花了一个深夜,才用C语言写了一个2048游戏雏形
共 1772字,需浏览 4分钟
·
2020-12-07 21:34
12年我毕业的第二个月工资,我就买了一个IPAD,然后在IPAD上下了一个2048游戏,玩起来非常爽。

然后这几天看到好几个公众号都发了自己写这个游戏的代码,然后我自己也想试试,所以就有了这篇文章,写代码还是很有意思的。
针对这个游戏我写几个比较关键的点
— — 在Linux 下输入不用按回车键也就能获取键值
我们平时输入的时候,需要按 Enter ,getchar 才能获取键值,所以这个需要设置下
/*设置之后不用按下回车就可以接收到字符*/void setBufferedInput(bool enable) {static bool enabled = true;static struct termios old;struct termios new;if (enable && !enabled) {// restore the former settingstcsetattr(STDIN_FILENO,TCSANOW,&old);// set the new stateenabled = true;} else if (!enable && enabled) {// get the terminal settings for standard inputtcgetattr(STDIN_FILENO,&new);// we want to keep the old setting to restore them at the endold = new;// disable canonical mode (buffered i/o) and local echonew.c_lflag &=(~ICANON & ~ECHO);// set the new settings immediatelytcsetattr(STDIN_FILENO,TCSANOW,&new);// set the new stateenabled = false;}}
如果设置为 false,就可以不输入回车就能获取键值,还需要注意我们有时候按下 Ctrl+c 退出程序,需要在这里的回调函数重新设置,要不然在正常的界面输入会出现问题。
— — 随机值的设置
我们需要在画盘上插入随机值,所以就需要随机值生成的方法,C 库里面就有这个随机函数,但是需要设置下。
随机值的设置需要遵循规则如下
//要取得[a,b)的随机整数,使用(rand() % (b-a))+ a (结果值含a不含b)。
//要取得[a,b]的随机整数,使用(rand() % (b-a+1))+ a (结果值含a和b)。
//要取得(a,b]的随机整数,使用(rand() % (b-a))+ a + 1 (结果值不含a含b)。
/*初始化几个数字在键盘上*/int add_random(void){static bool initialized = false;int pos,data,i;/*随机数需要设置种子,用时间来做随机数的种子*/if (!initialized) {srand(time(NULL));initialized = true;}/*检测如果原来的位置有数据了,就不能在原来的数据上加数据*/for(i=0;i<16;i++){pos = rand()%15;if(array_core[pos] != 0)continue;elsebreak;}/*获取 0~4 的随机值*/data = rand()%(4-0+1)+ 0;/*再通过数组把这个数值转换成我们需要的随机数*/place_xy(pos,array_rand[data]);return (0);}
— — 清除屏幕
我们需要循环显示画盘,所以需要每次显示之前都需要清除屏幕,关键代码如下
/*初始化一个键盘*/int show_board(void){printf("\033[H\033[J");/*清空屏幕 但是并不是每一个terminal都会生效*/printf("%s",board);printf("[ ←,↑,→,↓ or q ]\n");return(0);}
— — 几个关键的数组
我们需要几个关键的数组来协助我们计算,这部分根据自己的代码要求来设置。
