Spring Boot中Tomcat是怎么启动的
来源 | cnblogs.com/54chensongxia/p/13294470.html
Spring Boot一个非常突出的优点就是不需要我们额外再部署Servlet容器,它内置了多种容器的支持。我们可以通过配置来指定我们需要的容器。
本文以我们平时最常使用的容器Tomcat为列来介绍以下两个知识点:
Spring Boot是怎么整合启动Tomcat容器的;
在Spring Boot中,怎么进行Tomcat的深度配置。
Spring Boot整合启动Tomcat的流程
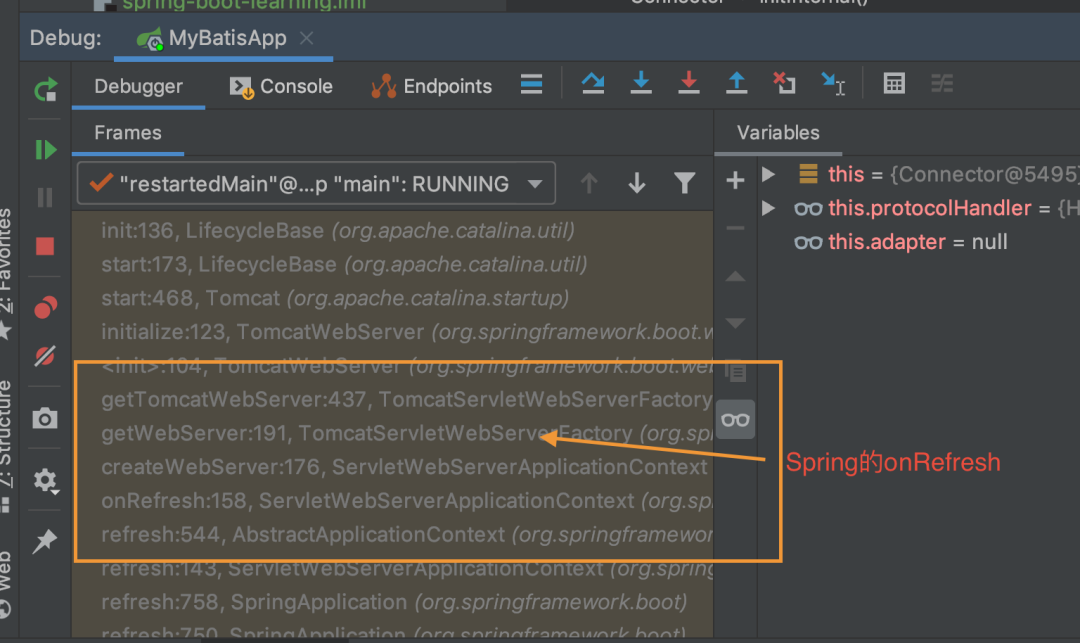
对于看源代码,每个人都有自己的方法。我自己在看源代码的时候喜欢结合IDEA的Debug功能一起看。比如说现在我们要研究Spring Boot是在哪个环节点启动Tomcat的,
我的思路是:Tomcat在启动时会调用各个组件的init方法和start方法,那么我只需要在这些方法上打上端点,然后就能在调用栈上看出Spring Boot是在哪个环节点启用
Tomcat的了。
按照这个思路,我在Tomcat的Connector组件的init方法上打了端点,通过调用栈能很清楚的看出Spring Boot是在容器的onRefresh方法中调用Tomcat的。
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
try {
this.createWebServer();
} catch (Throwable var2) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", var2);
}
}
找到了调用点,那么一切都好办了。从上面的方法中可以看出,重点内容就在this.createWebServer()这个方法中。
在Spring Boot中使用的容器类是ServletWebServerApplicationContext系列的容器,这个系列的容器可以内嵌Web容器。这个我们
可以从这个容器的属性和方法中可以看出来。
public class ServletWebServerApplicationContext extends GenericWebApplicationContext implements ConfigurableWebServerApplicationContext {
//...省略部分代码
public static final String DISPATCHER_SERVLET_NAME = "dispatcherServlet";
//内嵌容器
private volatile WebServer webServer;
private ServletConfig servletConfig;
//...省略部分代码
//创建Web容器
private void createWebServer() {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
ServletContext servletContext = this.getServletContext();
//webServer和servletContext都是null,表示还没创建容器,进入创建容器的逻辑
if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) {
//获取创建容器的工厂,可以通过WebServerFactoryCustomizer接口对这个工厂进行自定义设置
ServletWebServerFactory factory = this.getWebServerFactory();
//具体的创建容器的方法,我们进去具体看下
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(new ServletContextInitializer[]{this.getSelfInitializer()});
} else if (servletContext != null) {
try {
this.getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext);
} catch (ServletException var4) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot initialize servlet context", var4);
}
}
this.initPropertySources();
}
}下面是TomcatServletWebServerFactory的getWebServer方法。
public class TomcatServletWebServerFactory的getWebServer{
//...
