多图详解:二叉堆原理并手写一个优先队列
JAVA前线
欢迎大家关注公众号「JAVA前线」查看更多精彩分享,主要内容包括源码分析、实际应用、架构思维、职场分享、产品思考等等,同时也非常欢迎大家加我微信「java_front」一起交流学习
1 优先队列应用
队列是一种先进先出的数据结构,先放入队列的元素会先出队列。但是有这样一种场景,我们希望出队列顺序不是根据放入队列顺序,而是根据元素本身具有的优先级,例如元素优先级高则先出队列,这时就要使用优先队列。
1.1 应用一
我们设想这样一种发送消息的业务场景:消息具有优先级属性,在同一个队列中优先发送优先级高的消息,优先级定义如下:
// 优先级 P1 > P2 > p3
public enum PriorityEnum {
P1(1, "优先级1"),
P2(2, "优先级2"),
P3(3, "优先级3")
;
}
消息对象定义如下:
public class MyMessage implements Comparable {
/**
* 消息优先级
*/
private int priority;
/**
* 消息内容
*/
private String messge;
public MyMessage(int priority, String message) {
this.priority = priority;
this.messge = message;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Object obj) {
MyMessage message = (MyMessage) obj;
return this.priority - message.priority;
}
}
java.util.PriorityQueue可以实现上述功能:
public class PriorityQueueTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue messageQueue = new PriorityQueue();
MyMessage m1 = new MyMessage(PriorityEnum.P1.getCode(), "message1");
MyMessage m2 = new MyMessage(PriorityEnum.P2.getCode(), "message2");
MyMessage m3 = new MyMessage(PriorityEnum.P3.getCode(), "message3");
messageQueue.offer(m3);
messageQueue.offer(m1);
messageQueue.offer(m2);
while (messageQueue.size() > 0) {
System.out.println(messageQueue.poll());
}
}
}
代码执行结果:
send message=MyMessage(priority=1, messge=message1)
send message=MyMessage(priority=2, messge=message2)
send message=MyMessage(priority=3, messge=message3)
PriorityQueueTest消息放入优先队列顺序:
