
ES9 增加了异步迭代器,允许 await 与 for 循环一起使用,逐步执行异步操作。
async function process(array) {for await (const i of array) {doSomething(i);}}
2.promise.finally()
无论是成功(.then())还是失败(.catch()),Promise 后面都会执行的部分。
function process() {process1().then(process2).then(process3).catch(err => {console.log(err);}).finally(() => {console.log(`it must execut no matter success or fail`);});}
3. Rest, Spread
在 ES2015 中,Rest 不定长度参数…,可以转换成数组传入。
function restParams(p1, p2, ...p3) {console.log(p1); // 1console.log(p2); // 2console.log(p3); // [3, 4, 5]}restParams(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
而传播则与其他相反,将数组转换为单独的参数。
例如,Math.max() 返回传入数字中的最大值。
const values = [19, 90, -2, 6, 25];console.log( Math.max(...values) ); // 90
它还提供了对Objects进行解构赋值的功能。
const myObject = {a: 1,b: 2,c: 3};const { a, ...r } = myObject;// a = 1// r = { b: 2, c: 3 }// Can also be used in function input parametersfunction restObjectInParam({ a, ...r }) {console.log(a); // 1console.log(r); // {b: 2, c: 3}}restObjectInParam({a: 1,b: 2,c: 3});
4. 正则表达式组
RegExp 可以返回匹配的数据包
const regExpDate = /([0-9]{4})-([0-9]{2})-([0-9]{2})/;const match = regExpDate.exec('2020-06-25');const year = match[1]; // 2020const month = match[2]; // 06const day = match[3]; // 25
5.正则表达式前瞻否定
TBD6.正则表达式 dotAll
. 表示匹配除输入以外的任何符号,添加这些标志后,允许匹配输入。
/hello.world/.test('hello\nworld'); // false/hello.world/s.test('hello\nworld'); // true
六、ES10 (ES2019)
1.更友好的 JSON.stringify
如果输入是 Unicode 但超出范围,则 JSON.stringify 最初会返回格式错误的 Unicode 字符串。
现在是第 3 阶段的提案,使其成为有效的 Unicode 并以 UTF-8 呈现
2. Array.prototype.flat() & Array.prototype.flatMap()
展平阵列
const arr1 = [1, 2, [3, 4]];arr1.flat(); // [1, 2, 3, 4]const arr2 = [1, 2, [3, 4, [5, 6]]];arr2.flat(); // [1, 2, 3, 4, [5, 6]]// Pass in a number in flat, representing the flattening deptharr2.flat(2); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
flatMap(),相当于reduce with concat,可以展平一个维度
let arr = ["早安", "", "今天天氣不錯"]arr.map(s => s.split(""))// [["早", "安"], [""], ["今", "天", "天", "氣", "不", "錯"]]arr.flatMap(s => s.split(''));// ["早", "安", "", "今", "天", "天", "氣", "不", "錯"]
3. String.prototype.trimStart() & String.prototype.trimEnd()
trimStart() 方法从字符串的开头删除空格,trimLeft() 是此方法的别名。
const greeting = ‘ Hello world! ‘;console.log(greeting);// expected output: “ Hello world! “;console.log(greeting.trimStart());// expected output: “Hello world! “;
trimEnd() 方法从字符串末尾删除空格,trimRight() 是此方法的别名。
const greeting = ' Hello world! ';console.log(greeting);// expected output: " Hello world! ";console.log(greeting.trimEnd());// expected output: " Hello world!";
4. Object.fromEntries()
Object.fromEntries() 方法将键值对列表转换为对象。
const entries = new Map([['foo', 'bar'],['baz', 42]]);const obj = Object.fromEntries(entries);console.log(obj);// expected output: Object { foo: "bar", baz: 42 }
5. String.prototype.matchAll
matchAll() 方法返回将字符串与正则表达式匹配的所有结果的迭代器,包括捕获组。
const regexp = /t(e)(st(\d?))/g;const str = 'test1test2';const array = [...str.matchAll(regexp)];console.log(array[0]);// expected output: Array ["test1", "e", "st1", "1"]console.log(array[1]);// expected output: Array ["test2", "e", "st2", "2"]
6.fixed catch 绑定
在使用catch之前,不管有用与否,一定要传入一个eparameter来表示接收到的错误。
如果现在不用,可以省略。
try {...} catch(e) {...}// If e is not used, it can be omittedtry {...} catch {...}
7. BigInt(新数字类型)
BigInt 值,有时也称为 BigInt,是一个 bigint 原语,通过将 n 附加到整数文字的末尾,或通过调用 BigInt() 函数(没有 new 运算符)并给它一个整数值或字符串来创建 价值。
ES5:String, Number, Boolean, Null, Undefined
ES6 新增:Symbol,到ES6就一共有6 种类型
ES10 新增:BigInt,就达到 7 种类型
const theBiggestInt = 9007199254740991n;const alsoHuge = BigInt(9007199254740991);// ↪ 9007199254740991nconst hugeString = BigInt("9007199254740991");// ↪ 9007199254740991nconst hugeHex = BigInt("0x1fffffffffffff");// ↪ 9007199254740991nconst hugeBin = BigInt("0b11111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111");// ↪ 9007199254740991n
七、ES11 (ES2020)
1.Promise.allSettled()
Promise.allSettled() 方法返回一个在所有给定的 Promise 都已实现或拒绝后实现的 Promise,并带有一组对象,每个对象都描述了每个 Promise 的结果。
它通常用于当你有多个不依赖于彼此成功完成的异步任务,或者你总是想知道每个 Promise 的结果时。
相比之下,Promise.all() 返回的 Promise 可能更合适,如果任务相互依赖/如果你想立即拒绝其中任何一个拒绝。
const promise1 = Promise.resolve(3);const promise2 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => setTimeout(reject, 100, 'foo'));const promises = [promise1, promise2];Promise.allSettled(promises).then((results) => results.forEach((result) => console.log(result.status)));// expected output:// "fulfilled"// "rejected"
2. 可选链接?
