【NLP】简单学习一下NLP中的transformer的pytorch代码
经典transformer的学习 文章转自微信公众号【机器学习炼丹术】 作者:陈亦新(已授权) 联系方式: 微信cyx645016617 欢迎交流,共同进步
代码细讲
transformer
Embedding
Encoder_MultipleLayers
Encoder
完整代码
代码细讲
transformer
class transformer(nn.Sequential):
def __init__(self, encoding, **config):
super(transformer, self).__init__()
if encoding == 'drug':
self.emb = Embeddings(config['input_dim_drug'], config['transformer_emb_size_drug'], 50, config['transformer_dropout_rate'])
self.encoder = Encoder_MultipleLayers(config['transformer_n_layer_drug'],
config['transformer_emb_size_drug'],
config['transformer_intermediate_size_drug'],
config['transformer_num_attention_heads_drug'],
config['transformer_attention_probs_dropout'],
config['transformer_hidden_dropout_rate'])
elif encoding == 'protein':
self.emb = Embeddings(config['input_dim_protein'], config['transformer_emb_size_target'], 545, config['transformer_dropout_rate'])
self.encoder = Encoder_MultipleLayers(config['transformer_n_layer_target'],
config['transformer_emb_size_target'],
config['transformer_intermediate_size_target'],
config['transformer_num_attention_heads_target'],
config['transformer_attention_probs_dropout'],
config['transformer_hidden_dropout_rate'])
### parameter v (tuple of length 2) is from utils.drug2emb_encoder
def forward(self, v):
e = v[0].long().to(device)
e_mask = v[1].long().to(device)
print(e.shape,e_mask.shape)
ex_e_mask = e_mask.unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(2)
ex_e_mask = (1.0 - ex_e_mask) * -10000.0
emb = self.emb(e)
encoded_layers = self.encoder(emb.float(), ex_e_mask.float())
return encoded_layers[:,0]
只要有两个组件,一个是Embedding层,一个是Encoder_MultipleLayers模块; forward的输入v是一个元组,包含两个元素:第一个是数据,第二个是mask。对应有效数据的位置。
Embedding
class Embeddings(nn.Module):
"""Construct the embeddings from protein/target, position embeddings.
"""
def __init__(self, vocab_size, hidden_size, max_position_size, dropout_rate):
super(Embeddings, self).__init__()
self.word_embeddings = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, hidden_size)
self.position_embeddings = nn.Embedding(max_position_size, hidden_size)
self.LayerNorm = nn.LayerNorm(hidden_size)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout_rate)
def forward(self, input_ids):
seq_length = input_ids.size(1)
position_ids = torch.arange(seq_length, dtype=torch.long, device=input_ids.device)
position_ids = position_ids.unsqueeze(0).expand_as(input_ids)
words_embeddings = self.word_embeddings(input_ids)
position_embeddings = self.position_embeddings(position_ids)
embeddings = words_embeddings + position_embeddings
embeddings = self.LayerNorm(embeddings)
embeddings = self.dropout(embeddings)
return embeddings
包含三个组件,一个是Embedding,其他是LayerNorm和Dropout层。
torch.nn.Embedding(num_embeddings, embedding_dim, padding_idx=None,
max_norm=None, norm_type=2.0, scale_grad_by_freq=False,
sparse=False, _weight=None)