第一个数组是键盘,我们的数据都是在键盘上显示的,因为 2048 是4个数字,所以中间要预留4个空格出来。
d_xy 数组是用来保存这16个数字的位置的坐标数组,有了这些坐标,就可以知道如何摆放这些数值了。
另外两个数组的作用已经在注释里面写清楚了。
/*数组*/char board[] =" ---------------------\n \| | | | |\n \---------------------\n \| | | | |\n \---------------------\n \| | | | |\n \---------------------\n \| | | | |\n \---------------------\n";const int d_xy[16] = {25,30,35,40, 71,76,81,86, 117,122,127,132, 163,168,173,178};const int array_rand[5] = {2,4,4,2,8};/*随机数值*/int array_core[16] = {0};/*用来保存键盘上的16个数字*/
— — 最关键的移动算法
先说下我们键盘的位置
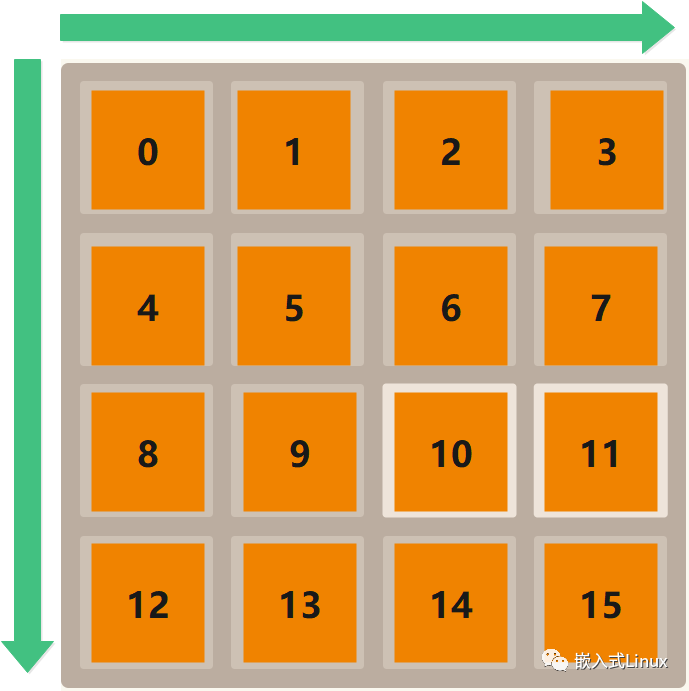
我没有用二维数组,后面想了下,如果用二维数组的话会方便很多,而且算法可能也会方便很多,特别是用到矩阵变换。
— 下移
从下往上的每一列,把相邻相同的数字加起来,放到下面那个位置,然后把上面的位置清0。
把0的数值往上移动,把数字往下移动。
其他方向的移动规则跟这个一样的思路
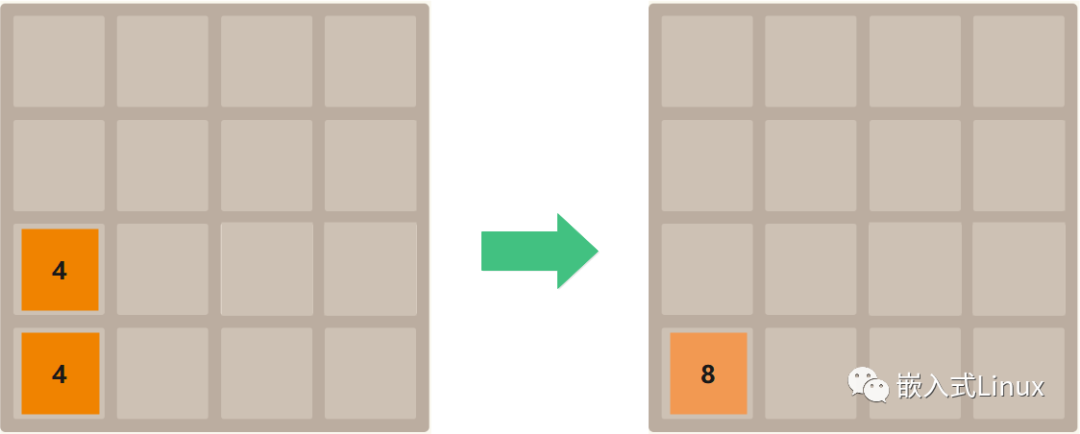
代码实现
/*下移*/int move_down(void){int i=0,j=0,x=0,y=0;int temp[4] = {0};/*1、合并相邻相同的两个元素*//*2、把0元素移动到最上面*/for(x=0;x<4;x++){for(y=x,i=0;y<=12+x;i++,y+=4){temp[i] = array_core[y];}/*合并相邻的两个非0值*/for(i=3;i>=0;i--){for(j=3;j>0;j--){if(temp[j] == temp[j-1] && temp[j-1] != 0){temp[j] = 2*temp[j-1];temp[j-1] = 0;}}}/*把0往上移动*/for(i=3;i>=0;i--){for(j=3;j>0;j--){if(temp[j] == 0 && temp[j-1] != 0){temp[j] = temp[j-1];temp[j-1] = 0;}}}for(y=x,i=0;y<=12+x;i++,y+=4){array_core[y] = temp[i];}}/*在键盘上显示*/for(i=0;i<16;i++)place_xy(i,array_core[i]);add_random();return (0);}
— — 完整代码如下
/*函数声明*/int show_board(void);void teset(void);int move_down(void);/*宏定义*//*数组*/char board[] =" ---------------------\n \| | | | |\n \---------------------\n \| | | | |\n \---------------------\n \| | | | |\n \---------------------\n \| | | | |\n \---------------------\n";const int d_xy[16] = {25,30,35,40, 71,76,81,86, 117,122,127,132, 163,168,173,178};const int array_rand[5] = {2,4,4,2,8};/*随机数值*/int array_core[16] = {0};/*用来保存键盘上的16个数字*/int move_left(void){int i=0,j=0,x=0,y=0;int