SpringBoot:如何优雅地进行参数传递、响应数据封装、异常处理?

作者:云深i不知处
blog.csdn.net/mu_wind/article/details/99960645
在项目开发中,接口与接口之间、前后端之间的数据传输都使用 JSON 格式。
1 fastjson使用
阿里巴巴的 fastjson是目前应用最广泛的JSON解析框架。本文也将使用fastjson。
1.1 引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.35</version>
</dependency>
2 统一封装返回数据
在web项目中,接口返回数据一般要包含状态码、信息、数据等,例如下面的接口示例:
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author guozhengMu
* @version 1.0
* @date 2019/8/21 14:55
* @description
* @modify
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/test", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping("/json")
public JSONObject test() {
JSONObject result = new JSONObject();
try {
// 业务逻辑代码
result.put("code", 0);
result.put("msg", "操作成功!");
result.put("data", "测试数据");
} catch (Exception e) {
result.put("code", 500);
result.put("msg", "系统异常,请联系管理员!");
}
return result;
}
}
这样的话,每个接口都这样处理,非常麻烦,需要一种更优雅的实现方式。
2.1 定义统一的JSON结构
统一的 JSON 结构中属性包括数据、状态码、提示信息,其他项可以自己根据需要添加。一般来说,应该有默认的返回结构,也应该有用户指定的返回结构。由于返回数据类型无法确定,需要使用泛型,代码如下:
public class ResponseInfo<T> {
/**
* 状态码
*/
protected String code;
/**
* 响应信息
*/
protected String msg;
/**
* 返回数据
*/
private T data;
/**
* 若没有数据返回,默认状态码为 0,提示信息为“操作成功!”
*/
public ResponseInfo() {
this.code = 0;
this.msg = "操作成功!";
}
/**
* 若没有数据返回,可以人为指定状态码和提示信息
* @param code
* @param msg
*/
public ResponseInfo(String code, String msg) {
this.code = code;
this.msg = msg;
}
/**
* 有数据返回时,状态码为 0,默认提示信息为“操作成功!”
* @param data
*/
public ResponseInfo(T data) {
this.data = data;
this.code = 0;
this.msg = "操作成功!";
}
/**
* 有数据返回,状态码为 0,人为指定提示信息
* @param data
* @param msg
*/
public ResponseInfo(T data, String msg) {
this.data = data;
this.code = 0;
this.msg = msg;
}
// 省略 get 和 set 方法
}
2.2 使用统一的JSON结构
我们封装了统一的返回数据结构后,在接口中就可以直接使用了。如下:
import com.example.demo.model.ResponseInfo;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author guozhengMu
* @version 1.0
* @date 2019/8/21 14:55
* @description
* @modify
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/test", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping("/json")
public ResponseInfo test() {
try {
// 模拟异常业务代码
int num = 1 / 0;
return new ResponseInfo("测试数据");
} catch (Exception e) {
return new ResponseInfo(500, "系统异常,请联系管理员!");
}
}
}
如上,接口的返回数据处理便优雅了许多。针对上面接口做个测试,启动项目,通过浏览器访问:localhost:8096/test/json,得到响应结果:
{"code":500,"msg":"系统异常,请联系管理员!","data":null}
3 全局异常处理
3.1 系统定义异常处理
新建一个 ExceptionHandlerAdvice 全局异常处理类,然后加上 @RestControllerAdvice 注解即可拦截项目中抛出的异常,如下代码中包含了几个异常处理,如参数格式异常、参数缺失、系统异常等,见下例:
@RestControllerAdvice
@Slf4j
public class ExceptionHandlerAdvice {
// 参数格式异常处理
@ExceptionHandler({IllegalArgumentException.class})
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