在开发中,很容易遇到先判断数据是否存在,判断是否写入。
const isUserExist = user && user.info;if (isUserExist) {username = user.info.name;}
如果返回的数据为null或者用户对象下没有.intounder,则会抛出Uncaught TypeError: Cannot read property...。
导致程序无法继续执行
使用 ?,语法更简单
const username = user?.info?.name;如果存在,获取name的值,如果不存在,赋值undefined
与 || 一起使用,只需一行!
const username = user?.name || 'guest';3. Nullish 合并运算符 ??
在JavaScript中,遇到0、null、undefuded时会自动转为false。
但有时0其实是一个正常的值,只能容错undefined和null
/*** user = {* level: 0* }*/const level = user.level || 'no level'; // output as no level instead of expected 0// to fix it, it must use if simple processingconst level = user.level !== undefined && user.level !== null ? user.level : 'no level';
但是使用??,你可以保持简洁
const username = user.level ?? 'no level';// output 0. if level is not available, it becomes 'no level'.
4.Dynamic-import
从字面上看,应该很容易理解,就是在需要的时候加载相关的逻辑。
el.onclick = () => {import(`/js/current-logic.js`).then((module) => {module.doSomthing();}).catch((err) => {handleError(err);})}
5. GlobalThis
全局 globalThis 属性包含全局 this 值,类似于全局对象。
过去的做法是:
// https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/globalThisconst getGlobal = function () {if (typeof self !== 'undefined') { return self; }if (typeof window !== 'undefined') { return window; }if (typeof global !== 'undefined') { return global; }throw new Error('unable to locate global object');};var globals = getGlobal();
现在,我们可以这样做:
function canMakeHTTPRequest() {return typeof globalThis.XMLHttpRequest === 'function';}console.log(canMakeHTTPRequest());// expected output (in a browser): true
八、ES12 (ES2021)
1.Promise.any()
Promise.any() 接受一个可迭代的 Promise 对象。它返回一个单一的 Promise,只要 iterable 中的任何一个 Promise 完成,就会返回一个 Promise,并带有已完成的 Promise 的值。
如果可迭代的实现中没有任何承诺(如果所有给定的承诺都被拒绝),则返回的承诺会被 AggregateError 拒绝,AggregateError 是 Error 的一个新子类,它将单个错误组合在一起。
const p1 = new Promise((resolve) => {setTimeout(() => {resolve('p1 resolved value')}, 1000)})const p2 = new Promise((resolve) => {setTimeout(() => {resolve('p2 resolved value')}, 500)})const p3 = new Promise((resolve) => {setTimeout(() => {resolve('p3 resolved value')}, 1800)})Promise.any([p1, p2, p3]).then(value=>{console.log(value)}) // p2 resolved value
2. 逻辑赋值运算符
在开发过程中,我们可以使用 ES2020 中提出的逻辑运算符 ||、&& 和 ??(Nullish coalescing operator)来解决一些问题。
而 ES2021 会提出 ||= , &&= , ??= ,概念类似于 += :
let b = 2b += 1// equal to b = b + 1let a = nulla ||= 'some random text' // a become to'some random text'// equal a = a || 'some random text'let c = 'some random texts'c &&= null // c become to null// equal to c = c && nulllet d = nulld ??= false // d become to false// equal to d = d ?? false
3. WeakRef
WeakRef 对象包含对对象的弱引用,该对象称为其目标或引用对象。对对象的弱引用是不会阻止对象被垃圾收集器回收的引用。
相反,普通(或强)引用将对象保存在内存中,当一个对象不再有任何强引用时,JavaScript 引擎的垃圾收集器可能会销毁该对象并回收其内存。
如果发生这种情况,你将无法再从弱引用中获取对象。
此示例启动一个显示在 DOM 元素中的计数器,当该元素不再存在时停止:
class Counter {constructor(element) {// Remember a weak reference to the DOM elementthis.ref = new WeakRef(element);this.start();}start() {if (this.timer) {return;}this.count = 0;const tick = () => {// Get the element from the weak reference, if it still existsconst element = this.ref.deref();if (element) {element.textContent = ++this.count;} else {// The element doesn't exist anymoreconsole.log("The element is gone.");this.stop();this.ref = null;}};tick();this.timer = setInterval(tick, 1000);}stop() {if (this.timer) {clearInterval(this.timer);this.timer = 0;}}}const counter = new Counter(document.getElementById("counter"));setTimeout(() => {document.getElementById("counter").remove();}, 5000);
到这里,今天要跟你分享的内容就全部结束了,这些都是我的一些练习和学习笔记总结,希望对你有用。
写在最后
今天分享的内容,如果觉得有用的话,请记得点赞我,关注我,并将这篇文章与你的开发者朋友一起来分享它。
最后,感谢你的阅读。
如果你身边还有想学习前端开发的朋友,也请将我们的公众号分享给他,也许对他的学习有帮助。
学习更多技能
请点击下方公众号
![]()