temp[4] = {0};/*1、合并相邻相同的两个元素*//*2、把0元素移动到最下面*/for(y=0;y<=12;y+=4){for(x=y,i=0;x<=3+y;i++,x++){temp[i] = array_core[x];}/*上移*/for(i=0;i<4;i++){for(j=0;j<3;j++){if(temp[j] == temp[j+1] && temp[j+1] != 0){temp[j] = 2*temp[j+1];temp[j+1] = 0;}}}/*上移*/for(i=0;i<4;i++){for(j=0;j<3;j++){if(temp[j] == 0 && temp[j+1] != 0){temp[j] = temp[j+1];temp[j+1] = 0;}}}for(x=y,i=0;x<=3+y;i++,x++){array_core[x] = temp[i];}}/*在键盘上显示*/for(i=0;i<16;i++){place_xy(i,array_core[i]);}add_random();return (0);}int move_right(void){int i=0,j=0,x=0,y=0;int temp[4] = {0};/*1、合并相邻相同的两个元素*//*2、把0元素移动到最上面*/for(y=0;y<=12;y+=4){for(x=y,i=0;x<=3+y;i++,x++){temp[i] = array_core[x];}/*合并相邻的两个非0值*/for(i=3;i>=0;i--){for(j=3;j>0;j--){if(temp[j] == temp[j-1] && temp[j-1] != 0){temp[j] = 2*temp[j-1];temp[j-1] = 0;}}}/*把0往上移动*/for(i=3;i>=0;i--){for(j=3;j>0;j--){if(temp[j] == 0 && temp[j-1] != 0){temp[j] = temp[j-1];temp[j-1] = 0;}}}for(x=y,i=0;x<=3+y;i++,x++){array_core[x] = temp[i];}}/*在键盘上显示*/for(i=0;i<16;i++)place_xy(i,array_core[i]);add_random();return (0);}/*上移动*/int move_up(void){int i=0,j=0,x=0,y=0;int temp[4] = {0};/*1、合并相邻相同的两个元素*//*2、把0元素移动到最下面*/for(x=0;x<4;x++){for(y=x,i=0;y<=12+x;i++,y+=4){temp[i] = array_core[y];}/*上移*/for(i=0;i<4;i++){for(j=0;j<3;j++){if(temp[j] == temp[j+1] && temp[j+1] != 0){temp[j] = 2*temp[j+1];temp[j+1] = 0;}}}/*上移*/for(i=0;i<4;i++){for(j=0;j<3;j++){if(temp[j] == 0 && temp[j+1] != 0){temp[j] = temp[j+1];temp[j+1] = 0;}}}for(y=x,i=0;y<=12+x;i++,y+=4){array_core[y] = temp[i];}}/*在键盘上显示*/for(i=0;i<16;i++){place_xy(i,array_core[i]);}add_random();return (0);}/*下移*/int move_down(void){int i=0,j=0,x=0,y=0;int temp[4] = {0};/*1、合并相邻相同的两个元素*//*2、把0元素移动到最上面*/for(x=0;x<4;x++){for(y=x,i=0;y<=12+x;i++,y+=4){temp[i] = array_core[y];}/*合并相邻的两个非0值*/for(i=3;i>=0;i--){for(j=3;j>0;j--){if(temp[j] == temp[j-1] && temp[j-1] != 0){temp[j] = 