其为一个简单的存储固定大小的词典的嵌入向量的查找表,意思就是说,给一个编号,嵌入层就能返回这个编号对应的嵌入向量,嵌入向量反映了各个编号代表的符号之间的语义关系。
输入为一个编号列表,输出为对应的符号嵌入向量列表。
num_embeddings (python:int) – 词典的大小尺寸,比如总共出现5000个词,那就输入5000。此时index为(0-4999) embedding_dim (python:int) – 嵌入向量的维度,即用多少维来表示一个符号。 padding_idx (python:int, optional) – 填充id,比如,输入长度为100,但是每次的句子长度并不一样,后面就需要用统一的数字填充,而这里就是指定这个数字,这样,网络在遇到填充id时,就不会计算其与其它符号的相关性。(初始化为0) max_norm (python:float, optional) – 最大范数,如果嵌入向量的范数超过了这个界限,就要进行再归一化。 norm_type (python:float, optional) – 指定利用什么范数计算,并用于对比max_norm,默认为2范数。 scale_grad_by_freq (boolean, optional) – 根据单词在mini-batch中出现的频率,对梯度进行放缩。默认为False. sparse (bool, optional) – 若为True,则与权重矩阵相关的梯度转变为稀疏张量。
举一个例子:

如果你的整数最大超过了设置的字典的容量,那么就会出错误: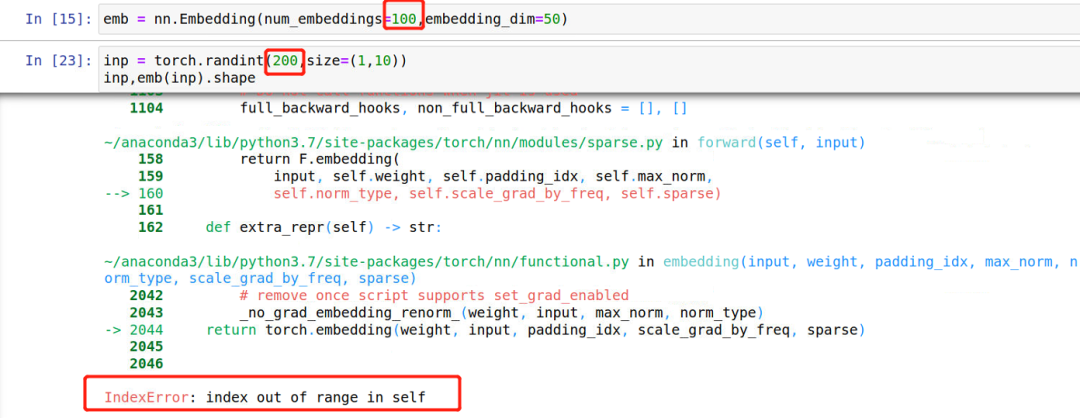
Embedding其中有可学习参数!是一个num_embedding * embedding_dim的矩阵。
Encoder_MultipleLayers
class Encoder_MultipleLayers(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_layer, hidden_size, intermediate_size, num_attention_heads, attention_probs_dropout_prob, hidden_dropout_prob):
super(Encoder_MultipleLayers, self).__init__()
layer = Encoder(hidden_size, intermediate_size, num_attention_heads, attention_probs_dropout_prob, hidden_dropout_prob)
self.layer = nn.ModuleList([copy.deepcopy(layer) for _ in range(n_layer)])
def forward(self, hidden_states, attention_mask, output_all_encoded_layers=True):
all_encoder_layers = []
for layer_module in self.layer:
hidden_states = layer_module(hidden_states, attention_mask)
return hidden_states
transformer中的embedding,目的是将数据转换成对应的向量。这个Encoder-multilayer则是提取特征的关键。 结构很简单,就是由==n_layer==个Encoder堆叠而成。
Encoder
class Encoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_size, intermediate_size, num_attention_heads, attention_probs_dropout_prob, hidden_dropout_prob):
super(Encoder, self).__init__()
self.attention = Attention(hidden_size, num_attention_heads, attention_probs_dropout_prob, hidden_dropout_prob)
self.intermediate = Intermediate(hidden_size, intermediate_size)
self.output = Output(intermediate_size, hidden_size, hidden_dropout_prob)
def forward(self, hidden_states, attention_mask):
attention_output = self.attention(hidden_states, attention_mask)
intermediate_output = self.intermediate(attention_output)
layer_output = self.output(intermediate_output, attention_output)
return layer_output
其中包含了Attention部分,Intermediate和Output。
class Attention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_size, num_attention_heads, attention_probs_dropout_prob, hidden_dropout_prob):
super(Attention, self).__init__()
self.self = SelfAttention(hidden_size, num_attention_heads, attention_probs_dropout_prob)
self.output = SelfOutput(hidden_size, hidden_dropout_prob)
def forward(self, input_tensor, attention_mask):
self_output = self.self(input_tensor, attention_mask)
attention_output = self.output(self_output, input_tensor)
return attention_output
class SelfAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_size, num_attention_heads, attention_probs_dropout_prob):
