用 python+grpc+yolo 进行目标检测

我们模型开发完成后往往需要基于一些web服务模块将模型部署成可被外部访问的服务形式,用的最多的就是flask框架了,可以很方便地将模型暴露成web服务接口,现在有一个新的需求就是需要使用grpc方式来开发接口,用于集群服务内部之间的相互访问调用。
gRPC有什么好处以及在什么场景下需要用gRPC既然是server/client模型,那么我们直接用restful api不是也可以满足吗,为什么还需要RPC呢?下面我们就来看看RPC到底有哪些优势gRPC vs. Restful APIgRPC和restful API都提供了一套通信机制,用于server/client模型通信,而且它们都使用http作为底层的传输协议(严格地说, gRPC使用的http2.0,而restful api则不一定)。不过gRPC还是有些特有的优势,如下:1、gRPC可以通过protobuf来定义接口,从而可以有更加严格的接口约束条件。关于protobuf可以参见笔者之前的小文Google Protobuf简明教程2、另外,通过protobuf可以将数据序列化为二进制编码,这会大幅减少需要传输的数据量,从而大幅提高性能。3、gRPC可以方便地支持流式通信(理论上通过http2.0就可以使用streaming模式, 但是通常web服务的restful api似乎很少这么用,通常的流式数据应用如视频流,一般都会使用专门的协议如HLS,RTMP等,这些就不是我们通常web服务了,而是有专门的服务器应用。)
在此之前我听过rpc(Remote Procedure Call),即:远程过程调用,但是对于grpc还是知之甚少,所以这里还是需要花点时间来学习了解一下的,这里就以一个实际的目标检测类的应用来进行实践学习。
grpc的官网介绍截图如下:
一个基础的grpc应用问题主要包含四个部分:
1、编写 .proto文件
RPC 是两个子系统之间进行的直接消息交互,它使用操作系统提供的套接字来作为消息的载体,以特定的消息格式来定义消息内容和边界。gRPC 是 Google 开源的基于 Protobuf 和 Http2.0 协议的通信框架,Google 深度学习框架 tensorflow 底层的 RPC 通信就完全依赖于 gRPC 库。gRPC通过protobuf来定义接口和数据类型。
这里我们编写的 data.proto 内容如下:
syntax = "proto3";//package example;service FormatData { //定义服务,用在rpc传输中rpc DoFormat(actionrequest) returns (actionresponse){}}message actionrequest {string text = 1;}message actionresponse{string text=1;}
2、运行命令生成 data_pb2_grpc.py 和data_pb2.py
python -m grpc_tools.protoc -I. --python_out=. --grpc_python_out=. ./data.proto上述命令执行结束后会生成上述两个脚本文件,内容如下:
data_pb2.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-# Generated by the protocol buffer compiler. DO NOT EDIT!# source: data.proto"""Generated protocol buffer code."""from google.protobuf import descriptor as _descriptorfrom google.protobuf import message as _messagefrom google.protobuf import reflection as _reflectionfrom google.protobuf import symbol_database as _symbol_database# @@protoc_insertion_point(imports)_sym_db = _symbol_database.Default()DESCRIPTOR = _descriptor.FileDescriptor(name='data.proto',package='',syntax='proto3',serialized_options=None,create_key=_descriptor._internal_create_key,serialized_pb='......')_ACTIONREQUEST = _descriptor.Descriptor(name='actionrequest',full_name='actionrequest',filename=None,file=DESCRIPTOR,containing_type=None,create_key=_descriptor._internal_create_key,fields=[_descriptor.FieldDescriptor(name='text', full_name='actionrequest.text', index=0,number=1, type=9, cpp_type=9, label=1,has_default_value=False, default_value=b"".decode('utf-8'),message_type=None, enum_type=None, containing_type=None,is_extension=False, extension_scope=None,serialized_options=None, file=DESCRIPTOR, create_key=_descriptor._internal_create_key),],extensions=[],nested_types=[],enum_types=[],serialized_options=None,is_extendable=False,syntax='proto3',extension_ranges=[],oneofs=[],serialized_start=14,serialized_end=43,)_ACTIONRESPONSE = _descriptor.Descriptor(name='actionresponse',full_name='actionresponse',filename=None,file=DESCRIPTOR,containing_type=None,create_key=_descriptor._internal_create_key,fields=[_descriptor.FieldDescriptor(name='text', full_name='actionresponse.text', index=0,number=1, type=9, cpp_type=9, label=1,has_default_value=False, default_value=b"".decode('utf-8'),message_type=None, enum_type=None, containing_type=None,is_extension=False, extension_scope=None,serialized_options=None, file=DESCRIPTOR, create_key=_descriptor._internal_create_key),],extensions=[],nested_types=[],enum_types=[],serialized_options=None,is_extendable=False,syntax='proto3',extension_ranges=[],oneofs=[],serialized_start=45,serialized_end=75,)DESCRIPTOR.message_types_by_name['actionrequest'] = _ACTIONREQUESTDESCRIPTOR.message_types_by_name['actionresponse'] = _ACTIONRESPONSE_sym_db.RegisterFileDescriptor(DESCRIPTOR)actionrequest = _reflection.GeneratedProtocolMessageType('actionrequest', (_message.Message,), {'DESCRIPTOR' : _ACTIONREQUEST,'__module__' : 'data_pb2'# @@protoc_insertion_point(class_scope:actionrequest)})_sym_db.RegisterMessage(actionrequest)actionresponse = _reflection.GeneratedProtocolMessageType('actionresponse', (_message.Message,), {'DESCRIPTOR' : _ACTIONRESPONSE,'__module__' : 'data_pb2'# @@protoc_insertion_point(class_scope:actionresponse)})_sym_db.RegisterMessage(actionresponse)_FORMATDATA = _descriptor.ServiceDescriptor(name='FormatData',full_name='FormatData',file=DESCRIPTOR,index=0,serialized_options=None,create_key=_descriptor._internal_create_key,serialized_start=77,serialized_end=136,methods=[_descriptor.MethodDescriptor(name='DoFormat',full_name='FormatData.DoFormat',index=0,containing_service=None,input_type=_ACTIONREQUEST,output_type=_ACTIONRESPONSE,serialized_options=None,create_key=_descriptor._internal_create_key,),])_sym_db.RegisterServiceDescriptor(_FORMATDATA)DESCRIPTOR.services_by_name['FormatData'] = _FORMATDATA# @@protoc_insertion_point(module_scope)