2*temp[j-1];temp[j-1] = 0;}}}/*把0往上移动*/for(i=3;i>=0;i--){for(j=3;j>0;j--){if(temp[j] == 0 && temp[j-1] != 0){temp[j] = temp[j-1];temp[j-1] = 0;}}}for(y=x,i=0;y<=12+x;i++,y+=4){array_core[y] = temp[i];}}/*在键盘上显示*/for(i=0;i<16;i++)place_xy(i,array_core[i]);add_random();return (0);}/*测试函数*/void teset(void){int i = 0;for(i = 0;i<16;i++){place_xy(i,i+1);}/*计算偏移值*/int i = 0;for(i = 0;i<strlen(board);i++){if(board[i] == '\n')printf(" %d ",i+3);}printf("\n");}int place_xy(int pos,int data){if(data == 0){board[d_xy[pos]] = 0x20; /*十位*/board[d_xy[pos] +1 ] = 0x20; /*个位*/board[d_xy[pos] +2 ] = 0x20; /*个位*/board[d_xy[pos] +3 ] = 0x20; /*个位*/}else if(data < 10){board[d_xy[pos]] = data + 48;/*如果数值是0,就不显示*/}else if(data < 100){board[d_xy[pos]] = data/10 + 48;board[d_xy[pos] +1] = data%10 + 48;}else if(data < 1000){board[d_xy[pos]] = data/100 + 48;board[d_xy[pos] +1] = data%100/10 + 48;board[d_xy[pos] +2] = data%100%10 + 48;}else{board[d_xy[pos]] = data/1000 + 48; /*千位*/board[d_xy[pos] +1] = data%1000/100 + 48; /*百位*/board[d_xy[pos] +2 ] = data%1000%100/10 + 48; /*十位*/board[d_xy[pos] +3 ] = data%1000%100%10 + 48; /*个位*/}/*把数字保存到键盘里面去*/array_core[pos] = data;/*显示键盘*/show_board();return(0);}/*初始化几个数字在键盘上*/int add_random(void){static bool initialized = false;int pos,data,i;/*随机数需要设置种子,用时间来做随机数的种子*/if (!initialized) {srand(time(NULL));initialized = true;}/*检测如果原来的位置有数据了,就不能在原来的数据上加数据*/for(i=0;i<16;i++){pos = rand()%15;if(array_core[pos] != 0)continue;elsebreak;}data = rand()%(4-0+1)+ 0;place_xy(pos,array_rand[data]);return (0);}/*初始化一个键盘*/int show_board(void){printf("\033[H\033[J");/*清空屏幕 但是并不是每一个terminal都会生效*/printf("%s",board);printf("[ ←,↑,→,↓ or q ]\n");return(0);}/*设置之后不用按下回车就可以接收到字符*/void setBufferedInput(bool enable) {static bool enabled = true;static struct termios old;struct termios new;if (enable && !enabled) {// restore