超全面的前端工程化配置指南
大厂技术 高级前端 Node进阶
点击上方 程序员成长指北,关注公众号
回复1,加入高级Node交流群
作者:molvqingtai
原文链接: https://juejin.cn/post/6971812117993226248
前端工程化配置指南
本文讲解如何构建一个工程化的前端库,并结合 Github Actions,自动发布到 Github 和 NPM 的整个详细流程。
示例
我们经常看到像 Vue、React 这些流行的开源项目有很多配置文件,他们是干什么用的?他们的 Commit、Release 记录都那么规范,是否基于某种约定?
废话少说,先上图!
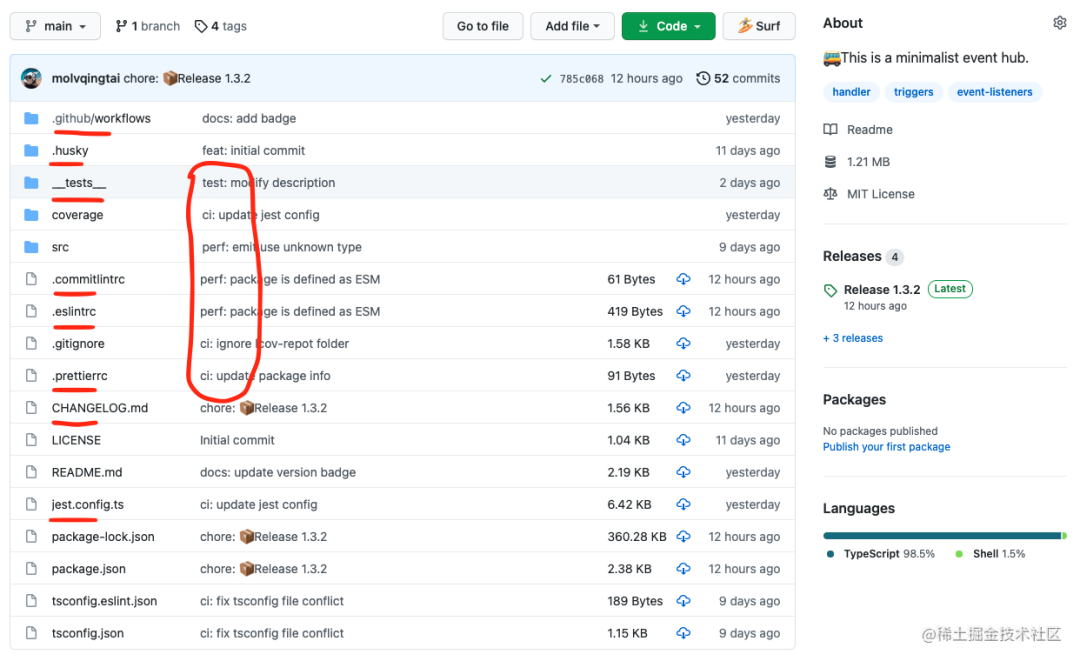 上图标红就是相关的工程化配置,有 Linter、Tests,Github Actions 等,覆盖开发、测试、发布的整个流程。
上图标红就是相关的工程化配置,有 Linter、Tests,Github Actions 等,覆盖开发、测试、发布的整个流程。
相关配置清单
Eslint Prettier Commitlint Husky Jest GitHub Actions Semantic Release
下面我们从创建一个 TypeScript 项目开始,一步一步完成所有的工程化配置,并说明每个配置含义以及容易踩的坑。
初始化
为了避免兼容性问题,建议先将 node 升级到最新的长期支持版本。
首先在 Github 上创建一个 repo,拉下来之后通过npm init -y初始化。然后创建src文件夹,写入index.ts。
package.json 生成之后,我需要添加如下配置项:
"main": "index.js",
+ "type": "module",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
+ "publishConfig": {
+ "access": "public"
+ }
我们将项目定义为ESM规范,前端社区正逐渐向ESM标准迁移,从Node v12.0.0开始,只要设置了 "type": "module", Node 会将整个项目视为ESM规范,我们就可以直接写裸写import/export。
publishConfig.access表示当前项目发布到NPM的访问级别,它有 restricted和public两个选项,restricted表示我们发布到NPM上的是私有包(收费),访问级别默认为restricted,因为我们是开源项目所以标记为public。
配置
创建项目之后,我们开始安装工程化相关的依赖,因为我们是 TypeScript 项目,所以也需要安装 TypeScript 的依赖。
Typescript
先安装 TypeScript,然后使用 tsc 命名生成 tsconfig.json。
npm i typescript -D
npx tsc --init
然后我们需要添加修改 tsconfig.json 的配置项,如下:
{
"compilerOptions": {
/* Basic Options */
"baseUrl": ".", // 模块解析根路径,默认为 tsconfig.json 位于的目录
"rootDir": "src", // 编译解析根路径,默认为 tsconfig.json 位于的目录
"target": "ESNEXT", // 指定输出 ECMAScript 版本,默认为 es5
"module": "ESNext", // 指定输出模块规范,默认为 Commonjs
"lib": ["ESNext", "DOM"], // 编译需要包含的 API,默认为 target 的默认值
"outDir": "dist", // 编译输出文件夹路径,默认为源文件同级目录
"sourceMap": true, // 启用 sourceMap,默认为 false
"declaration": true, // 生成 .d.ts 类型文件,默认为 false
"declarationDir": "dist/types", // .d.ts 类型文件的输出目录,默认为 outDir 目录
/* Strict Type-Checking Options */
"strict": true, // 启用所有严格的类型检查选项,默认为 true
"esModuleInterop": true, // 通过为导入内容创建命名空间,实现 CommonJS 和 ES 模块之间的互操作性,默认为 true