3、1、2
PriorityQueueTest从优先队列获取消息顺序:
1、2、3
1.2 应用二
现在消息优先级进行业务变更:
// 优先级 P3 > P2 > p1
public enum PriorityEnum {
P1(1, "优先级1"),
P2(2, "优先级2"),
P3(3, "优先级3")
;
}
此时预期输出顺序如下:
3、2、1
如果要达到预期输出顺序代码要进行如下变更:
public class MyMessage implements Comparable {
@Override
public int compareTo(Object obj) {
MyMessage message = (MyMessage) obj;
return message.priority - this.priority; // 比较关系变更
}
}
2 二叉堆
在第一章节我们看到PriorityQueue可以实现按照元素优先级顺序进行输出,那么其底层原理是什么呢?答案是二叉堆。
2.1 什么是二叉堆
二叉堆分为大顶堆和小顶堆,我们首先看大顶堆,从下图可以看到整棵树中最大值在根节点,所以称为大顶堆:
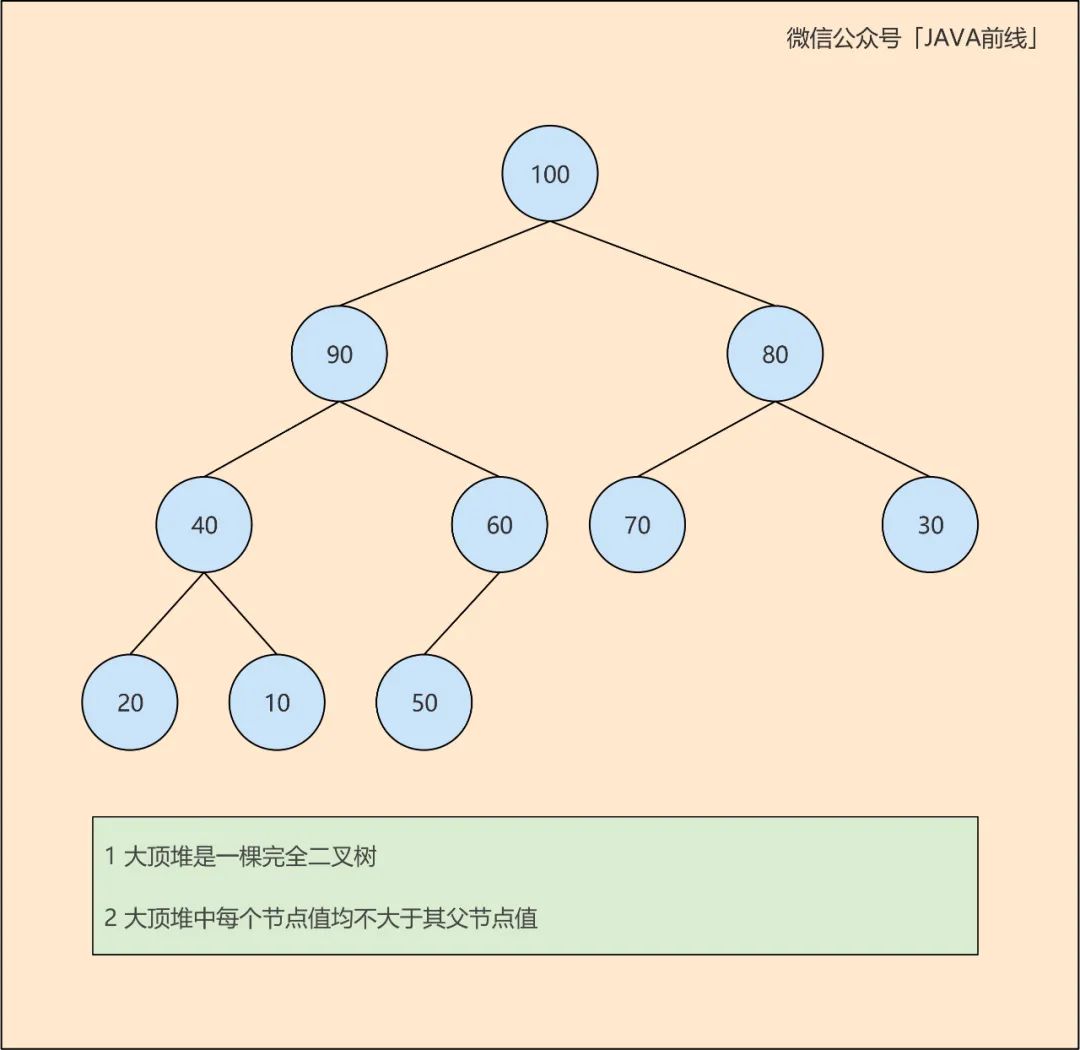
我们再看小顶堆,从下图可以看到整棵树中最小值在根节点,所以称为小顶堆:

2.2 怎么存储二叉堆
二叉堆看似复杂,其实用数组就可以表示,我们以大顶堆为例:
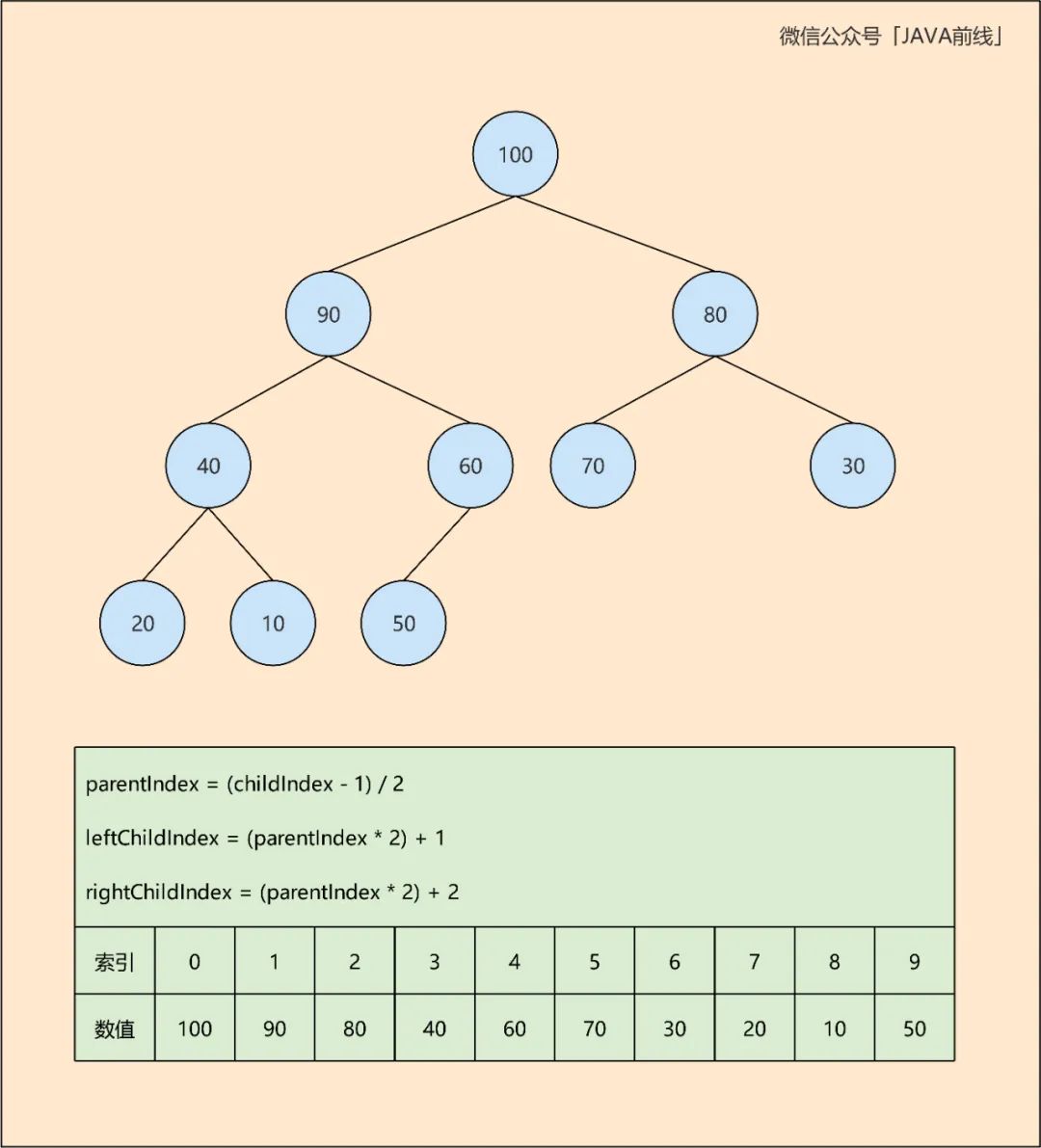
第一步声明一个长度为10的数组,因为二叉树总共有10个节点:
int[] array = new int[10]
第二步设置根节点100作为数组第一个元素:
array[0] = 100
第三步设置所有节点至数组相应位置:
leftChildIndex = (parentIndex * 2) + 1
rightChildIndex = (parentIndex * 2) + 2
例如设置90至数组相应位置,其父节点100索引等于0,90是100左子节点:
parentIndex = 0
leftChildIndex = (0 * 2) + 1 = 1
array[1] = 90
例如设置80至数组相应位置,其父节点100索引等于0,80是100右子节点:
parentIndex = 0
leftChildIndex = (0 * 2) + 2 = 2
array[2] = 80
例如设置30至数组相应位置,其父节点80索引等于2,30是80右子节点:
parentIndex = 2
leftChildIndex = (2 * 2) + 2 = 6
array[6] = 30
第四步如果已知子节点数组索引,也可以反推出其父节点索引:
parentIndex = (childIndex - 1) / 2
例如已知节点30索引等于6,那么可以反推其父节点80索引等于2:
childIndex = 6
parentIndex = (6 - 1) / 2 = 2
2.3 新增元素
现在向二叉堆新增节点92,第一步在数组最后一个索引位置插入此元素:
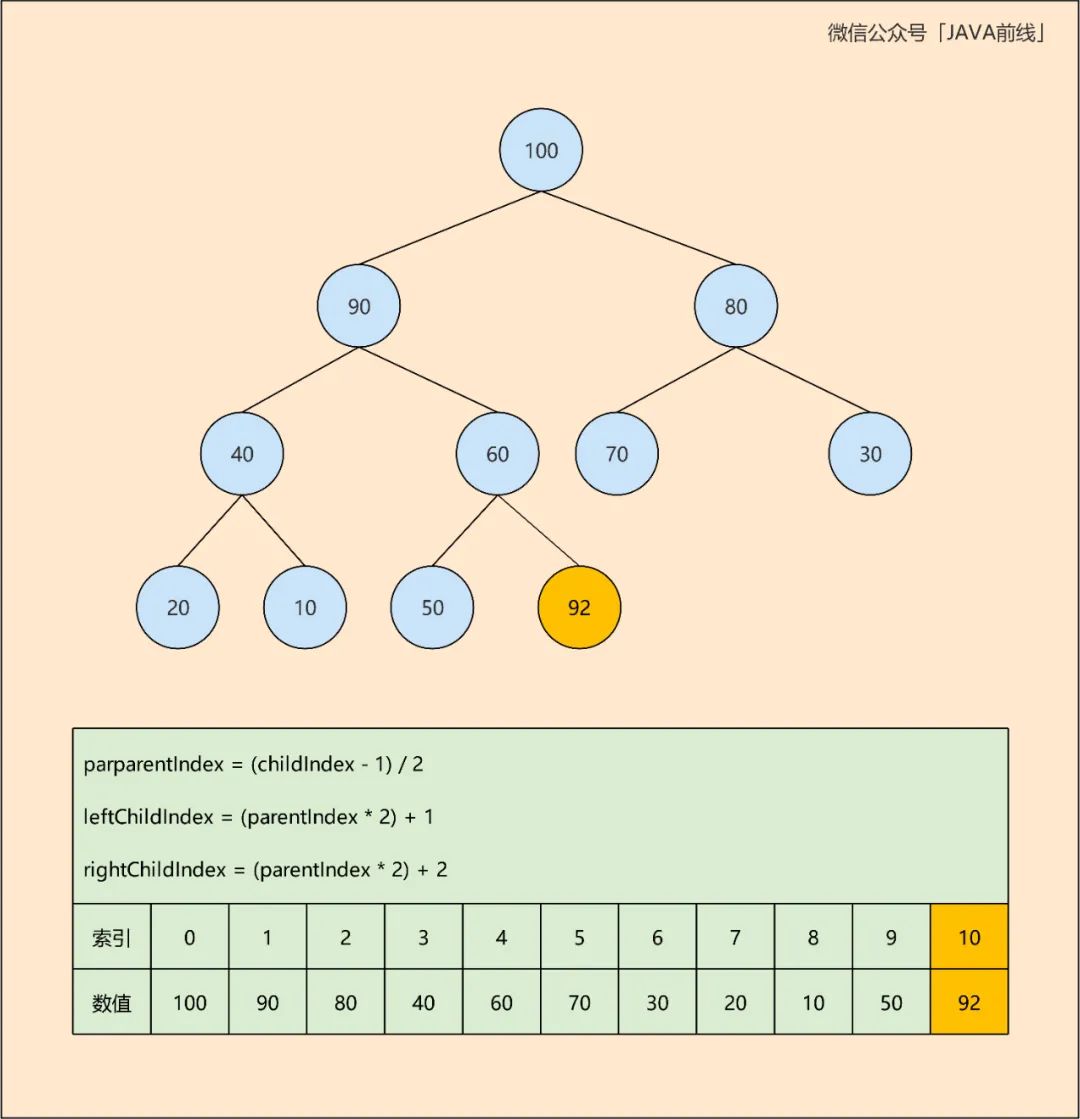
这显然不符合二叉堆的基本要求,需要循环与其父节点进行比较,如果发现大于父节点则交换位置,否则退出循环。第一轮比较92大于60,二者交换位置:
