SpringBoot+Mybatis+MySQL实现读写分离
点击上方蓝色字体,选择“标星公众号”
优质文章,第一时间送达
作者 | loimh
来源 | urlify.cn/NNV7rm
在Springboot中使用数据库主从复制实现读写分离,操作数据时操作主表,查询操作使用从表。
我就直接跳过创建SpringBoot应用的步骤了,直接开始操作如何配置读写分离。
1、我的Maven依赖如下,大家可以复制
"1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
"http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
4.0.0
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.3.3.RELEASE
com.example
demo
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
demo
Demo project for Spring Boot
1.8
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-aop
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-jdbc
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.mybatis.spring.boot
mybatis-spring-boot-starter
1.3.2
org.apache.commons
commons-lang3
3.8
mysql
mysql-connector-java
runtime
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
com.alibaba
fastjson
1.2.46
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-data-redis
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-mail
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-devtools
true
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
2、配置数据源,我的application.yml配置如下,大家根据自己的配置进行修改。
#主从数据库配置
spring:
datasource:
master:
jdbc-url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/task_db?serverTimezone=UTC
username: root
password: Caiyi0.0
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
slave1:
jdbc-url: jdbc:mysql://172.18.237.231:3307/task_db?serverTimezone=UTC
username: root # 只读账户
password: mysql
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
3、然后我们进行多数据源配置,新建一个config目录,创建一个DataSourceConfig.class文件,加上@Configuration注解。
package com.example.demo.config;
import com.example.demo.bean.MyRoutingDataSource;
import com.example.demo.enums.DBTypeEnum;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.jdbc.DataSourceBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Configuration
public class DataSourceConfig {
@Bean(name = "masterDataSource")
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource.master")
public DataSource masterDataSource(){
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean(name = "slave1DataSource")
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource.slave1")
public DataSource slave1DataSource() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean
@Primary
public DataSource myRoutingDataSource(@Qualifier("masterDataSource") DataSource masterDataSource, @Qualifier("slave1DataSource") DataSource slave1DataSource) {
Map targetDataSources = new HashMap<>();
targetDataSources.put(DBTypeEnum.MASTER, masterDataSource);
targetDataSources.put(DBTypeEnum.SLAVE1, slave1DataSource);
MyRoutingDataSource myRoutingDataSource = new MyRoutingDataSource();
myRoutingDataSource.setDefaultTargetDataSource(masterDataSource);
myRoutingDataSource.setTargetDataSources(targetDataSources);
return myRoutingDataSource;
}
}
这里我们配置了3个数据源,一个主数据源,一个从数据源,一个路由数据源。前2个数据源都是为了生成第3个数据源,而且后续我们只用这最后一个路由数据源。