@Override
public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
//创建Tomcat容器
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null ? this.baseDirectory
: createTempDir("tomcat"));
tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
//创建连接器,默认NIO模式,可以通过WebServerFactoryCustomizer改变具体模式
Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
//自定义连接器
customizeConnector(connector);
tomcat.setConnector(connector);
tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());
//可以通过WebServerFactoryCustomizer添加额外的连接器,这边将这些连接器绑定到Tomcat
for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) {
tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector);
}
//组测Listener、Filter和Servlet,自定义Context等操作
//这个方法可以重点看下
prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
//创建TomcatWebServer,并调用start方法
return getTomcatWebServer(tomcat);
}
//内嵌的Tomcat容器
public TomcatWebServer(Tomcat tomcat, boolean autoStart) {
Assert.notNull(tomcat, "Tomcat Server must not be null");
this.tomcat = tomcat;
this.autoStart = autoStart;
//这边触发Tomcat的启动流程,是Tomcat启动的入口点
initialize();
}
//...省略部分代码
}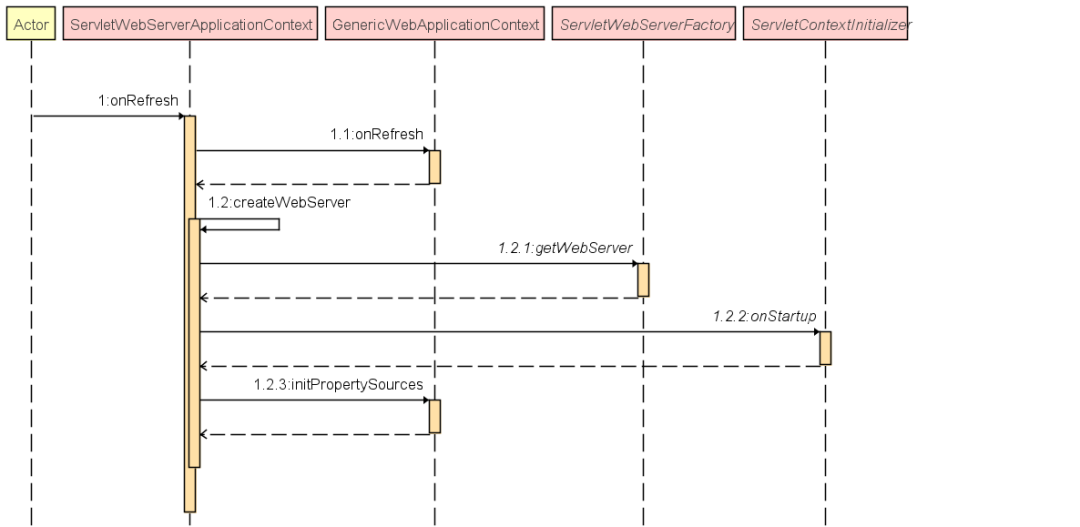
至此Spring Boot内嵌的Tomcat已将顺序启动了。那么Spring Boot是在什么时候注册DispatchServlet的呢?