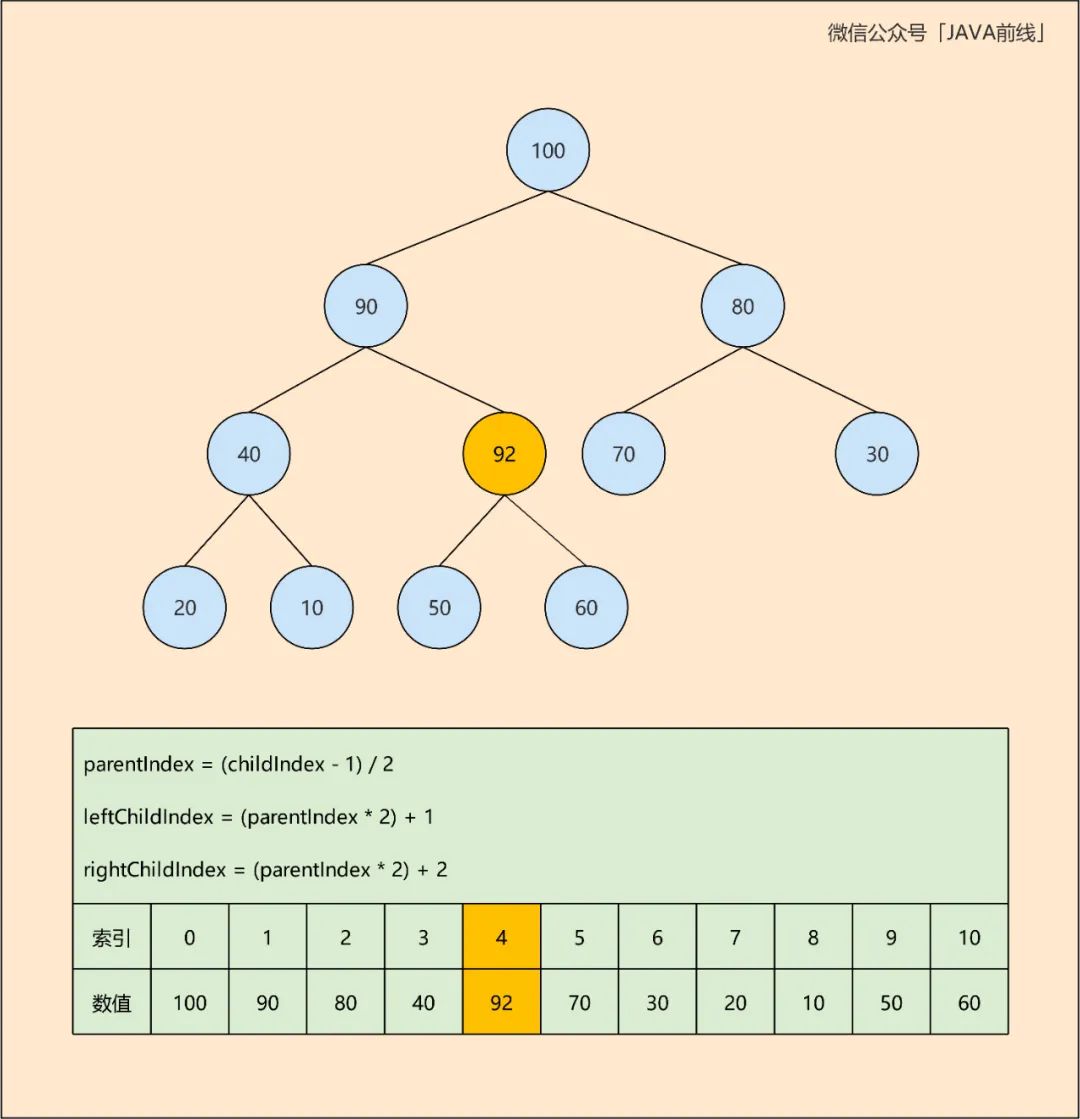
第二轮比较92大于90,二者交换位置:

第三轮比较92小于100,无需交换并退出循环:
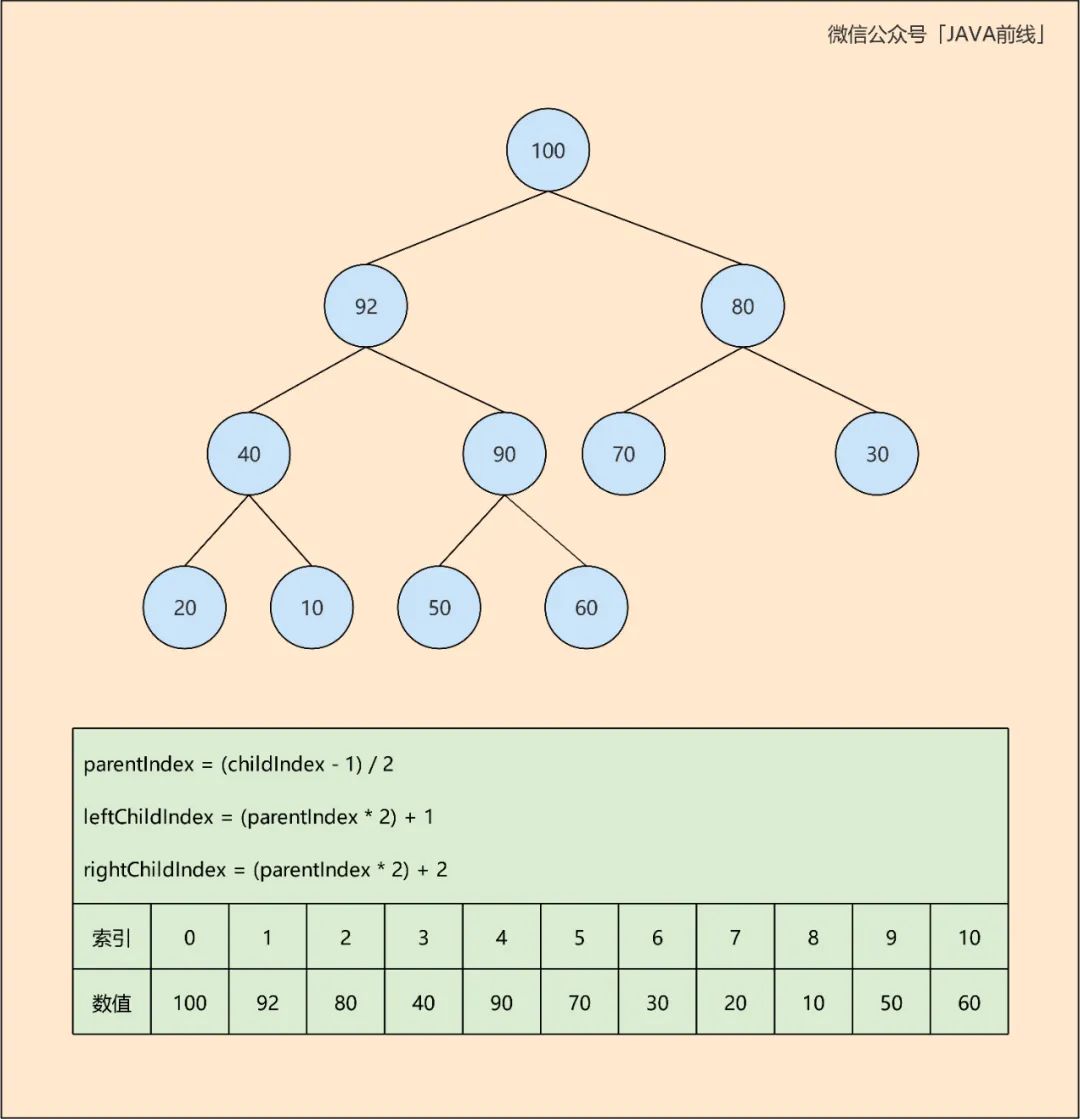
最后一个节点92开始在最后,通过循环比较向上不断移动至相应位置,这个过程被称为SiftUp,可以理解为上浮。
2.4 获取并删除堆顶元素
整棵树哪一个元素对业务最有价值?无疑是堆顶元素。以大顶堆为例,最大值永远都在堆顶,可以理解为优先级最高的元素永远在堆顶,只要循环取出堆顶元素,那么可以达到按照优先级顺序进行处理目的。
当获取到堆顶元素后需要移除此元素,这就可能涉及到二叉堆元素位置变化,下面演示这个过程,第一轮获取堆顶元素100:
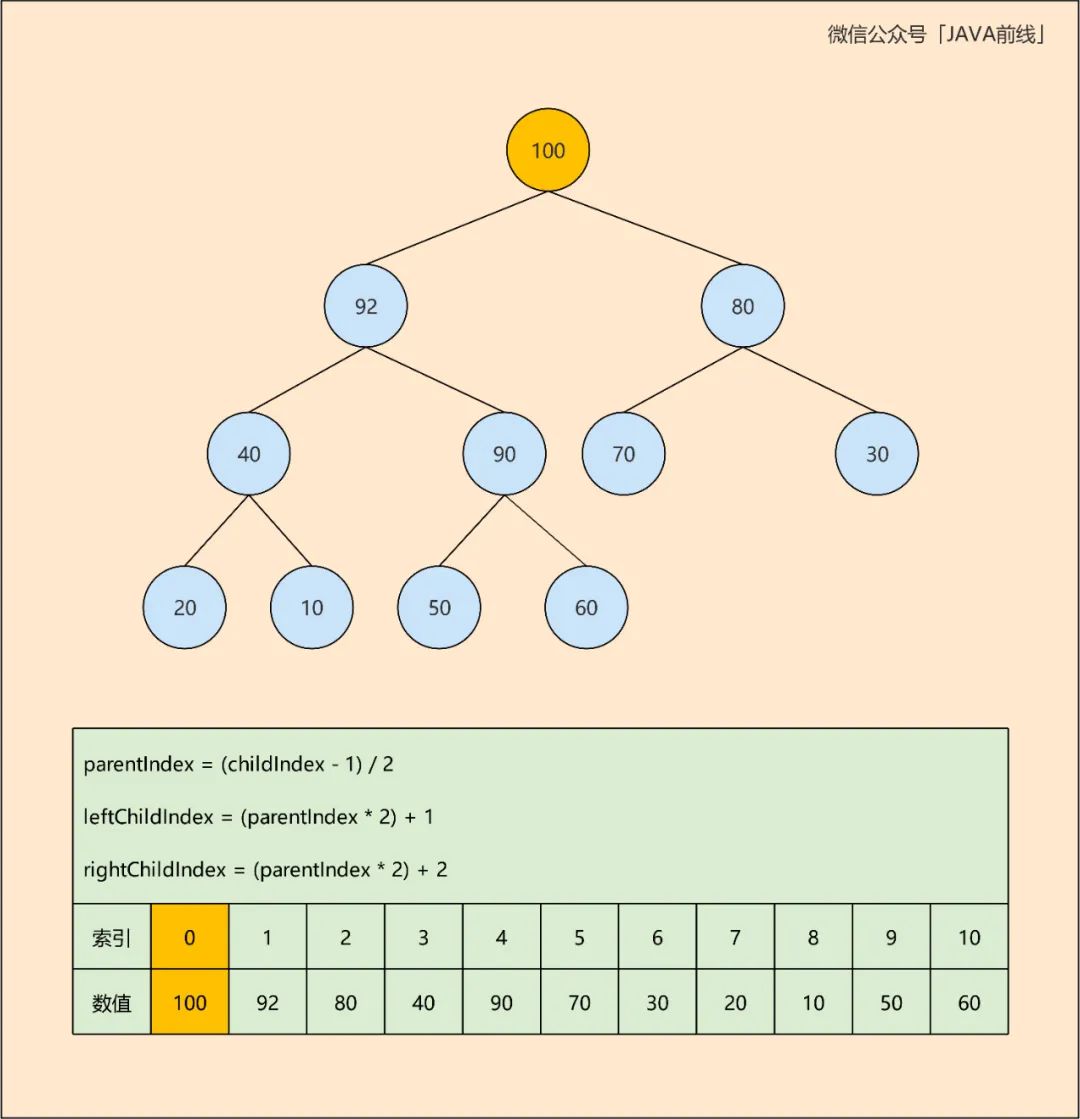
第二轮将最后一个元素60从原有位置删除,并设置到堆顶位置:
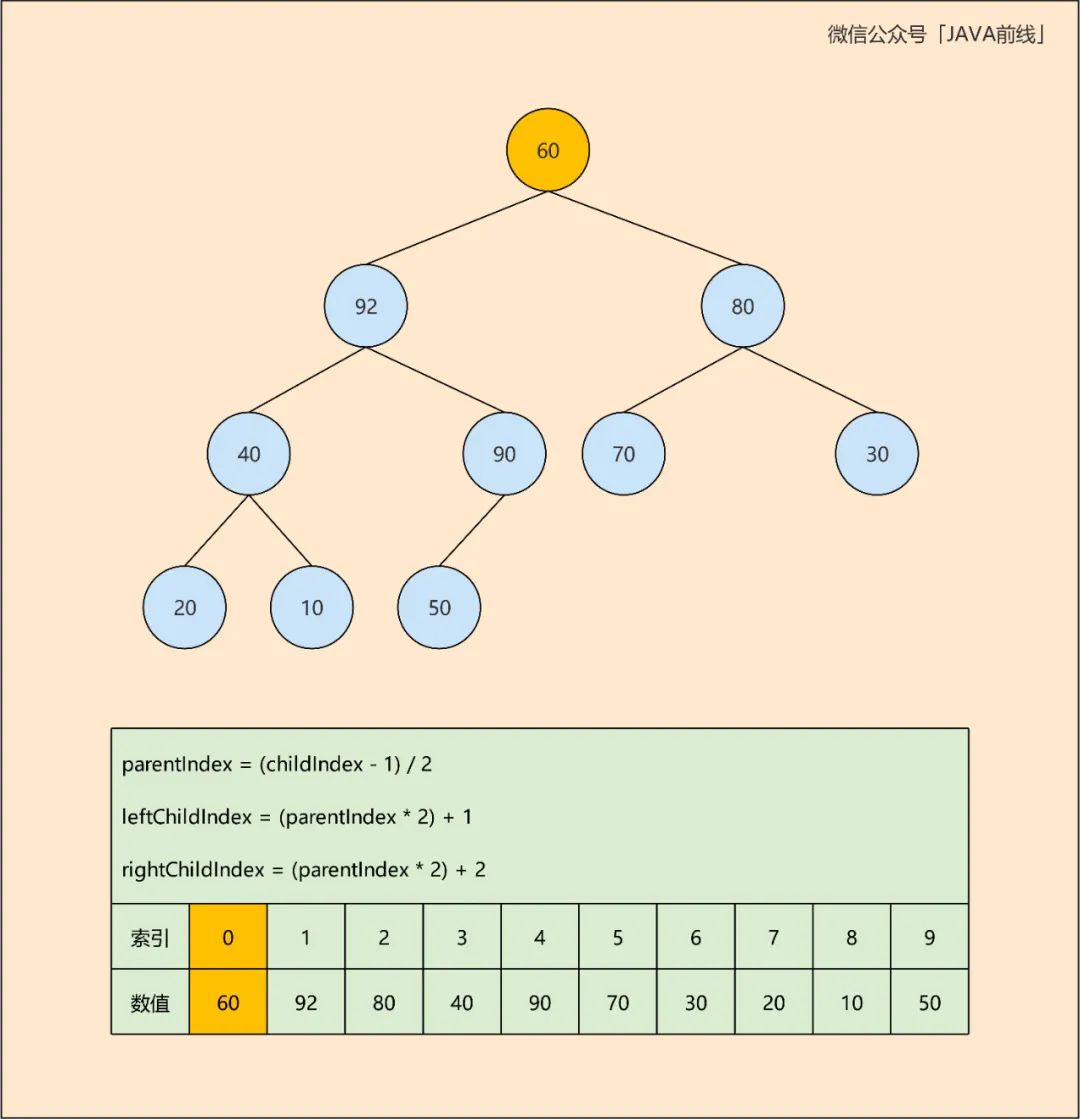
第三轮比较60与左右子节点92和80,选取较大子节点92,92大于60,二者交换位置:

第四轮比较60与左右子节点40和90,选取较大子节点90,90大于60,二者交换位置:
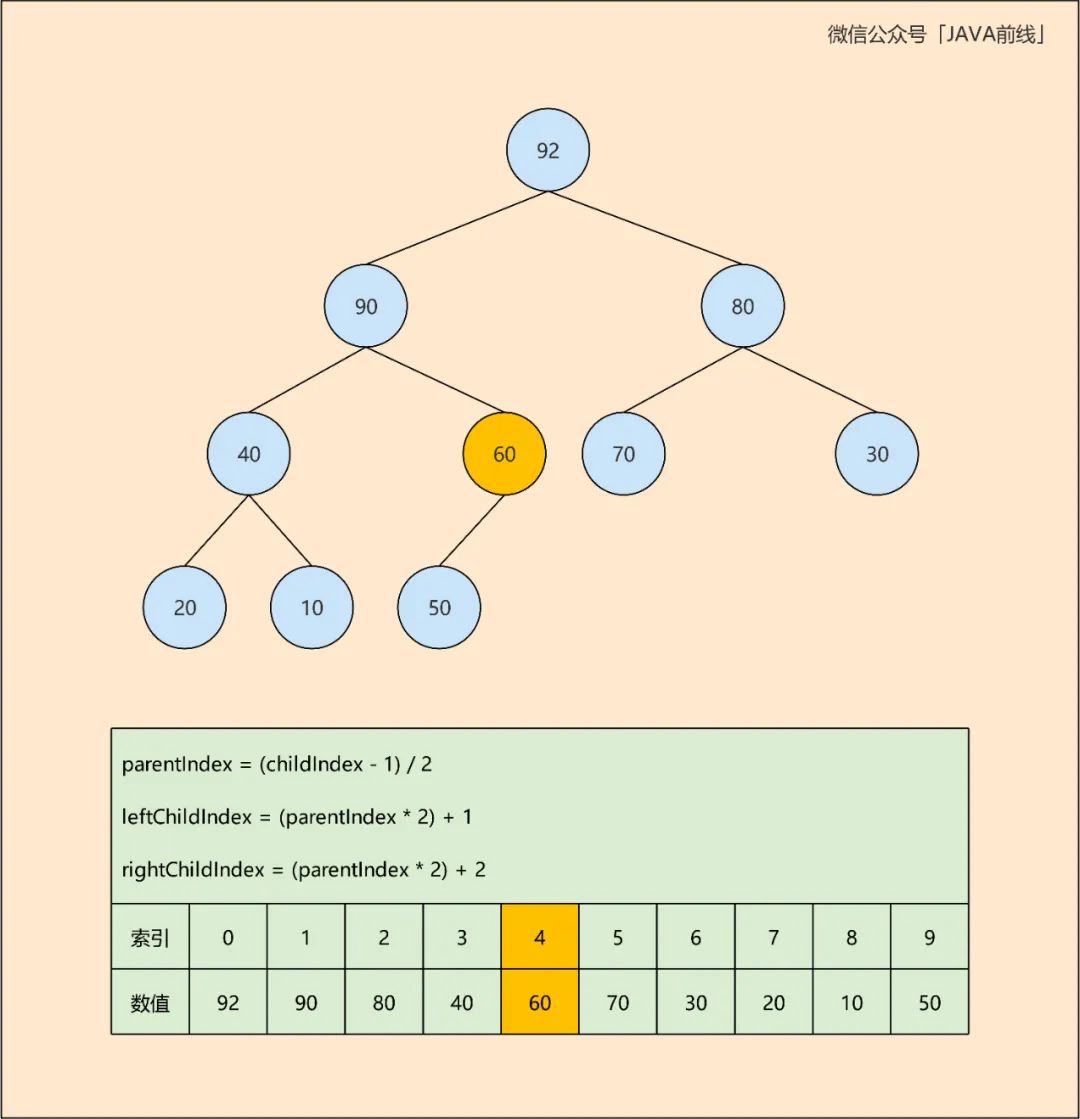
第五轮比较60与左子节点50,50小于60,无需交换并退出循环:

最后一个节点60首先移动至根节点,再通过循环比较向下移动至相应位置,这个过程被称为SiftDown,可以理解为下沉。
3 手写大顶堆
经过第二章节分析我们知道,二叉堆最重要方法是新增元素和获取并删除堆顶元素,其中最重要的是SiftUp和SiftDown两个过程。
3.1 接口声明
public interface IMaxHeap<E extends Comparable> {
/**
* 新增元素
*
* @param element 待新增元素
* @return true表示成功
*/
public boolean offer(E element);
/**
* 获取并删除堆顶元素
*
* @return 最大值
*/
public E getAndRemoveTop();
/**
* 堆大小
*
* @return 堆大小
*/
public int size();
}
3.2 大顶堆实现
public class MyMaxHeap<E extends Comparable> implements IMaxHeap<E> {
private ArrayList array;
public MyMaxHeap() {
array = new ArrayList();
}
@Override
public boolean offer(E element) {
// 1.新增至数组最后
int lastIndex = size();
array.add(lastIndex, element);
// 2.ShfitUp
shiftUp(lastIndex);
return Boolean.TRUE;
}
@Override
public E getAndRemoveTop() {
// 1.根节点为最大值
E max = array.get(0);
// 2.最后节点移动至根节点并删除
int lastIndex = size() - 1;