"skipLibCheck": true, // 跳过导入第三方 lib 声明文件的类型检查,默认为 true
"forceConsistentCasingInFileNames": true, // 强制在文件名中使用一致的大小写,默认为 true
"moduleResolution": "Node", // 指定使用哪种模块解析策略,默认为 Classic
},
"include": ["src"] // 指定需要编译文件,默认当前目录下除了 exclude 之外的所有.ts, .d.ts,.tsx 文件
}
更多详细配置参考:www.typescriptlang.org/tsconfig
注意的点,如果你的项目涉及到WebWorker API,需要添加到 lib 字段中
"lib": ["ESNext", "DOM", "WebWorker"],
然后我们将编译后的文件路径添加到 package.json,并在 scripts 中添加编译命令。
- "main": "index.js",
+ "main": "dist/index.js",
+ "types": "dist/types/index.d.ts"
"type": "module",
- "scripts": {
- "test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
- },
+ "scripts": {
+ "dev": "tsc --watch",
+ "build": "npm run clean && tsc",
+ "clean": "rm -rf dist"
+ },
"publishConfig": {
"access": "public"
}
types 配置项是指定编译生成的类型文件,如果 compilerOptions.declarationDir 指定的是dist,也就是源码和 .d.ts 同级,那么types可以省略。
验证配置是否生效,在 index.ts 写入
const calc = (a: number, b: number) => {
return a - b
}
console.log(calc(1024, 28))
在控制台中执行
npm run build && node dist/index.js
会在 dist 目录中生成 types/index.d.ts、index.js、index.js.map,并打印 996。
Eslint & Prettier
代码规范离不开各种 Linter, 之所以把这两个放在一起讲,借用 Prettier 官网的一句话:“使用 Prettier 解决代码格式问题,使用 linters 解决代码质量问题”。虽然eslint也有格式化功能,但是prettier的格式化功能更强大。
大部分同学编辑器都装了prettier-vscode和eslint-vscode这两个插件,如果你项目只有其中一个的配置,因为这两者部分格式化的功能有差异,那么就会造成一个的问题,代码分别被两个插件分别格式化一次,网上解决prettier+eslint冲突的方案五花八门,甚至还有把整个rules列表贴出来的。
那这里我们按照官方推荐,用最少的配置去解决prettier和eslint的集成问题。
Eslint
首先安装 eslint,然后利用 eslint 的命令行工具生成基本配置。
npm i eslint -D
npx eslint --init
执行上面命令后会提示一些选项,我们依次选择符合我们项目的配置。
注意,这里 eslint 推荐了三种社区主流的规范,Airbnb、Standard、Google,因个人爱好我选择了不写分号的 Standard规范。
生成的.eslintrc.cjs文件应该长这样
module.exports = {
env: {
browser: true,
es2021: true,
node: true
},
extends: [
'standard'
],
parser: '@typescript-eslint/parser',
parserOptions: {
ecmaVersion: 12,
sourceType: 'module'
},
plugins: [
'@typescript-eslint'
],
rules: {
}
}
有些同学可能就要问了,这里为什么生成的配置文件名称是.eslintrc.cjs而不是.eslintrc.js?