public ResponseInfo badRequestException(IllegalArgumentException exception) {
log.error("参数格式不合法:" + e.getMessage());
return new ResponseInfo(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST.value() + "", "参数格式不符!");
}
// 权限不足异常处理
@ExceptionHandler({AccessDeniedException.class})
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN)
public ResponseInfo badRequestException(AccessDeniedException exception) {
return new ResponseInfo(HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN.value() + "", exception.getMessage());
}
// 参数缺失异常处理
@ExceptionHandler({MissingServletRequestParameterException.class})
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
public ResponseInfo badRequestException(Exception exception) {
return new ResponseInfo(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST.value() + "", "缺少必填参数!");
}
// 空指针异常
@ExceptionHandler(NullPointerException.class)
@ResponseStatus(value = HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
public ResponseInfo handleTypeMismatchException(NullPointerException ex) {
log.error("空指针异常,{}", ex.getMessage());
return new JsonResult("500", "空指针异常");
}
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
@ResponseStatus(value = HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
public JsonResult handleUnexpectedServer(Exception ex) {
log.error("系统异常:", ex);
return new JsonResult("500", "系统发生异常,请联系管理员");
}
// 系统异常处理
@ExceptionHandler(Throwable.class)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
public ResponseInfo exception(Throwable throwable) {
log.error("系统异常", throwable);
return new ResponseInfo(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value() + "系统异常,请联系管理员!");
}
}
@RestControllerAdvice 注解包含了 @Component 注解,说明在 Spring Boot 启动时,也会把该类作为组件交给 Spring 来管理。 @RestControllerAdvice 注解包含了 @ResponseBody 注解,为了异常处理完之后给调用方输出一个 JSON 格式的封装数据。 @RestControllerAdvice 注解还有个 basePackages 属性,该属性用来拦截哪个包中的异常信息,一般我们不指定这个属性,我们拦截项目工程中的所有异常。 在方法上通过 @ExceptionHandler 注解来指定具体的异常,然后在方法中处理该异常信息,最后将结果通过统一的 JSON 结构体返回给调用者。 但在项目中,我们一般都会比较详细地去拦截一些常见异常,拦截 Exception 虽然可以一劳永逸,但是不利于我们去排查或者定位问题。实际项目中,可以把拦截 Exception 异常写在 GlobalExceptionHandler 最下面,如果都没有找到,最后再拦截一下 Exception 异常,保证输出信息友好。
下面我们通过一个接口来进行测试:
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/test", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping("/json")
public ResponseInfo test(@RequestParam String userName, @RequestParam String password) {
try {
String data = "登录用户:" + userName + ",密码:" + password;
return new ResponseInfo("0", "操作成功!", data);
} catch (Exception e) {
return new ResponseInfo("500", "系统异常,请联系管理员!");
}
}
}
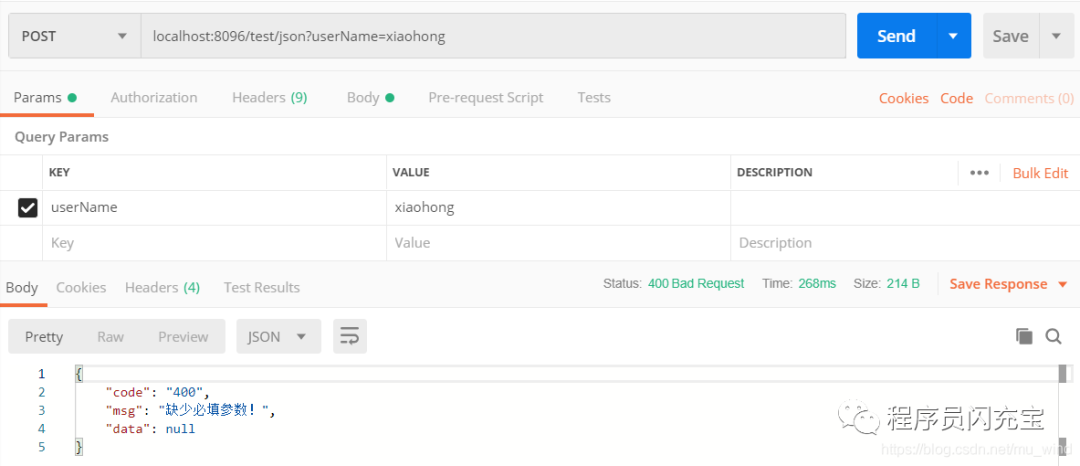
接口调用,password这项故意空缺:
评论

