利用Python制作雷达图

下面以实际例子给大家讲解一下雷达图的应用场景和绘制方法:
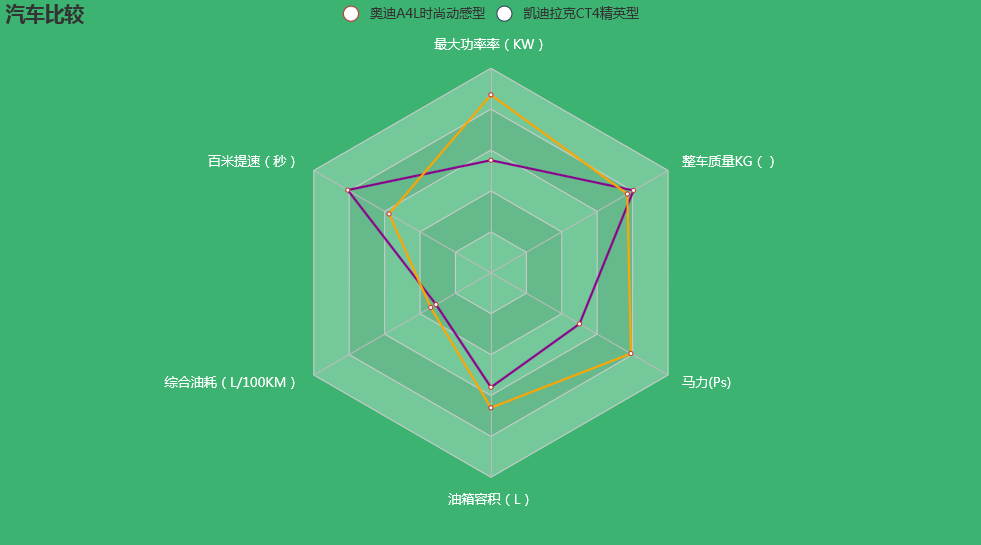
一、比较汽车性能
这类雷达图一般用于比较同类事物不同纬度性能的优劣,以奥迪A4L时尚动感型和凯迪拉克CT4精英型为例,我们来画一下这两种汽车的雷达图,代码如下:
import pyecharts.options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Radar
v1 = [[110, 9.7, 6.2, 56, 150, 1610]]
v2 = [[174, 6.9, 6.8, 66, 237, 1540]]
c=(
Radar(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(bg_color="#3CB371")) #设置背景颜色
.add_schema(
schema=[
opts.RadarIndicatorItem(name="最大功率率(KW)", max_=200),
opts.RadarIndicatorItem(name="百米提速(秒)", max_=12),
opts.RadarIndicatorItem(name="综合油耗(L/100KM)", max_=20),
opts.RadarIndicatorItem(name="油箱容积(L)", max_=100),
opts.RadarIndicatorItem(name="马力(Ps)", max_=300),
opts.RadarIndicatorItem(name="整车质量KG()", max_=2000),
],
splitarea_opt=opts.SplitAreaOpts(
is_show=True, areastyle_opts=opts.AreaStyleOpts(opacity=1) #是否显示分隔区域,透明度设置为1
),
textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(color="#fff"),
)
.add(
series_name="奥迪A4L时尚动感型",
data=v1,
linestyle_opts=opts.LineStyleOpts(color="#8B008B",width=2), #线的颜色、宽度
)
.add(
series_name="凯迪拉克CT4精英型",
data=v2,
linestyle_opts=opts.LineStyleOpts(color="#FFA500",width=2), #线的颜色、宽度
)
.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=False)) #不显示数字
.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="汽车性能比较"), legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts()
)
)
c.render_notebook()
参数介绍:
1.通过设置InitOpts的bg_color参数,可以改变背景颜色
2.通过设置add_schema的schema参数,可以添加更多纬度变量
3.通过设置LineStyleOpts的color参数,可以设置线的颜色和宽度
通过雷达图,可以清晰的比较两种汽车性能指标的好坏,非常直观
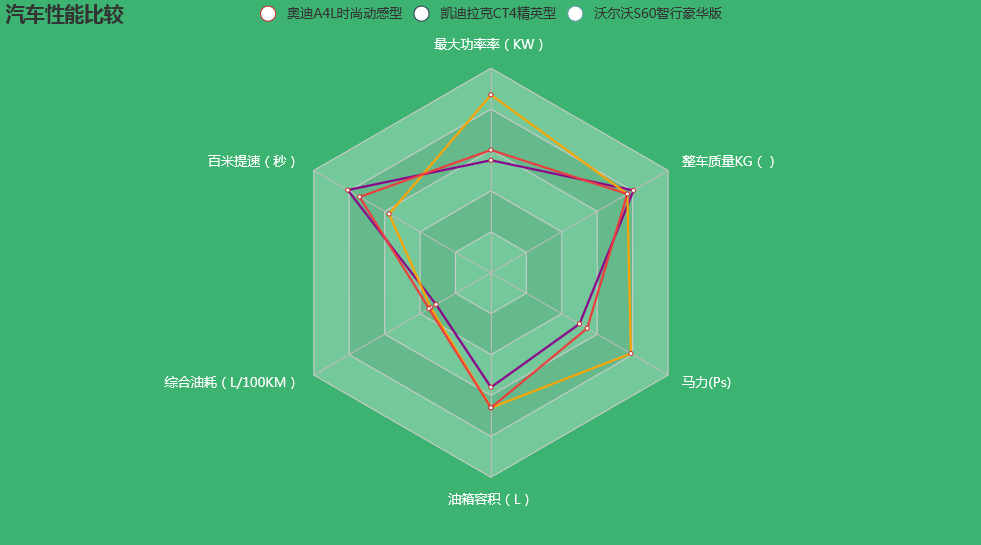
如果感觉两台车不过瘾,我们可以再加1台:
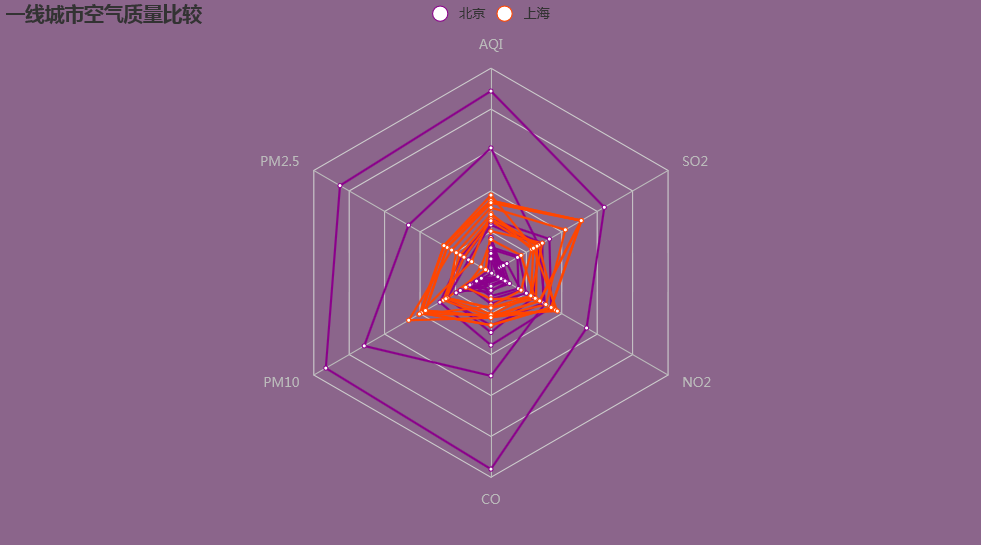