the former settingstcsetattr(STDIN_FILENO,TCSANOW,&old);// set the new stateenabled = true;} else if (!enable && enabled) {// get the terminal settings for standard inputtcgetattr(STDIN_FILENO,&new);// we want to keep the old setting to restore them at the endold = new;// disable canonical mode (buffered i/o) and local echonew.c_lflag &=(~ICANON & ~ECHO);// set the new settings immediatelytcsetattr(STDIN_FILENO,TCSANOW,&new);// set the new stateenabled = false;}}/*需要检测ctrl+c 按键,要不然输入变成一直输入了不转回来,键盘就输入不了了*/void signal_callback_handler(int signum) {printf(" TERMINATED \n");setBufferedInput(true);printf("\033[?25h\033[m");exit(signum);}int main(){char c;bool success;memset(array_core,0,sizeof(array_core)/sizeof(array_core[0]));/*在键盘上添加三个随机数*/add_random();add_random();add_random();/*显示键盘*/show_board();setBufferedInput(false);teset();/*注册信号量*/signal(SIGINT, signal_callback_handler);while(true){c=getchar();//printf("%d",c);if (c == -1){puts("\nError! Cannot read keyboard input!");break;}switch(c) {case 97: // 'a' keycase 104: // 'h' keycase 68: // left arrowsuccess = move_left(); break;case 100: // 'd' keycase 108: // 'l' keycase 67: // right arrowsuccess = move_right(); break;case 119: // 'w' keycase 107: // 'k' keycase 65: // up arrowsuccess = move_up(); break;case 115: // 's' keycase 106: // 'j' keycase 66: // down arrow//printf("move_down\n");success = move_down(); break;default: success = false;}/*判断是否退出*/if (c=='q') {printf(" 退出? (y/n) \n");c=getchar();if (c=='y') {break;}}usleep(150000);}setBufferedInput(true);//teset();return (0);}
— — 运行起来
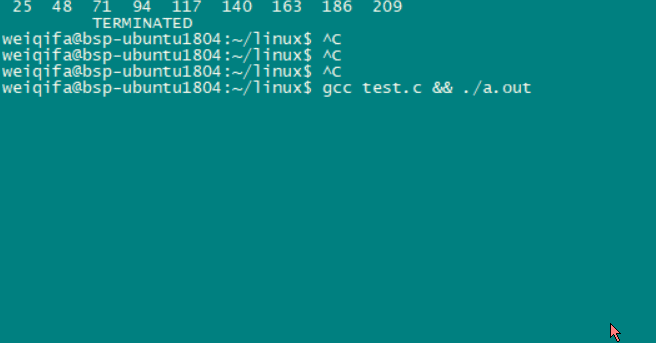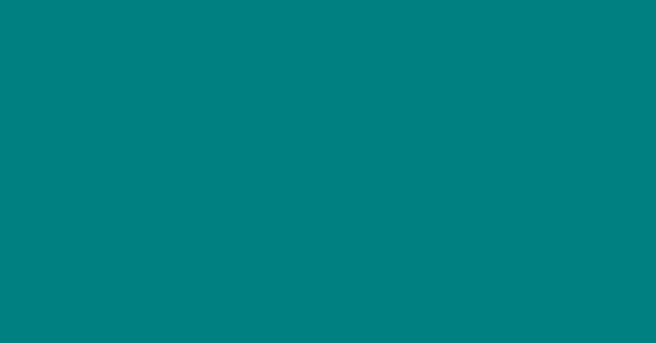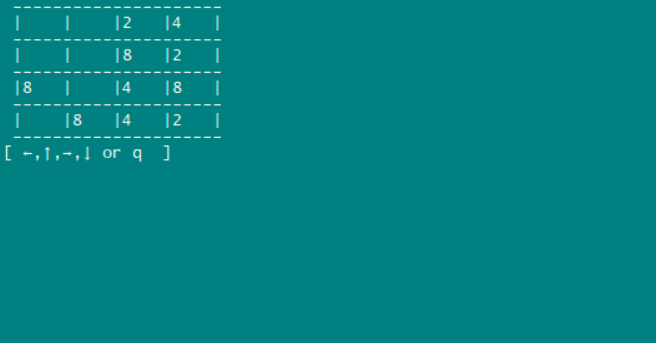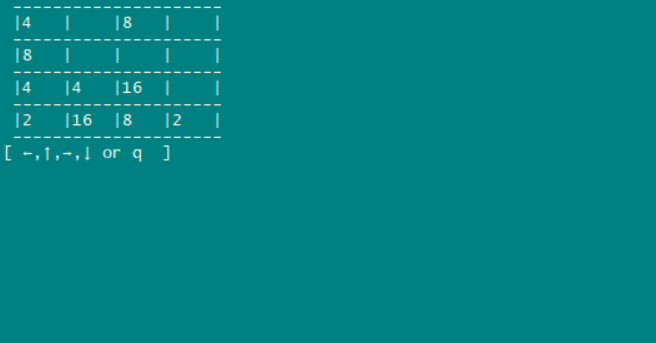
— — 程序缺陷
1、没有分数判断
2、没有最终结果判断,比如所有格子都不能移动了,需要判断胜负。
3、随机值加入也比较随意
4、没有设置格子颜色,比较单调
5、有一些你不知道的bug。