E lastNode = array.get(lastIndex);
array.set(0, lastNode);
array.remove(lastIndex);
// 3.ShiftDown
shiftDown(0);
// 4.返回最大值
return max;
}
@Override
public int size() {
return array.size();
}
// 节点上浮
private void shiftUp(int currentIndex) {
// 根节点无需上浮
while (currentIndex != 0) {
// 当前节点
E currentValue = array.get(currentIndex);
// 父索引
int parentIndex = getParentIndex(currentIndex);
// 父节点
E parentValue = array.get(parentIndex);
// 当前节点小于父节点则退出循环
if (currentValue.compareTo(parentValue) < 0) {
break;
}
// 当前节点大于等于父节点则交换位置
array.set(parentIndex, currentValue);
array.set(currentIndex, parentValue);
currentIndex = parentIndex;
}
}
// 节点下沉
private void shiftDown(int currentIndex) {
// 当前节点没有左子节点则不需要再下沉
while (getLeftChildIndex(currentIndex) < size()) {
// 当前节点
E currentValue = array.get(currentIndex);
// 左子索引
int leftChildIndex = getLeftChildIndex(currentIndex);
// 左子节点
E leftChildValue = array.get(leftChildIndex);
// 右子索引
Integer rightChildIndex = null;
E rightChildValue = null;
if (getRightChildIndex(currentIndex) < size()) {
rightChildIndex = getRightChildIndex(currentIndex);
rightChildValue = array.get(rightChildIndex);
}
// 右子节点存在
if (null != rightChildIndex) {
// 找出左右子节点较大节点
int biggerIndex = rightChildIndex;
if (leftChildValue.compareTo(rightChildValue) > 0) {
biggerIndex = leftChildIndex;
}
// 较大节点小于当前节点则退出循环
E biggerValue = array.get(biggerIndex);
if (biggerValue.compareTo(currentValue) < 0) {
break;
}
// 较大节点大于等于当前节点则交换位置
array.set(currentIndex, biggerValue);