二、比较不同城市近期天气状况
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Radar
value_bj = [
[55, 9, 56, 0.46, 18, 6, 1],
[25, 11, 21, 0.65, 34, 9, 2],
[56, 7, 63, 0.3, 14, 5, 3],
[33, 7, 29, 0.33, 16, 6, 4],
[42, 24, 44, 0.76, 40, 16, 5],
[82, 58, 90, 1.77, 68, 33, 6],
[74, 49, 77, 1.46, 48, 27, 7],
[78, 55, 80, 1.29, 59, 29, 8],
[267, 216, 280, 4.8, 108, 64, 9],
[185, 127, 216, 2.52, 61, 27, 10],
[39, 19, 38, 0.57, 31, 15, 11],
[41, 11, 40, 0.43, 21, 7, 12],
]
value_sh = [
[91, 45, 125, 0.82, 34, 23, 1],
[65, 27, 78, 0.86, 45, 29, 2],
[83, 60, 84, 1.09, 73, 27, 3],
[109, 81, 121, 1.28, 68, 51, 4],
[106, 77, 114, 1.07, 55, 51, 5],
[109, 81, 121, 1.28, 68, 51, 6],
[106, 77, 114, 1.07, 55, 51, 7],
[89, 65, 78, 0.86, 51, 26, 8],
[53, 33, 47, 0.64, 50, 17, 9],
[80, 55, 80, 1.01, 75, 24, 10],
[117, 81, 124, 1.03, 45, 24, 11],
[99, 71, 142, 1.1, 62, 42, 12],
]
c_schema = [
{"name": "AQI", "max": 300, "min": 5},
{"name": "PM2.5", "max": 250, "min": 20},
{"name": "PM10", "max": 300, "min": 5},
{"name": "CO", "max": 5},
{"name": "NO2", "max": 200},
{"name": "SO2", "max": 100},
]
c = (
Radar(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(bg_color="#8B658B"))
.add_schema(schema=c_schema, shape="polygon")
.add("北京", value_bj,color="#8B008B",linestyle_opts=opts.LineStyleOpts(width=2))
.add("上海", value_sh,color="#FF4500",linestyle_opts=opts.LineStyleOpts(width=2))
.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=False))
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="一线城市空气质量比较"))
)
c.render_notebook()
通过增加数据种类,可以比较同一纬度、不同时间下的差距,如上图,通过展示北京、上海两座城市12天的天气情况,可以清晰的看出上海的天气要比北京好。





评论