data_pb2_grpc.py
# Generated by the gRPC Python protocol compiler plugin. DO NOT EDIT!"""Client and server classes corresponding to protobuf-defined services."""import grpcimport data_pb2 as data__pb2class FormatDataStub(object):"""定义服务,用在rpc传输中"""def __init__(self, channel):"""Constructor.Args:channel: A grpc.Channel."""self.DoFormat = channel.unary_unary('/FormatData/DoFormat',request_serializer=data__pb2.actionrequest.SerializeToString,response_deserializer=data__pb2.actionresponse.FromString,)class FormatDataServicer(object):"""定义服务,用在rpc传输中"""def DoFormat(self, request, context):"""Missing associated documentation comment in .proto file."""context.set_code(grpc.StatusCode.UNIMPLEMENTED)context.set_details('Method not implemented!')raise NotImplementedError('Method not implemented!')def add_FormatDataServicer_to_server(servicer, server):rpc_method_handlers = {'DoFormat': grpc.unary_unary_rpc_method_handler(servicer.DoFormat,request_deserializer=data__pb2.actionrequest.FromString,response_serializer=data__pb2.actionresponse.SerializeToString,),}generic_handler = grpc.method_handlers_generic_handler('FormatData', rpc_method_handlers)server.add_generic_rpc_handlers((generic_handler,))# This class is part of an EXPERIMENTAL API.class FormatData(object):"""定义服务,用在rpc传输中"""@staticmethoddef DoFormat(request,target,options=(),channel_credentials=None,call_credentials=None,insecure=False,compression=None,wait_for_ready=None,timeout=None,metadata=None):return grpc.experimental.unary_unary(request, target, '/FormatData/DoFormat',data__pb2.actionrequest.SerializeToString,data__pb2.actionresponse.FromString,options, channel_credentials,insecure, call_credentials, compression, wait_for_ready, timeout, metadata)
至此,第二部分的工作就结束了。
3、编写sever端代码, server.py
这里主要是编写服务端的处理代码。
#!usr/bin/env python#encoding:utf-8from __future__ import division'''__Author__:沂水寒城功能: grpc 服务端'''import ioimport osimport cv2import grpcimport timeimport jsonimport base64import numpy as npfrom PIL import Imagefrom concurrent import futuresimport data_pb2, data_pb2_grpcfrom detect import *_ONE_DAY_IN_SECONDS = 60 * 60 * 24_HOST = 'localhost'_PORT = '8080'class FormatData(data_pb2_grpc.FormatDataServicer):'''重写接口函数'''def DoFormat(self, request, context):content = request.textdecode_img = base64.b64decode(content)image = io.BytesIO(decode_img)img = Image.open(image)detect_res=detectImg('name',img)detect_res=str(detect_res)return data_pb2.actionresponse(text=detect_res)def serve():'''服务端处理计算'''grpcServer = grpc.server(futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=4))data_pb2_grpc.add_FormatDataServicer_to_server(FormatData(), grpcServer)grpcServer.add_insecure_port(_HOST + ':' + _PORT)grpcServer.start()try:while True:print('=================================start=================================')time.sleep(_ONE_DAY_IN_SECONDS)except KeyboardInterrupt:grpcServer.stop(0)if __name__ == '__main__':serve()
4、编写客户端代码,client.py
这里主要是实现客户端的请求代码:
#!usr/bin/env python#encoding:utf-8from __future__ import divisionimport osimport cv2import jsonimport timeimport grpcimport base64import numpy as npfrom PIL import Imageimport data_pb2, data_pb2_grpc_HOST = 'localhost'_PORT = '8080'def run():connection = grpc.insecure_channel(_HOST + ':' + _PORT)print('connection: ', connection)client = data_pb2_grpc.FormatDataStub(channel=connection)print('client: ', client)string = base64.b64encode(img)response = client.DoFormat(data_pb2.actionrequest(text=string))print("response: " + response.text)if __name__ == '__main__':run()
到这里,一个基础的grpc应用已经开发完成,可以进行实际的测试使用了,首先在终端启动服务端,之后执行客户端的请求操作,查看结果输出。
服务端启动后输出如下:

客户端启动后输出如下:

我们这里是借助于yolov3实现的目标检测服务,原图如下:
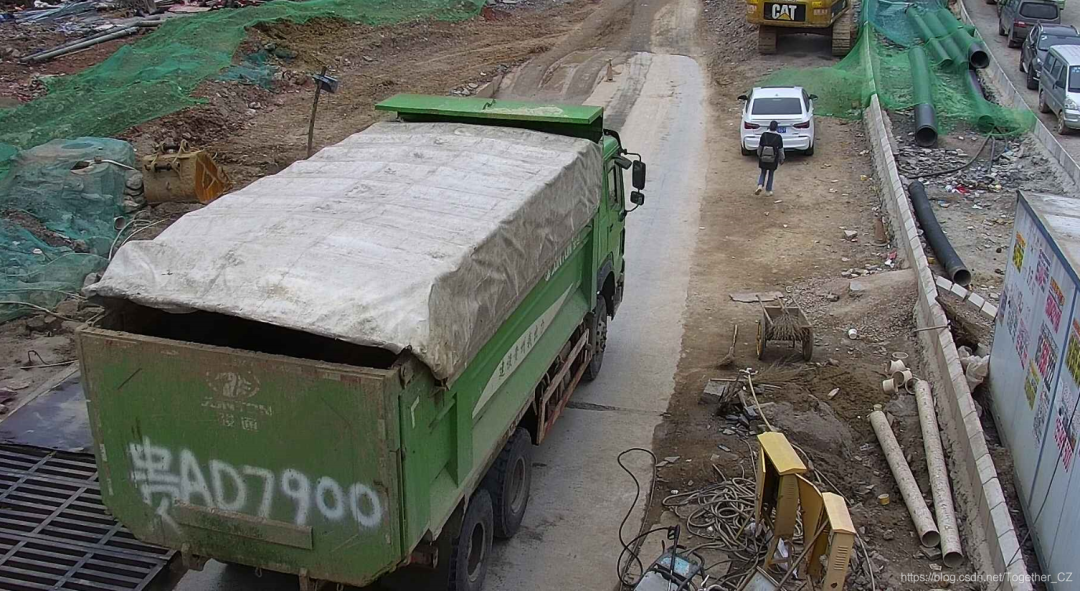

检测结果如下:
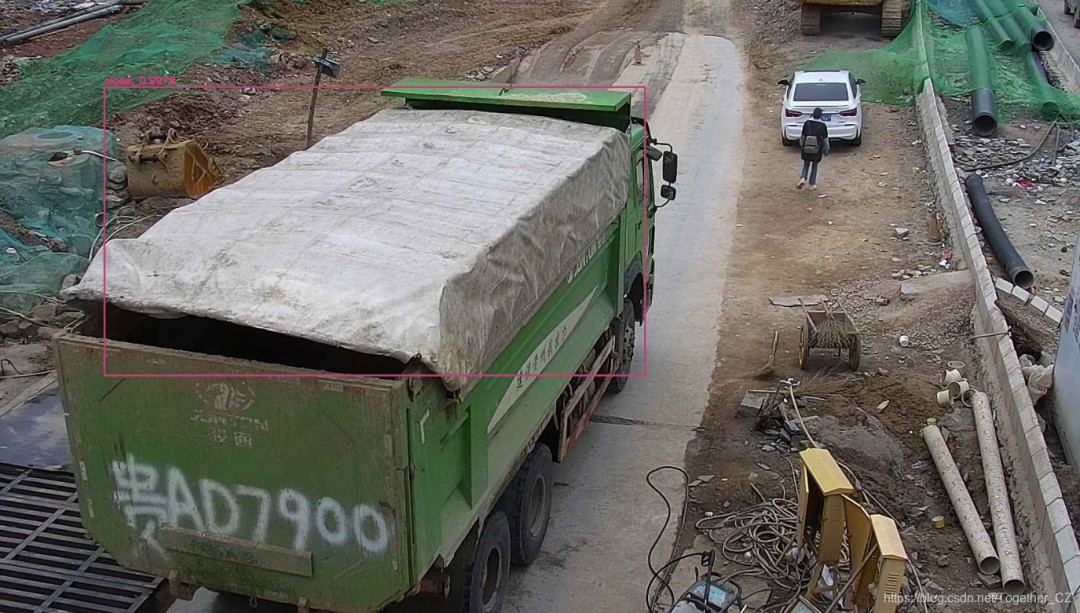

可以看到已经正常计算出来的结果。
作者:沂水寒城,CSDN博客专家,个人研究方向:机器学习、深度学习、NLP、CV
Blog: http://yishuihancheng.blog.csdn.net
赞 赏 作 者



点击下方阅读原文加入社区会员