因为我们将项目定义为ESM,eslit --init会自动识别type,并生成兼容的配置文件名称,如果我们改回.js结尾,再运行eslint将会报错。出现这个问题是eslint内部使用了require()语法读取配置。
同样,这个问题也适用于其他功能的配置,比如后面会讲到的Prettier、Commitlint等,配置文件都不能以xx.js结尾,而要改为当前库支持的其他配置文件格式,如:.xxrc、.xxrc.json、.xxrc.yml。
验证配置是否生效,修改index.ts
const calc = (a: number, b: number) => {
return a - b
}
- console.log(calc(1024, 28))
+ // console.log(calc(1024, 28))
在package.json中添加lint命令
"scripts": {
"dev": "tsc --watch",
"build": "npm run clean && tsc",
+ "lint": "eslint src --ext .js,.ts --cache --fix",
"clean": "rm -rf dist"
},
然后在控制台执行 lint,eslint将会提示 1 条错误信息,说明校验生效。
npm run lint
# 1:7 error 'calc' is assigned a value but never used no-unused-vars
因为是 Typescript 项目所以我们还要添加Standard规范提供的 TypeScrip 扩展配置(其他规范同理)
安装eslint-config-standard-with-typescript
npm i eslint-config-standard-with-typescript -D添加修改 .eslintrc.cjs
module.exports = {
env: {
browser: true,
es2021: true,
node: true
},
- extends: ['standard']
+ extends: ['standard', 'eslint-config-standard-with-typescript'],
parser: '@typescript-eslint/parser',
parserOptions: {
ecmaVersion: 12,
sourceType: 'module',
+ project: './tsconfig.json'
},
plugins: ['@typescript-eslint'],
rules: {}
}
验证配置是否生效
在控制台执行lint,eslint将会提示 2 条错误信息,说明校验生效。
npm run lint
# 1:7 error 'calc' is assigned a value but never used no-unused-vars
# 1:14 error Missing return type on function
Prettier
现在我们按照官网的推荐方式,把 prettier 集成到 eslint 的校验中。
安装 prettier 并初始化配置文件
npm i prettier -D
echo {}> .prettierrc.json
然后在.prettierrc.json添加配置,这里只需要添加和你所选规范冲突的部分。
{
"semi": false, // 是否使用分号
"singleQuote": true, // 使用单引号代替双引号
"trailingComma": "none" // 多行时尽可能使用逗号结尾
}
更多配置详见:prettier.io/docs/en/opt…
安装解决冲突需要用到的两个依赖
eslint-config-prettier 关闭可能与 prettier冲突的规则eslint-plugin-prettier 使用 prettier代替eslint格式化
npm i eslint-config-prettier eslint-plugin-prettier -D
再添加修改 .eslintrc.cjs,如下:
module.exports = {
env: {
browser: true,
es2021: true,
node: true,
},
- extends: ['standard', 'eslint-config-standard-with-typescript'],
+ extends: ['standard', 'eslint-config-standard-with-typescript', 'prettier'],
parser: '@typescript-eslint/parser',
parserOptions: {
ecmaVersion: 12,