array.set(biggerIndex, currentValue);
currentIndex = biggerIndex;
}
// 右子节点不存在
else {
// 左子节点小于当前节点则退出循环
if (leftChildValue.compareTo(currentValue) < 0) {
break;
}
// 左子节点大于等于当前节点则交换位置
array.set(currentIndex, leftChildValue);
array.set(leftChildIndex, currentValue);
currentIndex = leftChildIndex;
}
}
}
// 获取左子节点索引
private int getLeftChildIndex(int currentIndex) {
return currentIndex * 2 + 1;
}
// 获取右子节点索引
private int getRightChildIndex(int currentIndex) {
return currentIndex * 2 + 2;
}
// 获取父节点索引
private int getParentIndex(int currentIndex) {
if (currentIndex == 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("root node has no parent");
}
return (currentIndex - 1) / 2;
}
public ArrayList getArray() {
return array;
}
public void setArray(ArrayList array) {
this.array = array;
}
}
3.3 代码测试
public class MyMaxHeapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyMaxHeap maxHeap = new MyMaxHeap();
maxHeap.offer(70);
maxHeap.offer(90);
maxHeap.offer(80);
maxHeap.offer(100);
maxHeap.offer(60);
System.out.println("maxHeap test offer, heapInfo=" + maxHeap.getArray());
Integer maxValue = maxHeap.getAndRemoveTop();
System.out.println("maxHeap test getAndRemoveTop, maxValue=" + maxValue + ", heapInfo=" + maxHeap.getArray());
}
}
代码执行结果:
maxHeap test offer, heapInfo=[100, 90, 80, 70, 60]
maxHeap test getAndRemoveTop, maxValue=100, heapInfo=[90, 70, 80, 60]
4 手写优先队列
我们在第三章节手写了大顶堆,那么手写优先队列就很简单了,只需要声明一个队列对大顶堆进行封装,并提供队列相关访问方法即可。
4.1 接口声明
