浅谈运行时修改Java注解的值
这里介绍如何在运行时修改注解的值
基本原理
查看JDK中Annotation接口的注释,说明所有注解都扩展自Annotation接口。换言之,注解本质上就是一个继承了Annotation的接口
package java.lang.annotation;
/**
* The common interface extended by all annotation types.
* ...
* @author Josh Bloch
* @since 1.5
*/
public interface Annotation {
...
}
这里,我们先自定义一个注解@MyLog,同时定义一个类UserInfoService来使用该注解
/**
* 自定义注解
*/
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyLog {
String level() default "TRACE";
}
...
public class UserInfoService {
@MyLog( level = "DEBUG")
public void attachById(Integer userId) {
}
@MyLog( level = "INFO")
public void batchDelete(List<Integer> ids) {
}
}
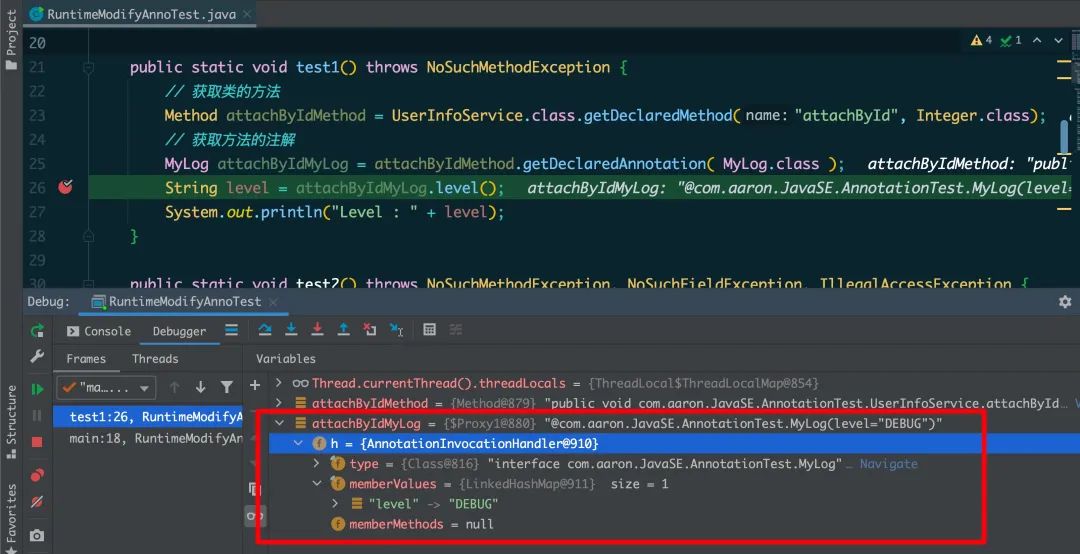
现在我们通过debug的方式来查看反射后的注解对象。由于注解的具体实现类是利用JDK动态代理生成的。故我们通过反射获得的注解对象,实际上是运行时生成的动态代理对象Proxy
public class RuntimeModifyAnnoTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException {
test1();
}
public static void test1() throws NoSuchMethodException {
// 获取类的方法
Method attachByIdMethod = UserInfoService.class.getDeclaredMethod("attachById", Integer.class);
// 获取方法的注解
MyLog attachByIdMyLog = attachByIdMethod.getDeclaredAnnotation( MyLog.class );
String level = attachByIdMyLog.level();
System.out.println("Level : " + level);
}
}
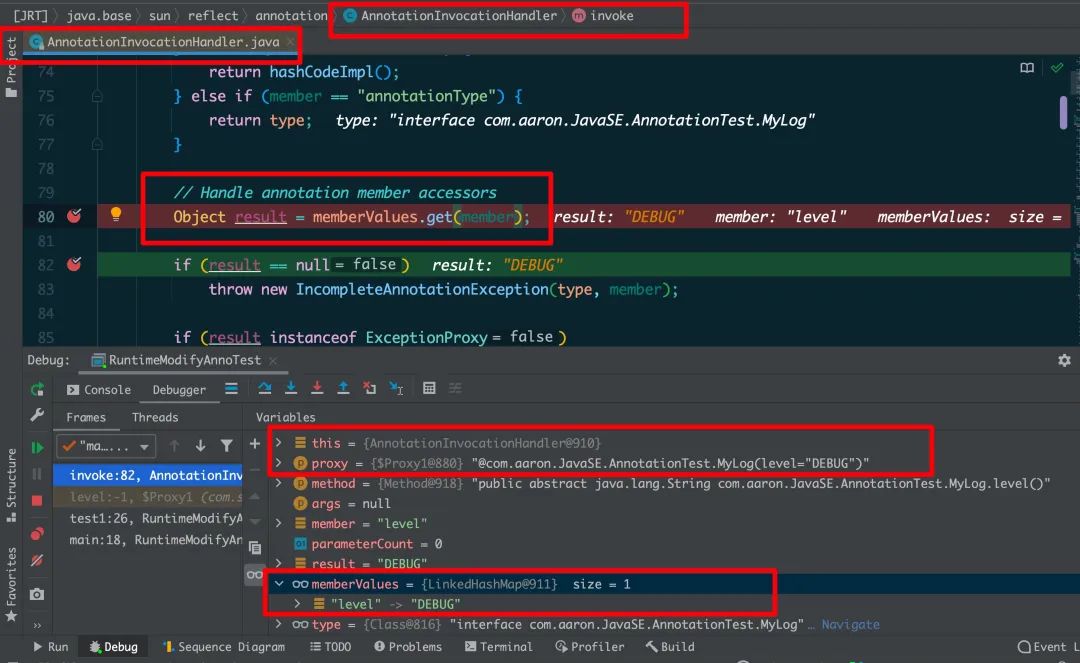
而当我们通过这个动态代理对象Proxy访问level属性值时,其会通过调用 AnnotationInvocationHandler 的invoke方法来实现。进一步地观察invoke方法的源码,不难看出其最终是从memberValues这个Map中获取到对应的值
实践
现在,我们如果期望在运行时修改注解的属性值就非常简单了。只需先通过反射获取注解的代理对象,然后获取该代理对象的InvocationHandler实例,最后修改AnnotationInvocationHandler实例的memberValues字段中属性值即可。下述代码,尝试将attachById方法上@MyLog注解的值由DEBUG修改为WARN;而batchDelete方法上@MyLog注解的值则不会受到影响
