SkipList 跳表的原理以及实现
一、概念
何为跳表呢?
我们先维基百科对其定义继续剖析:
跳跃列表是一种数据结构。它允许快速查询一个有序连续元素的数据链表,而其快速查询是通过维护一个多层次的链表,且每一层链表中的元素是前一层链表元素的子集。
一开始时,算法在最稀疏的层次进行搜索,直至需要查找的元素在该层两个相邻的元素中间。这时,算法将跳转到下一个层次,重复刚才的搜索,直到找到需要查找的元素为止。跳过的元素的方法可以是随机性选择或确定性选择,其中前者更为常见。
什么意思呢?
我们知道二分法查询是依赖数组的随机访问,也只能应用于数组结构,而链表基于`二分法查询`类似的查询也就成了我们所讲的跳表结构。
其原理就是对有序的链表增加上附加的前进链接,增加是以随机化的方式进行的,所以在列表中的查找可以快速的跳过部分列表,因此得名。所有操作都以对数随机化的时间进行。
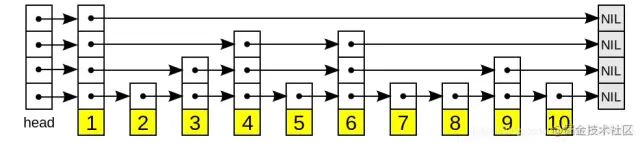
跳表最底层是一个全量的有序链表,上层可以说是下层的“快速跑道”
二、性质
(1)由很多层结构组成;
(2)每一层都是一个有序的链表;
(3)最底层(Level 1)的链表包含所有元素;
(4)如果一个元素出现在 Level i 的链表中,则它在 Level i 之下的链表也都会出现;
(5)每个节点包含两个指针,一个指向同一链表中的下一个元素,一个指向下面一层的元素。
三、实现
(一)初始化
// 构建一个跳表节点属性
private static class SkipListNode<T>{
T val; 
SkipListNode<T> next,down; 
double sorce;
SkipListNode(){}
SkipListNode(T val,double sorce){
this.val = val;
this.sorce =sorce;
}
}
// 层数
private int level = 0;
// 顶层节点
private SkipListNode<T> top;
public SkipList(int level){
this.level=level;
int i = level;
SkipListNode<T> temp = null;
SkipListNode<T> pre = null;
while (i--!==0){
temp = new SkipListNode<T>(null,Double.MIN_VALUE);
temp.down = pre;
pre = temp;
}
top = temp;
}
(二)查找
public T get(double socre){
SkipListNode<T> t = top;
while (t!=null){
if(t.sorce==socre){
return t.val;
}
if(t.next==null){
if(t.down!=null){
t = t.down;
continue;
}else {
return null;
}
}
if(t.next.sorce>socre){
t = t.down;
}else {
t = t.next;
}
}
return null;
}
(三)插入
public void put(double socre,T val){
//1,找到需要插入的位置
SkipListNode<T> t = top, cur = null;//若cur不为空,表示当前score值的节点存在
List<SkipListNode<T>> path = new ArrayList<>();//记录每一层当前节点的前驱节点
while (t != null) {
if (t.score == score) {
cur = t;
break;//表示存在该值的点,表示需要更新该节点
}
if (t.next == null) {
path.add(t);//需要向下查找,先记录该节点
if (t.down != null) {
t = t.down;
continue;
} else {
break;
}
}
if (t.next.score > score) {
path.add(t);//需要向下查找,先记录该节点
if (t.down == null) {
break;
}
t = t.down;
} else
t = t.next;
}
if (cur != null) {
while (cur != null) {
cur.val = val;
cur = cur.down;
}
} else {//当前表中不存在score值的节点,需要从下到上插入
int lev = getRandomLevel();
if (lev > level) {//需要更新top这一列的节点数量,同时需要在path中增加这些新的首节点
SkipListNode<T> temp = null;
SkipListNode<T> prev = top;//前驱节点现在是top了
while (level++ != lev) {
temp = new SkipNode<T>(null, Double.MIN_VALUE);
path.add(0, temp);//加到path的首部
temp.down = prev;
prev = temp;
}
top = temp;//头节点
level = lev;//level长度增加到新的长度
}
//从后向前遍历path中的每一个节点,在其后面增加一个新的节点
SkipListNode<T> downTemp = null, temp = null, prev = null;
// System.out.println("当前深度为"+level+",当前path长度为"+path.size());
for (int i = level - 1; i >= level - lev; i--) {
temp = new SkipNode<T>(val, score);
prev = path.get(i);
temp.next = prev.next;
prev.next = temp;
temp.down = downTemp;
downTemp = temp;
}
}
}
private int getRandomLevel(){
int lev = 1;
while (random.nextInt() % 2 == 0)
lev++;
return lev;
}
(四)删除
public void delete(double sorce){
SkipListNode<T> t = top;
while (t != null) {
if (t.next == null) {
t = t.down;
continue;
}
if (t.next.score == score) {
// 在这里说明找到了该删除的节点
t.next = t.next.next;
t = t.down;
//删除当前节点后,还需要继续查找之后需要删除的节点
continue;
}
if (t.next.score > score)
t = t.down;
else
t = t.next;
}
}来源:https://juejin.cn/post/6844903869873389582
评论