4、然后我们配置一个MyBatis的配置,因为我们现在有3个数据源,所以我们需要为事务管理器和MyBatis手动指定一个明确的数据源。
package com.example.demo.config;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration
public class MyBatisConfig {
@Resource(name = "myRoutingDataSource")
private DataSource myRoutingDataSource;
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory() throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
sqlSessionFactoryBean.setDataSource(myRoutingDataSource);
sqlSessionFactoryBean.setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources("classpath:mapper/*.xml"));
return sqlSessionFactoryBean.getObject();
}
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager platformTransactionManager() {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(myRoutingDataSource);
}
}
5 、设置路由Key/查找数据源
目标数据源就是两个数据源,一个主数据源和从数据源,但是使用的时候要查找数据源。
首先,我们先定义一个枚举类来代表这三个数据源
package com.example.demo.enums;
public enum DBTypeEnum {
MASTER, SLAVE1;
}
接下来,我们通过ThreadLocal将数据源设置到每个线程上下文中
package com.example.demo.bean;
import com.example.demo.enums.DBTypeEnum;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class DBContextHolder {
private static final ThreadLocal contextHolder = new ThreadLocal<>();
private static final AtomicInteger counter = new AtomicInteger(-1);
public static void set(DBTypeEnum dbType) {
contextHolder.set(dbType);
}
public static DBTypeEnum get() {
return contextHolder.get();
}
public static void master() {
set(DBTypeEnum.MASTER);
System.out.println("切换到master");
}
public static void slave() {
set(DBTypeEnum.SLAVE1);
System.out.println("切换到slave1");
}
}
获取路由Key
package com.example.demo.bean;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup.AbstractRoutingDataSource;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
public class MyRoutingDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
@Nullable
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
return DBContextHolder.get();
}
}
默认情况下,所有的查询都走从库,插入/修改/删除走主库。我们通过方法名来区分操作类型(CRUD),我们通过过Spring的AOP来进行配置
package com.example.demo.aop;
import com.example.demo.bean.DBContextHolder;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Aspect
@Component
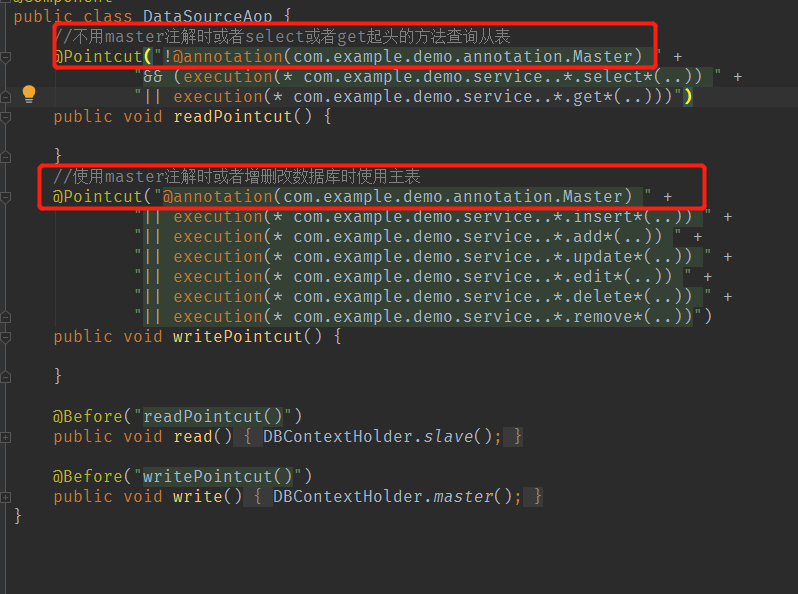
public class DataSourceAop {
//不用master注解时或者select或者get起头的方法查询从表
@Pointcut("!@annotation(com.example.demo.annotation.Master) " +
"&& (execution(* com.example.demo.service..*.select*(..)) " +
"|| execution(* com.example.demo.service..*.get*(..)))")
public void readPointcut() {
}
//使用master注解时或者增删改数据库时使用主表
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.example.demo.annotation.Master) " +
"|| execution(* com.example.demo.service..*.insert*(..)) " +
"|| execution(* com.example.demo.service..*.add*(..)) " +
"|| execution(* com.example.demo.service..*.update*(..)) " +
"|| execution(* com.example.demo.service..*.edit*(..)) " +
"|| execution(* com.example.demo.service..*.delete*(..)) " +
"|| execution(* com.example.demo.service..*.remove*(..))")