super(SelfAttention, self).__init__()
if hidden_size % num_attention_heads != 0:
raise ValueError(
"The hidden size (%d) is not a multiple of the number of attention "
"heads (%d)" % (hidden_size, num_attention_heads))
self.num_attention_heads = num_attention_heads
self.attention_head_size = int(hidden_size / num_attention_heads)
self.all_head_size = self.num_attention_heads * self.attention_head_size
self.query = nn.Linear(hidden_size, self.all_head_size)
self.key = nn.Linear(hidden_size, self.all_head_size)
self.value = nn.Linear(hidden_size, self.all_head_size)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(attention_probs_dropout_prob)
def transpose_for_scores(self, x):
# num_attention_heads = 8, attention_head_size = 128 / 8 = 16
new_x_shape = x.size()[:-1] + (self.num_attention_heads, self.attention_head_size)
x = x.view(*new_x_shape)
return x.permute(0, 2, 1, 3)
def forward(self, hidden_states, attention_mask):
# hidden_states.shape = [batch,50,128]
mixed_query_layer = self.query(hidden_states)
mixed_key_layer = self.key(hidden_states)
mixed_value_layer = self.value(hidden_states)
query_layer = self.transpose_for_scores(mixed_query_layer)
key_layer = self.transpose_for_scores(mixed_key_layer)
value_layer = self.transpose_for_scores(mixed_value_layer)
# query_layer.shape = [batch,8,50,16]
# Take the dot product between "query" and "key" to get the raw attention scores.
attention_scores = torch.matmul(query_layer, key_layer.transpose(-1, -2))
# attention_score.shape = [batch,8,50,50]
attention_scores = attention_scores / math.sqrt(self.attention_head_size)
attention_scores = attention_scores + attention_mask
# Normalize the attention scores to probabilities.
attention_probs = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)(attention_scores)
# This is actually dropping out entire tokens to attend to, which might
# seem a bit unusual, but is taken from the original Transformer paper.
attention_probs = self.dropout(attention_probs)
context_layer = torch.matmul(attention_probs, value_layer)
context_layer = context_layer.permute(0, 2, 1, 3).contiguous()
new_context_layer_shape = context_layer.size()[:-2] + (self.all_head_size,)
context_layer = context_layer.view(*new_context_layer_shape)
return context_layer
这一段和一般的vit处理的流程类似。虽然transformer是从NLP到CV的,但从CV的vit再回看NLP的transformer也是有一种乐趣。里面要注意的点是multihead的概念。本来hidden-size是128,如果设置multihead的数量为8,那么其实好比卷积里面的通道数量。会把128的token看成8个16个token,然后分别做自注意力。但是把multihead比作卷积的概念感觉说的过去,比作分组卷积的概念好像也OK:
比作卷积。如果固定了每一个head的size数量为16,那么head就好比通道数,那么增加head的数量,其实就是增加了卷积核通道数的感觉; 比作分组卷积。如果固定了hidden-size的数量为128,那么head的数量就是分组的数量,那么增加head的数量就好比卷积分组变多,降低了计算量。
-其他部分的代码都是FC + LayerNorm +Dropout,不再赘述。
完整代码
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import copy,math
class Embeddings(nn.Module):
"""Construct the embeddings from protein/target, position embeddings.
