Spring奇技淫巧之扩展点的应用
❝最近在看公司项目和中间件的时候,看到一些Spring扩展点的使用,写篇文章学习下,对大家之后看源码都有帮助
❞
「首先先介绍下Bean的生命周期」
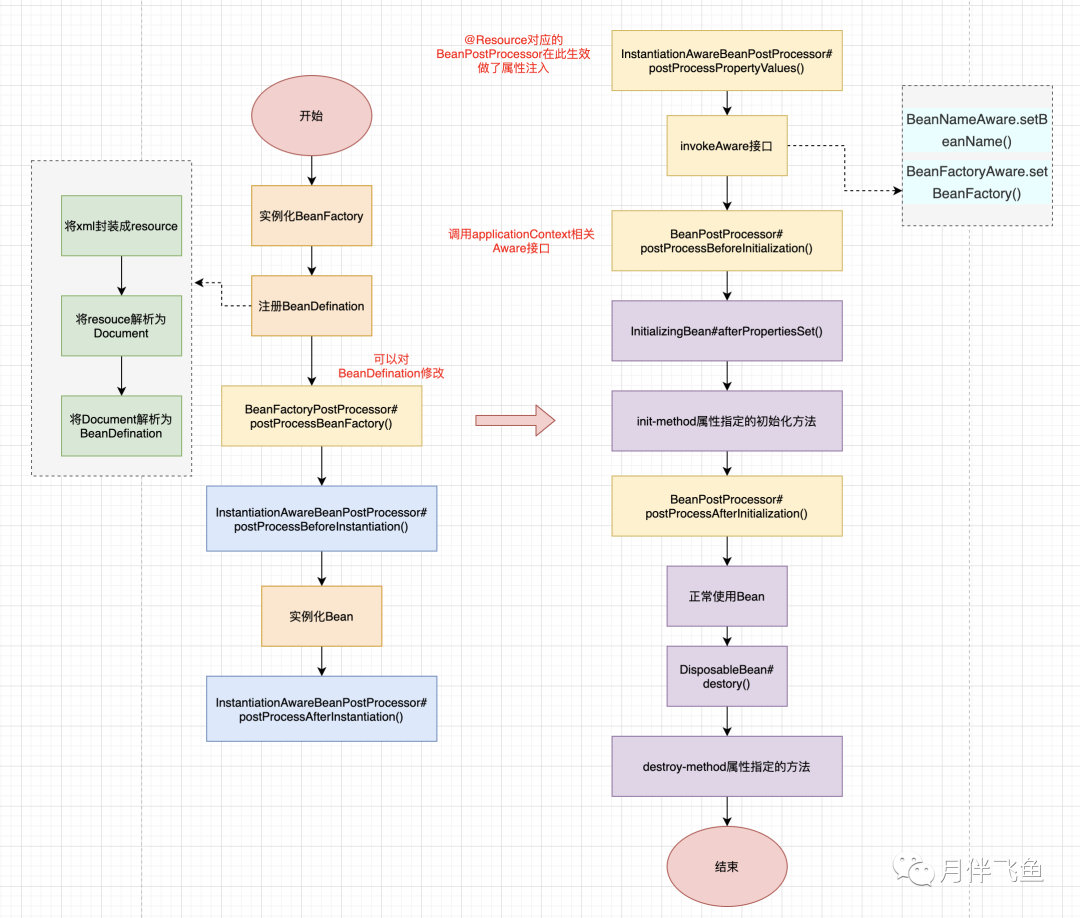
我们知道Bean的生命周期分为几个主干流程
-
Bean(单例非懒加载)的实例化阶段 -
Bean的属性注入阶段 -
Bean的初始化阶段 -
Bean的销毁阶段
下面是整个Spring容器的启动流程,可以看到除了上述几个主干流程外,Spring还提供了很多扩展点
下面详细介绍下Spring的常见的扩展点
Spring常见扩展点
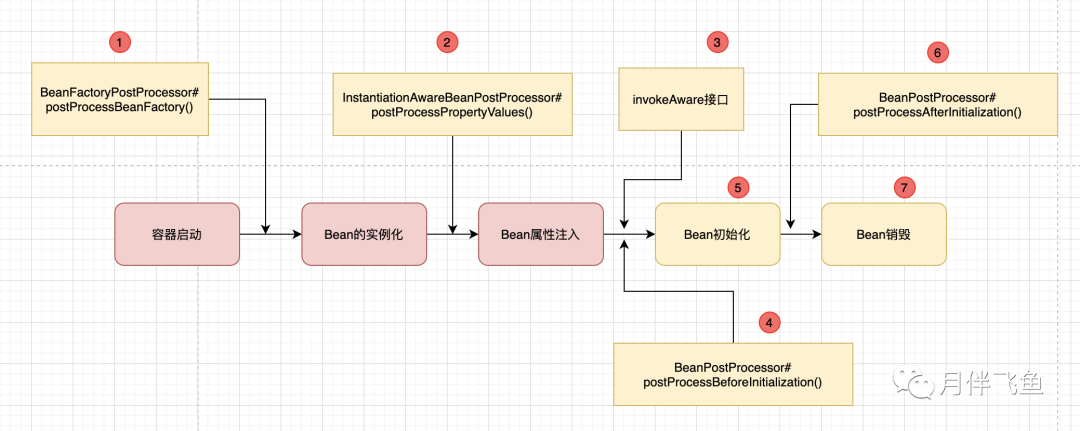
「BeanFactoryPostProcessor#postProcessBeanFactory」
有时候整个项目工程中bean的数量有上百个,而大部分单测依赖都是整个工程的xml,导致单测执行时需要很长时间(大部分时间耗费在xml中数百个单例非懒加载的bean的实例化及初始化过程)
解决方法:利用Spring提供的扩展点将xml中的bean设置为懒加载模式,省去了Bean的实例化与初始化时间
public class LazyBeanFactoryProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
DefaultListableBeanFactory fac = (DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory;
Map<String, AbstractBeanDefinition> map = (Map<String, AbstractBeanDefinition>) ReflectionTestUtils.getField(fac, "beanDefinitionMap");
for (Map.Entry<String, AbstractBeanDefinition> entry : map.entrySet()) {
//设置为懒加载
entry.getValue().setLazyInit(true);
}
}
}
「InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessPropertyValues」
非常规的配置项比如
<context:component-scan base-package="com.zhou" />
Spring提供了与之对应的特殊解析器
正是通过这些特殊的解析器才使得对应的配置项能够生效
而针对这个特殊配置的解析器为 ComponentScanBeanDefinitionParser
在这个解析器的解析方法中,注册了很多特殊的Bean
public BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
//...