sourceType: 'module',
project: './tsconfig.json',
},
- plugins: ['@typescript-eslint'],
+ plugins: ['@typescript-eslint', 'prettier'],
- rules: {},
+ rules: {
+ 'prettier/prettier': 'error'
+ },
}
然后验证配置是否生效,修改index.ts
- const calc = (a: number, b: number) => {
+ const calc = (a: number, b: number): number => {
return a - b
}
- // console.log(calc(1024, 28))
+ console.log(calc(1024, 28))
然后在控制台执行lint,这里prettier和eslint的行为已保持一致,如果没有报错,那就成功了。
npm run lint
我们现在已经完成了eslint和prettier的集成配置。和编辑器无关,也就是说无论你使用什么编辑器,有没有安装相关插件,都不会影响代码校验的效果。
Husky
因为一个项目通常是团队合作,我们不能保证每个人在提交代码之前执行一遍lint校验,所以需要git hooks 来自动化校验的过程,否则禁止提交。
安装Husky并生成.husky文件夹
npm i husky -D
npx husky install
然后我们需要在每次执行npm install时自动启用husky
如果你的npm版本大于等于7.1.0
npm set-script prepare "husky install"
否则手动在package.json中添加
"scripts": {
"dev": "tsc --watch",
"build": "npm run clean && tsc",
"lint": "eslint src --ext .js,.ts --cache --fix",
"clean": "rm -rf dist",
+ "prepare": "husky install"
},
然后添加一个lint钩子
npx husky add .husky/pre-commit "npm run lint"相当于手动在.husky/pre-commit文件写入以下内容:
#!/bin/sh
. "$(dirname "$0")/_/husky.sh"
npm run lint
测试钩子是否生效,修改index.ts
const calc = (a: number, b: number): number => {
return a - b
}
- console.log(calc(1024, 28))
+ // console.log(calc(1024, 28))
然后提交一条commit,如果配置正确将会自动执行lint并提示 1 条错误信息,commit提交将会失败。
git add .
git commit -m 'test husky'
# 1:7 error 'calc' is assigned a value but never used
Commitlint
为什么需要 Commitlint,除了在后续的生成changelog文件和语义发版中需要提取commit中的信息,也利于其他同学分析你提交的代码,所以我们要约定commit的规范。
安装 Commitlint
@commitlint/cli Commitlint 命令行工具 @commitlint/config-conventional 基于 Angular 的约定规范
npm i @commitlint/config-conventional @commitlint/cli -D
最后将Commitlint添加到钩子
npx husky add .husky/commit-msg 'npx --no-install commitlint --edit "$1"'
创建.commitlintrc,并写入配置
{
"extends": [
"@commitlint/config-conventional"
]
}
注意,这里配置文件名使用的是.commitlintrc而不是默认的.commitlintrc.js,详见 Eslint 章节
测试钩子是否生效,修改index.ts,让代码正确
const calc = (a: number, b: number): void => {
console.log(a - b)
}
- // calc(1024, 28)
+ calc(1024, 28)
提交一条不符合规范的commit,提交将会失败
git add .
git commit -m 'add eslint and commitlint'
修改为正确的commit,提交成功!