"""
def __init__(self, vocab_size, hidden_size, max_position_size, dropout_rate):
super(Embeddings, self).__init__()
self.word_embeddings = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, hidden_size)
self.position_embeddings = nn.Embedding(max_position_size, hidden_size)
self.LayerNorm = nn.LayerNorm(hidden_size)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout_rate)
def forward(self, input_ids):
seq_length = input_ids.size(1)
position_ids = torch.arange(seq_length, dtype=torch.long, device=input_ids.device)
position_ids = position_ids.unsqueeze(0).expand_as(input_ids)
words_embeddings = self.word_embeddings(input_ids)
position_embeddings = self.position_embeddings(position_ids)
embeddings = words_embeddings + position_embeddings
embeddings = self.LayerNorm(embeddings)
embeddings = self.dropout(embeddings)
return embeddings
class Encoder_MultipleLayers(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_layer, hidden_size, intermediate_size, num_attention_heads, attention_probs_dropout_prob, hidden_dropout_prob):
super(Encoder_MultipleLayers, self).__init__()
layer = Encoder(hidden_size, intermediate_size, num_attention_heads, attention_probs_dropout_prob, hidden_dropout_prob)
self.layer = nn.ModuleList([copy.deepcopy(layer) for _ in range(n_layer)])
def forward(self, hidden_states, attention_mask, output_all_encoded_layers=True):
all_encoder_layers = []
for layer_module in self.layer:
hidden_states = layer_module(hidden_states, attention_mask)
#if output_all_encoded_layers:
# all_encoder_layers.append(hidden_states)
#if not output_all_encoded_layers:
# all_encoder_layers.append(hidden_states)
return hidden_states
class Encoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_size, intermediate_size, num_attention_heads, attention_probs_dropout_prob, hidden_dropout_prob):
super(Encoder, self).__init__()
self.attention = Attention(hidden_size, num_attention_heads, attention_probs_dropout_prob, hidden_dropout_prob)
self.intermediate = Intermediate(hidden_size, intermediate_size)
self.output = Output(intermediate_size, hidden_size, hidden_dropout_prob)
def forward(self, hidden_states, attention_mask):
attention_output = self.attention(hidden_states, attention_mask)
intermediate_output = self.intermediate(attention_output)
layer_output = self.output(intermediate_output, attention_output)
return layer_output
class Attention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_size, num_attention_heads, attention_probs_dropout_prob, hidden_dropout_prob):
super(Attention, self).__init__()
self.self = SelfAttention(hidden_size, num_attention_heads, attention_probs_dropout_prob)
self.output = SelfOutput(hidden_size, hidden_dropout_prob)
def forward(self, input_tensor, attention_mask):
self_output = self.self(input_tensor, attention_mask)
attention_output = self.output(self_output, input_tensor)
return attention_output
class SelfAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_size, num_attention_heads, attention_probs_dropout_prob):
super(SelfAttention, self).__init__()
if hidden_size % num_attention_heads != 0:
raise ValueError(
"The hidden size (%d) is not a multiple of the number of attention "
"heads (%d)" % (hidden_size, num_attention_heads))
self.num_attention_heads = num_attention_heads
self.attention_head_size = int(hidden_size / num_attention_heads)
self.all_head_size = self.num_attention_heads * self.attention_head_size
self.query = nn.Linear(hidden_size, self.all_head_size)
self.key = nn.Linear(hidden_size, self.all_head_size)
self.value = nn.Linear(hidden_size, self.all_head_size)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(attention_probs_dropout_prob)
def transpose_for_scores(self, x):
new_x_shape = x.size()[:-1] + (self.num_attention_heads, self.attention_head_size)
x = x.view(*new_x_shape)
return x.permute(0, 2, 1, 3)
def forward(self, hidden_states, attention_mask):
mixed_query_layer = self.query(hidden_states)
mixed_key_layer = self.key(hidden_states)
mixed_value_layer = self.value(hidden_states)
query_layer = self.transpose_for_scores(mixed_query_layer)
key_layer = self.transpose_for_scores(mixed_key_layer)
value_layer = self.transpose_for_scores(mixed_value_layer)