public void writePointcut() {
}
@Before("readPointcut()")
public void read() {
DBContextHolder.slave();
}
@Before("writePointcut()")
public void write() {
DBContextHolder.master();
}
}
如果有特殊情况,例如某些情况下我们需要强制读主库,针对这种情况,我们可以自定义一个注解,然后用这注解标注的方法就读主库。
package com.example.demo.annotation;
public @interface Master {
}
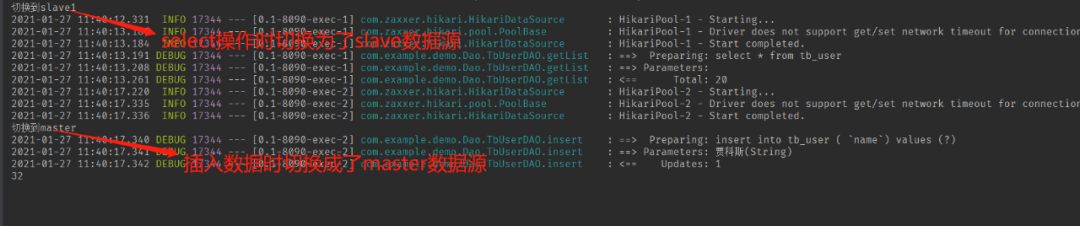
至此,配置完成,下面我们进行测试。
6、测试
假设我们有一个User表。
package com.example.demo.serviceImpl;
import com.example.demo.Dao.TbUserDAO;
import com.example.demo.entity.TbUser;
import com.example.demo.service.UserService;
import org.apache.tomcat.util.http.fileupload.IOUtils;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.UUID;
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(UserServiceImpl.class);
@Autowired
TbUserDAO userDAO;
@CachePut(value = "user", key = "#user.id")
@Transactional
@Override
public int insert(TbUser user) {
int i=userDAO.insert(user);
System.out.println(user.getId());
return i;
}
@CacheEvict(value = {"userById"}, key = "#id")
@Override
public int deleteByPrimaryKey(String id) {
Integer userId= new Integer(id);
return userDAO.deleteByPrimaryKey(userId);
}
@Override
public List getList(TbUser user) {
return userDAO.getList(user);
}
@Cacheable(value ={"userById"}, key = "#id")
@Override
public TbUser selectById(String id) {
System.out.println("从数据库查");
Integer userId= new Integer(id);
return userDAO.selectByPrimaryKey(userId);
}
@CacheEvict(value = {"userById"}, key = "#user.id")
@Override
public int updateByPrimaryKey(TbUser user) {
return userDAO.updateByPrimaryKey(user);
}
@Override
public String uploadFile(MultipartFile zipFile) {
String targetFilePath = "H:\\uploadFile";
String fileName = UUID.randomUUID().toString().replace("-", "");
File targetFile = new File(targetFilePath + File.separator + fileName);
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
try {
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(targetFile);
IOUtils.copy(zipFile.getInputStream(), fileOutputStream);
logger.info("------>>>>>>uploaded a file successfully!<<<<<<------");
} catch (IOException e) {
return "false";
} finally {
try {
fileOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
logger.error("", e);
}
}
return "成功";
}
}
Controller代码如下:
package com.example.demo.controller;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import com.example.demo.Dao.TbUserDAO;
import com.example.demo.entity.TbUser;
import com.example.demo.service.UserService;
import com.example.demo.utils.APIException;
import com.example.demo.utils.ResultVO;
import com.example.demo.utils.SendMailUtil;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.util.JSONPObject;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.MethodArgumentNotValidException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/User")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
UserService userService;
@Autowired
SendMailUtil sendMailUtil;
@Autowired
RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@RequestMapping(value = "/insertUser",method = RequestMethod.POST )
public int insertUser(@RequestBody String Json){
TbUser jsonpObject=JSONObject.parseObject(Json, (Type) TbUser.class);
return userService.insert(jsonpObject);
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/updateUser",method = RequestMethod.POST )
public int updateUser(@RequestBody String Json){
TbUser jsonpObject=JSONObject.parseObject(Json, (Type) TbUser.class);
return userService.updateByPrimaryKey(jsonpObject);
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String hello(){
return "hello world";
}
@PostMapping("/deleteUser")
public int deleteUserById(@RequestParam String id){
return userService.deleteByPrimaryKey(id);
}
@PostMapping("/selectById")
public TbUser selectUserById(@RequestParam String id){
return userService.selectById(id);
}
@PostMapping("/getList")
public List getList(@RequestBody String json) {
//给qq邮箱发送邮件事例
// sendMailUtil.sendMail("765783376@qq.com","邮件标题","邮件内容");
// try{
// int i=1/0;
// }catch (Exception e){
// throw new APIException(3000,e.getMessage());
// }
TbUser jsonpObject=JSONObject.parseObject(json, (Type) TbUser.class);
return userService.getList(jsonpObject);
}
/**
* 图片上传接口
* @param
* @return
*/
@PostMapping("/upload")
public String Upload(@RequestParam("file") MultipartFile zipFile) {
return userService.uploadFile(zipFile);
}
}
如果项目启动出错,请查看启动类是否配置了@SpringBootApplication(exclude= {DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class})

锋哥最新SpringCloud分布式电商秒杀课程发布
👇👇👇
👆长按上方微信二维码 2 秒
感谢点赞支持下哈 