public interface IPriorityQueue<E extends Comparable> {
/**
* 新增元素
*
* @param element 元素
*/
public void offer(E element);
/**
* 获取队列首元素
*
* @return 首元素
*/
public E poll();
/**
* 获取队列长度
*
* @return 队列长度
*/
public int size();
}
4.2 优先队列实现
public class MyPriorityQueue<E extends Comparable> implements IPriorityQueue<E> {
private MyMaxHeap myMaxHeap;
public MyPriorityQueue() {
myMaxHeap = new MyMaxHeap();
}
@Override
public void offer(E element) {
myMaxHeap.add(element);
}
@Override
public E poll() {
return myMaxHeap.getAndRemoveTop();
}
@Override
public int size() {
return myMaxHeap.size();
}
}
4.3 代码测试
public class PriorityQueueTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyPriorityQueue myPriorityQueue = new MyPriorityQueue();
myPriorityQueue.offer(10);
myPriorityQueue.offer(30);
myPriorityQueue.offer(20);
while (myPriorityQueue.size() > 0) {
System.out.println(myPriorityQueue.poll());
}
}
}
代码执行结果:
30
20
10
5 源码分析
5.1 PriorityQueue
我们看到在offer方法进行了siftUp,规则是当前节点小于父节点则交换位置,在poll方法进行了siftDown,规则是当前节点大于较大子节点则交换位置。
这两个规则表示使用了小顶堆,可以解释第一章节应用一输出顺序。在应用二修改对象比较规则,交换比较顺序,那么可以实现大顶堆功能。
package java.util;
public class PriorityQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E> implements java.io.Serializable {
private static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 11;
transient Object[] queue;
private int size = 0;
private final Comparatorsuper E> comparator;
public PriorityQueue() {
this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, null);