# Take the dot product between "query" and "key" to get the raw attention scores.
attention_scores = torch.matmul(query_layer, key_layer.transpose(-1, -2))
attention_scores = attention_scores / math.sqrt(self.attention_head_size)
attention_scores = attention_scores + attention_mask
# Normalize the attention scores to probabilities.
attention_probs = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)(attention_scores)
# This is actually dropping out entire tokens to attend to, which might
# seem a bit unusual, but is taken from the original Transformer paper.
attention_probs = self.dropout(attention_probs)
context_layer = torch.matmul(attention_probs, value_layer)
context_layer = context_layer.permute(0, 2, 1, 3).contiguous()
new_context_layer_shape = context_layer.size()[:-2] + (self.all_head_size,)
context_layer = context_layer.view(*new_context_layer_shape)
return context_layer
class SelfOutput(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_size, hidden_dropout_prob):
super(SelfOutput, self).__init__()
self.dense = nn.Linear(hidden_size, hidden_size)
self.LayerNorm = nn.LayerNorm(hidden_size)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(hidden_dropout_prob)
def forward(self, hidden_states, input_tensor):
hidden_states = self.dense(hidden_states)
hidden_states = self.dropout(hidden_states)
hidden_states = self.LayerNorm(hidden_states + input_tensor)
return hidden_states
class Intermediate(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_size, intermediate_size):
super(Intermediate, self).__init__()
self.dense = nn.Linear(hidden_size, intermediate_size)
def forward(self, hidden_states):
hidden_states = self.dense(hidden_states)
hidden_states = F.relu(hidden_states)
return hidden_states
class Output(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, intermediate_size, hidden_size, hidden_dropout_prob):
super(Output, self).__init__()
self.dense = nn.Linear(intermediate_size, hidden_size)
self.LayerNorm = nn.LayerNorm(hidden_size)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(hidden_dropout_prob)
def forward(self, hidden_states, input_tensor):
hidden_states = self.dense(hidden_states)
hidden_states = self.dropout(hidden_states)
hidden_states = self.LayerNorm(hidden_states + input_tensor)
return hidden_states
class transformer(nn.Sequential):
def __init__(self, encoding, **config):
super(transformer, self).__init__()
if encoding == 'drug':
self.emb = Embeddings(config['input_dim_drug'], config['transformer_emb_size_drug'], 50, config['transformer_dropout_rate'])
self.encoder = Encoder_MultipleLayers(config['transformer_n_layer_drug'],
config['transformer_emb_size_drug'],
config['transformer_intermediate_size_drug'],
config['transformer_num_attention_heads_drug'],
config['transformer_attention_probs_dropout'],
config['transformer_hidden_dropout_rate'])
elif encoding == 'protein':
self.emb = Embeddings(config['input_dim_protein'], config['transformer_emb_size_target'], 545, config['transformer_dropout_rate'])
self.encoder = Encoder_MultipleLayers(config['transformer_n_layer_target'],
config['transformer_emb_size_target'],
config['transformer_intermediate_size_target'],
config['transformer_num_attention_heads_target'],
config['transformer_attention_probs_dropout'],
config['transformer_hidden_dropout_rate'])
### parameter v (tuple of length 2) is from utils.drug2emb_encoder
def forward(self, v):
e = v[0].long().to(device)
e_mask = v[1].long().to(device)
print(e.shape,e_mask.shape)
ex_e_mask = e_mask.unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(2)
ex_e_mask = (1.0 - ex_e_mask) * -10000.0
emb = self.emb(e)
encoded_layers = self.encoder(emb.float(), ex_e_mask.float())
return encoded_layers[:,0]
往期精彩回顾
适合初学者入门人工智能的路线及资料下载 (图文+视频)机器学习入门系列下载 中国大学慕课《机器学习》(黄海广主讲) 机器学习及深度学习笔记等资料打印 《统计学习方法》的代码复现专辑 机器学习交流qq群955171419,加入微信群请扫码:
评论