git commit -m 'ci: add eslint and commitlint'
Angular 规范说明:
feat:新功能 fix:修补 BUG docs:修改文档,比如 README, CHANGELOG, CONTRIBUTE 等等 style:不改变代码逻辑 (仅仅修改了空格、格式缩进、逗号等等) refactor:重构(既不修复错误也不添加功能) perf:优化相关,比如提升性能、体验 test:增加测试,包括单元测试、集成测试等 build:构建系统或外部依赖项的更改 ci:自动化流程配置或脚本修改 chore:非 src 和 test 的修改,发布版本等 revert:恢复先前的提交
Jest
美好生活从测试覆盖率 100% 开始。
安装jest,和类型声明@types/jest,它执行需要ts-node和ts-jest
这里暂时固定了ts-node的版本为 v9.1.1,新版的ts-node@v10.0.0会导致jest报错,等待官方修复,详见:issues
npm i jest @types/jest ts-node@9.1.1 ts-jest -D
初始化配置文件
npx jest --init然后修改jest.config.ts文件
// A preset that is used as a base for Jest's configuration
- // preset: undefined,
+ preset: 'ts-jest'
将测试命令添加到package.json中。
"scripts": {
"dev": "tsc --watch",
"build": "npm run clean && tsc",
"lint": "eslint src --ext .js,.ts --cache --fix",
"clean": "rm -rf dist",
"prepare": "husky install",
+ "test": "jest"
},
创建测试文件夹__tests__和测试文件__tests__/calc.spec.ts
修改index.ts
const calc = (a: number, b: number): number => {
return a - b
}
- // console.log(calc(1024, 28))
+ export default calc
然后在calc.spec.ts中写入测试代码
import calc from '../src'
test('The calculation result should be 996.', () => {
expect(calc(1024, 28)).toBe(996)
})
验证配置是否生效
在控制台执行test,将会看到测试覆盖率 100% 的结果。
npm run test
最后我们给__tests__目录也加上lint校验
修改package.json
"scripts": {
"dev": "tsc --watch",
"build": "npm run clean && tsc",
- "lint": "eslint src --ext .js,.ts --cache --fix",
+ "lint": "eslint src __tests__ --ext .js,.ts --cache --fix",
"clean": "rm -rf dist",
"prepare": "husky install",
"test": "jest"
},
这里如果我们直接执行npm run lint将会报错,提示__tests__文件夹没有包含在tsconfig.json的include中,当我们添加到include之后,输出的dist中就会包含测试相关的文件,这并不是我们想要的效果。
我们使用typescript-eslint官方给出的解决方案,如下操作:
新建一个tsconfig.eslint.json文件,写入以下内容:
{
"extends": "./tsconfig.json",
"include": ["**/*.ts", "**/*.js"]
}
在.eslintrc.cjs中修改
parserOptions: {
ecmaVersion: 12,
sourceType: 'module',
- project: './tsconfig.json'
+ project: './tsconfig.eslint.json'
},
然后验证配置是否生效,直接提交我们添加的测试文件,能正确提交说明配置成功。
git add .
git commit -m 'test: add unit test'
Github Actions
我们通过Github Actions实现代码合并或推送到主分支,dependabot机器人升级依赖等动作,会自动触发测试和发布版本等一系列流程。
在项目根目录创建.github/workflows文件夹,然后在里面新建ci.yml文件和cd.yml文件
在ci.yml文件中写入:
name: CI
on:
push:
branches:
- '**'
pull_request:
branches:
- '**'
jobs:
linter:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- uses: actions/setup-node@v2
with:
node-version: 16
- run: npm ci
- run: npm run lint
tests:
needs: linter
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- uses: actions/setup-node@v2
with:
node-version: 16
- run: npm ci
- run: npm run test
上面配置大概意思就是,监听所有分支的push和pull_request动作,自动执行linter和tests任务。
GithubActions 更多用法参考:github.com/features/ac…
然后推送代码,验证配置是否生效
git add .