}
public PriorityQueue(Comparatorsuper E> comparator) {
this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, comparator);
}
// 新增元素
public boolean offer(E e) {
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
modCount++;
int i = size;
if (i >= queue.length)
grow(i + 1);
size = i + 1;
if (i == 0)
queue[0] = e;
else
// 上浮
siftUp(i, e);
return true;
}
private void siftUp(int k, E x) {
if (comparator != null)
siftUpUsingComparator(k, x);
else
siftUpComparable(k, x);
}
private void siftUpComparable(int k, E x) {
Comparablesuper E> key = (Comparablesuper E>) x;
while (k > 0) {
// 父索引
int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1;
// 父节点
Object e = queue[parent];
// 当前节点大于等于父节点则退出循环
if (key.compareTo((E) e) >= 0)
break;
// 当前节点小于父节点则交换位置上浮
queue[k] = e;
k = parent;
}
queue[k] = key;
}
// 获取并删除队首元素
public E poll() {
if (size == 0)
return null;
int s = --size;
modCount++;
E result = (E) queue[0];
E x = (E) queue[s];
queue[s] = null;
if (s != 0)
// 下沉
siftDown(0, x);
return result;
}
private void siftDown(int k, E x) {
if (comparator != null)
siftDownUsingComparator(k, x);
else
siftDownComparable(k, x);
}
private void siftDownComparable(int k, E x) {
Comparablesuper E> key = (Comparablesuper E>)x;
int half = size >>> 1;
while (k < half) {
// 左子索引
int child = (k << 1) + 1;
// 左子节点
Object c = queue[child];
// 右子索引
int right = child + 1;
// 比较左右子节点较大节点
if (right < size && ((Comparablesuper E>) c).compareTo((E) queue[right]) > 0)