registerComponents(parserContext.getReaderContext(), beanDefinitions, element);
//...
return null;
}
public static Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Object source) {
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefs = new LinkedHashSet<BeanDefinitionHolder>(4);
//...
//@Autowire
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// Check for JSR-250 support, and if present add the CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
//@Resource
if (jsr250Present && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
//特殊的Bean
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
//...
return beanDefs;
}
以@Resource为例,看看这个特殊的bean做了什么
public class CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor extends InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
implements InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor, BeanFactoryAware, Serializable {
public PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues(PropertyValues pvs, PropertyDescriptor[] pds,
Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
InjectionMetadata metadata = findResourceMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass());
try {
//属性注入
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of resource dependencies failed", ex);
}
return pvs;
}
}
我们看到在postProcessPropertyValues方法中,进行了属性注入
「invokeAware」
实现BeanFactoryAware接口的类,会由容器执行setBeanFactory方法将当前的容器BeanFactory注入到类中
@Bean
class BeanFactoryHolder implements BeanFactoryAware{
private static BeanFactory beanFactory;
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
}
「BeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization」
实现ApplicationContextAware接口的类,会由容器执行setApplicationContext方法将当前的容器applicationContext注入到类中
@Bean
class ApplicationContextAwareProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
private final ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext;
public ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(final Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
//...
invokeAwareInterfaces(bean);
return bean;
}
private void invokeAwareInterfaces(Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware) {
((ApplicationContextAware) bean).setApplicationContext(this.applicationContext);
}
}
}
我们看到是在BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization中进行了setApplicationContext方法的调用
class ApplicationContextHolder implements ApplicationContextAware{
private static ApplicationContext applicationContext;
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
}
「afterPropertySet()和init-method」
目前很多Java中间件都是基本Spring Framework搭建的,而这些中间件经常把入口放到afterPropertySet或者自定义的init中
「BeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInitialization」
熟悉aop的同学应该知道,aop底层是通过动态代理实现的
当配置了<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>时候,默认开启aop功能,相应地调用方需要被aop织入的对象也需要替换为动态代理对象
不知道大家有没有思考过动态代理是如何「在调用方无感知情况下替换原始对象」的?
❝根据上文的讲解,我们知道:
❞
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
Spring也提供了特殊的解析器,和其他的解析器类似,在核心的parse方法中注册了特殊的bean
这里是一个BeanPostProcessor类型的bean
class AspectJAutoProxyBeanDefinitionParser implements BeanDefinitionParser {
@Override
public BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
//注册特殊的bean
AopNamespaceUtils.registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(parserContext, element);
extendBeanDefinition(element, parserContext);
return null;
}
}
将于当前bean对应的动态代理对象返回即可,该过程对调用方全部透明
public class AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator extends AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator {
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean != null) {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
if (!this.earlyProxyReferences.containsKey(cacheKey)) {
//如果该类需要被代理,返回动态代理对象;反之,返回原对象
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}
}
正是利用Spring的这个扩展点实现了动态代理对象的替换
「destroy()和destroy-method」
bean生命周期的最后一个扩展点,该方法用于执行一些bean销毁前的准备工作,比如将当前bean持有的一些资源释放掉
最后
「写文章画图不易,喜欢的话,希望帮忙点赞,转发下哈,谢谢」
微信搜索:月伴飞鱼,交个朋友
公众号后台回复666,获得免费电子书籍,必读经典书籍这里全都有
参考书籍:
-
Spring技术内幕
-
Spring源码深度解析

社招一年半面经分享(含阿里美团头条京东滴滴)

条件语句的多层嵌套问题优化,助你写出不让同事吐槽的代码