git commit -m 'ci: use github actions'
git push
此时打开当前项目的 Github 页面,然后点击顶部 Actions 菜单就会看到正在进行的两个任务,一个将会成功(测试),一个将会失败(发布)。
上面只是实现了代码自动测试流程,下面实现自动发布的流程。
在此之前需要到NPM网站上注册一个账号(已有可忽略),并创建一个package。
然后创建GH_TOKEN和NPM_TOKEN(注意,不要在代码中包含任何的 TOKEN 信息):
如何创建 GITHUB\_TOKEN(创建时勾选 repo 和 workflow 权限) 如何创建 NPM\_TOKEN(创建时选中 Automation 权限)
将创建好的两个TOKEN添加到项目的 Actions secrets 中:
Github 项目首页 -> 顶部 Settings 菜单 -> 侧边栏 Secrets
然后修改package.json中的“name”,“name”就是你在NPM上创建的package的名称。
在cd.yml文件中写入:
name: CD
on:
push:
branches:
- main
pull_request:
branches:
- main
jobs:
release:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- uses: actions/setup-node@v2
with:
node-version: 16
# https://github.com/semantic-release/git/issues/209
- run: npm ci --ignore-scripts
- run: npm run build
- run: npx semantic-release
env:
GH_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GH_TOKEN }}
NPM_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.NPM_TOKEN }}
由于“黑命贵”,Github 已将新项目的默认分支名称更改为 “main”,详见:issues, 为了方便,后面统一称为 主分支
所以如果你的主分支名称是“main”,上面的branches需要修改为:
on:
push:
branches:
- main
pull_request:
branches:
- main
然后安装语义发版依赖,需要用到semantic-release和它的插件:
semantic-release:语义发版核心库 @semantic-release/changelog:用于自动生成 changelog.md @semantic-release/git:用于将发布时产生的更改提交回远程仓库
npm i semantic-release @semantic-release/changelog @semantic-release/git -D在项目根目录新建配置文件.releaserc并写入:
{
"branches": ["master"],
"plugins": [
"@semantic-release/commit-analyzer",
"@semantic-release/release-notes-generator",
"@semantic-release/changelog",
"@semantic-release/github",
"@semantic-release/npm",
"@semantic-release/git"
]
}
这里同样,如果你的主分支名称是“main”,上面的branches需要修改为:
"branches": ["+([0-9])?(.{+([0-9]),x}).x", "main"],
最后新建分支 develop 分支并提交工作内容。
git checkout -b develop
git add .
git commit -m 'feat: complete the CI/CD workflow'
git push --set-upstream origin develop
git push
然后将 develop 分支合并到 主分支,并提交,注意:这个提交会触发测试并 发布版本 (自动创建tag和changelog)
git checkout master
git merge develop
git push
完成上面操作之后,打开 Github 项目主页 和 NPM 项目主页 可以看到一个 Release 的更新记录。
最后切回到 develop 分支,创建一个自动更新依赖的workflow。
在.github文件夹中创建dependabot.yml文件,并写入内容:
version: 2
updates:
# Enable version updates for npm
- package-ecosystem: 'npm'
# Look for `package.json` and `lock` files in the `root` directory
directory: '/'
# Check the npm registry for updates every day (weekdays)
schedule:
interval: 'weekly'
提交并查看 workflows 是否全部通过,再合并到 主分支 并提交,这个提交不会触发版本发布。
git pull origin master
git add .
git commit -m 'ci: add dependabot'
git push
git checkout master
git merge develop
git push
触发版本发布需要两个条件:
只有当 push和pull_request到 主分支 上才会触发版本发布只有 commit前缀为feat、fix、perf才会发布,否则跳过。
更多发布规则,详见:github.com/semantic-re…
SemanticRelease 使用方式,详见:semantic-release.gitbook.io
如果你能正确配置上面所有步骤,并成功发布,那么恭喜你!你拥有了一个完全自动化的项目,它拥有:自动依赖更新、测试、发布,和自动生成版本信息等功能。
完整的项目示例:@resreq/event-hub
结语
本文未涉及到:组件库、Monorepo、Jenkins CI 等配置,但能覆盖绝大部前端项目 CI/CD 流程。
有些地方讲得比较细,甚至有些啰嗦,但还是希望能帮助到大家!撒花!🎉🎉🎉
Node 社群
我组建了一个氛围特别好的 Node.js 社群,里面有很多 Node.js小伙伴,如果你对Node.js学习感兴趣的话(后续有计划也可以),我们可以一起进行Node.js相关的交流、学习、共建。下方加 考拉 好友回复「Node」即可。
如果你觉得这篇内容对你有帮助,我想请你帮我2个小忙:
1. 点个「在看」,让更多人也能看到这篇文章 2. 订阅官方博客 www.inode.club 让我们一起成长 点赞和在看就是最大的支持