c = queue[child = right];
// 当前节点小于等于较大节点则退出循环
if (key.compareTo((E) c) <= 0)
break;
// 当前节点大于较大节点则交换位置下沉
queue[k] = c;
k = child;
}
queue[k] = key;
}
}
5.2 DelayQueue
延时队列底层使用优先队列,优先级指标是元素本身时间属性,在新增元素时越靠近队列头部,元素到期时间越早。
在取出堆顶元素时,首先调用元素getDelay方法,通常是元素时间减去当前时间,如果元素时间小于等于当前时间,表示元素已经到期则取出并删除队首元素。
package java.util.concurrent;
public class DelayQueue<E extends Delayed> extends AbstractQueue<E> implements BlockingQueue<E> {
private final transient ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private final PriorityQueue q = new PriorityQueue();
public boolean offer(E e) {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
q.offer(e);
if (q.peek() == e) {
leader = null;
available.signal();
}
return true;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public E poll() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
// 获取队首元素
E first = q.peek();
// 队首元素时间大于当前时间表示没到期
if (first == null || first.getDelay(NANOSECONDS) > 0)
return null;
// 队首元素时间小于等于当前时间表示到期则取出并删除
else
return q.poll();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
6 文章总结
第一本文首先使用了java.util.PriorityQueue进行功能演示,从应用一可以看出其默认使用了小顶堆,从应用二可以看出当改变对象比较关系之后,可以达到大顶堆效果。
第二本文介绍了二叉堆相关概念,二叉堆分为大顶堆和小顶堆,其中最重要的两个方法是新增元素和获取并删除堆顶元素,最重要的两个过程是上浮和下沉。
第三本文手写了大顶堆和优先队列,其中大顶堆最重要的是处理上浮和下沉这两个过程,优先队列在大顶堆基础上进行封装。
第四本文分析了PriorityQueue与DelayQueue源码,其中优先队列默认使用小顶堆,延时队列底层使用优先队列,优先级指标是时间,希望本文对大家有所帮助。
JAVA前线
欢迎大家关注公众号「JAVA前线」查看更多精彩分享,主要内容包括源码分析、实际应用、架构思维、职场分享、产品思考等等,同时也非常欢迎大家加我微信「java_front」一起交流学习