/**
* 动态修改注解值
*/
public class RuntimeModifyAnnoTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
test2();
}
public static void test2() throws NoSuchMethodException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
// 获取类的方法
Method attachByIdMethod = UserInfoService.class.getDeclaredMethod("attachById", Integer.class);
// 获取方法的注解
MyLog attachByIdMyLog = attachByIdMethod.getDeclaredAnnotation( MyLog.class );
// 获取注解level属性的值
String level = attachByIdMyLog.level();
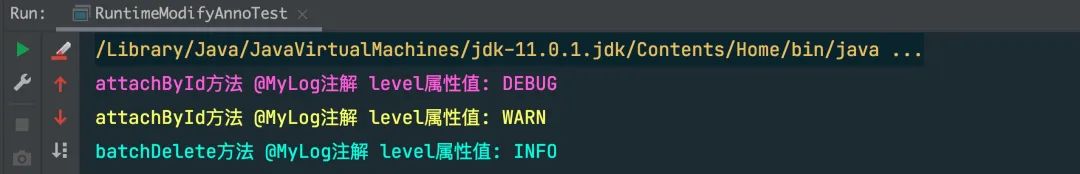
System.out.println("attachById方法 @MyLog注解 level属性值: " + level);
//获取该代理对象的InvocationHandler调用处理器实例
InvocationHandler invocationHandler = Proxy.getInvocationHandler( attachByIdMyLog );
// 获取AnnotationInvocationHandler类的的私有字段 memberValues
Field memberValuesField = invocationHandler.getClass().getDeclaredField("memberValues");
// 因为 memberValues 字段为private,故需设置为可访问
memberValuesField.setAccessible(true);
// 获取 memberValues 字段的值
Map<String, Object> memberValues = (Map<String, Object>) memberValuesField.get(invocationHandler);
// 修改注解属性为level的值
memberValues.put("level", "WARN");
// 获取注解level属性的值
level = attachByIdMyLog.level();
System.out.println("attachById方法 @MyLog注解 level属性值: " + level);
// 获取类的方法
Method batchDeleteMethod = UserInfoService.class.getDeclaredMethod("batchDelete", List.class);
// 获取方法的注解
MyLog batchDeleteMyLog = batchDeleteMethod.getDeclaredAnnotation( MyLog.class );
// 获取注解level属性的值
level = batchDeleteMyLog.level();
System.out.println("batchDelete方法 @MyLog注解 level属性值: " + level);
}
}
效果如下所示
评论