配置Listener、Filter和Servlet
Spring Boot配置Listener、Filter和Servlet可以參考我之前写的文章Spring Boot使用嵌入式容器,那怎么配置自定义Filter呢
推荐使用ServletListenerRegistrationBean、FilterRegistrationBean和ServletRegistrationBean的方式注册Listener、Filter和Servlet。
Spring Boot注册DispatcherServlet
在传统的Spring MVC项目中,我们都会在web.xml中注册DispatcherServlet这个入口类,那么在Spring Boot中是在哪里注册的呢?
大家如果看Spring Boot的源代码,这边有个小技巧大家可以参考下。就是Spring Boot把之前传统项目中的配置项都通过AutoConfig的形式
做配置了。所以这边在寻找DispatcherServlet是在哪里配置的也可以顺着这个思路去寻找。
在IDEA的类查找功能中输入DispatcherServlet关键字,我们能看到一个DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration类。从名字上就能看出这个
类是DispatcherServlet的自动配置类,我们点进去看下是否是在这个类内部注册的DispatcherServlet?
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
@ConditionalOnClass(DispatcherServlet.class)
@AutoConfigureAfter(ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ServerProperties.class)
public class DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration {
/*
* The bean name for a DispatcherServlet that will be mapped to the root URL "/"
*/
public static final String DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME = "dispatcherServlet";
/*
* The bean name for a ServletRegistrationBean for the DispatcherServlet "/"
*/
public static final String DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_REGISTRATION_BEAN_NAME = "dispatcherServletRegistration";
@Configuration
@Conditional(DefaultDispatcherServletCondition.class)
@ConditionalOnClass(ServletRegistration.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(WebMvcProperties.class)
protected static class DispatcherServletConfiguration {
private final WebMvcProperties webMvcProperties;
public DispatcherServletConfiguration(WebMvcProperties webMvcProperties) {
this.webMvcProperties = webMvcProperties;
}
@Bean(name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME)
public DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet() {
DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet = new DispatcherServlet();
dispatcherServlet.setDispatchOptionsRequest(
this.webMvcProperties.isDispatchOptionsRequest());
dispatcherServlet.setDispatchTraceRequest(
this.webMvcProperties.isDispatchTraceRequest());
dispatcherServlet.setThrowExceptionIfNoHandlerFound(
this.webMvcProperties.isThrowExceptionIfNoHandlerFound());
return dispatcherServlet;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnBean(MultipartResolver.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = DispatcherServlet.MULTIPART_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME)
public MultipartResolver multipartResolver(MultipartResolver resolver) {
// Detect if the user has created a MultipartResolver but named it incorrectly
return resolver;
}
}
@Configuration
@Conditional(DispatcherServletRegistrationCondition.class)
@ConditionalOnClass(ServletRegistration.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(WebMvcProperties.class)
@Import(DispatcherServletConfiguration.class)
protected static class DispatcherServletRegistrationConfiguration {
private final ServerProperties serverProperties;
private final WebMvcProperties webMvcProperties;
private final MultipartConfigElement multipartConfig;
public DispatcherServletRegistrationConfiguration(
ServerProperties serverProperties, WebMvcProperties webMvcProperties,
ObjectProvider
multipartConfigProvider)
{
this.serverProperties = serverProperties;
this.webMvcProperties = webMvcProperties;
this.multipartConfig = multipartConfigProvider.getIfAvailable();
}
//很熟悉的代码有没有,ServletRegistrationBean就是我们上一节中介绍的注册Servlet的方式
//只不过这边注册的是DispatcherServlet这个特殊的Servlet
@Bean(name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_REGISTRATION_BEAN_NAME)
@ConditionalOnBean(value = DispatcherServlet.class, name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME)
public ServletRegistrationBean
dispatcherServletRegistration
(
DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet)
{
ServletRegistrationBean
registration =
new ServletRegistrationBean<>(
dispatcherServlet,
this.serverProperties.getServlet().getServletMapping());
registration.setName(DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME);
registration.setLoadOnStartup(
this.webMvcProperties.getServlet().getLoadOnStartup());
if (
this.multipartConfig !=
null) {
registration.setMultipartConfig(
this.multipartConfig);
}
return registration;
}
}
//...省略部分代码
}
好了通过这边的介绍,我们直到DispatcherServlet是通过DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration这个自动配置类注册的。
Spring Boot中关于Tomcat的一些其他配置
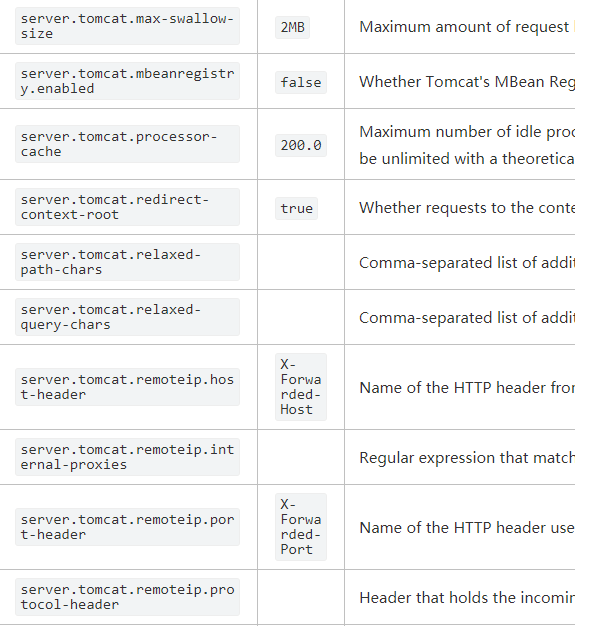
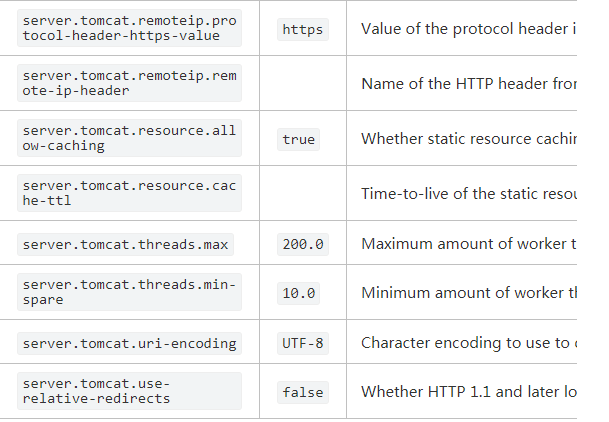
这边给出一个配置的列子
server:
port: ${port:9999}
tomcat:
accept-count: 200
#最好进行这段配置,默认会在tmp目录下创建,Linux有时会有定时任务删除tmp目录下的内容
basedir: my-tomcat
accesslog:
enabled: true
pattern: '%t %a "%r" %s %S (%b M) (%D ms)'
max-http-post-size: 2MB
max-swallow-size: 2M
uri-encoding: GBK
threads:
max: 100
min-spare: 10具体使用时可以参考Spring Boo官网关于Tomcat的配置。
一些其他类
Spring Boot还提供了很多自定义类,让用户对Tomcat的组件做自定义配置。这个符合Spring的设计哲学:只提供选择,而不是强制用户使用某项技术。
关于Tomcat的自定义配置类还有以下几个,大家可以按需使用。
WebServerFactoryCustomizer接口:自定义Web容易工厂
WebServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor处理类:WebServerFactoryCustomizer类通过WebServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor类生效
TomcatConnectorCustomizer:连接器自定义处理类
TomcatContextCustomizer:Context自定义接口

下载方式
1. 首先扫描下方二维码
2. 后台回复「555」即可获取
注明:仅仅作为知识分享,切勿用于其它商业活动 。感谢所有技术分享者的付出。
点赞是最大的支持 
