[文末赠书]面试被问到Flutter/Dart的HashMap你会吗?
点击上方 Java学习之道,选择 设为星标
来源: juejin.cn/post/6964427316046856229
作者: ad6623
Part1前言
相信不少同学在面试的时候有被问到关于HashMap的问题,特别是Java/Android程序员,HashMap几乎是必然会被提及的。因为这里面可以挖掘的点实在是太多了。关于Java的HashMap面经在网上可以说是随处可见了。自然而然,随着Flutter的火爆,后面大家也可能在面试中被问到关于Flutter/Dart的HashMap相关问题。与其到时候一问三不知,不如现在就来了解一下Flutter/Dart的HashMap吧。
本文中,关于Dart的HashMap我先列一些有可能在面试中遇到的问题,然后会对照源码做一些介绍,最后会给出这些问题的一个粗浅的答案。希望能帮到大家。
-
HashMap和LinkedHashMap有什么区别? -
这个表达式 final map = Map();得到的map是上面两种Map的那一种? -
HashMap底层的数据结构是什么样的? -
HashMap默认大小是多大? -
HashMap如何处理hash冲突? -
HashMap何时扩容?如何扩容? -
LinkedHashMap底层的数据结构是什么样的? -
LinkedHashMap如何处理hash冲突? -
LinkedHashMap何时扩容?如何扩容?
下面我们就带着这些问题来看一下源码
Part2使用HashMap和LinkedHashMap
创建一个HashMap实例:
final map = HashMap();
创建一个LinkedHashMap实例
final map = LinkedHashMap();
创建一个Map实例
final map = Map();
这里你得到的map其实是一个LinkedHashMap。其工厂构造函数如下:
@patch
class Map<K, V> {
...
@patch
factory Map() => new LinkedHashMap<K, V>();
...
}
增/改
map['one'] = 1;
删
map.remove('one');
查
final value = map['one'];
增,改,查的操作和操作数组一样,删除要调用remove()。
迭代器
final it = map.entries.iterator;
while(it.moveNext()) {
print(it.current);
}
Dart语言一大特点就是特别灵活,这里只是列举了一些常见操作,其他不同的写法大家可以参考API文档。
接下来我们深入源码来一探究竟。
Part3HashMap
构造函数
@patch
class HashMap<K, V> {
@patch
factory HashMap(
{bool equals(K key1, K key2)?,
int hashCode(K key)?,
bool isValidKey(potentialKey)?}) {
if (isValidKey == null) {
if (hashCode == null) {
if (equals == null) {
return new _HashMap<K, V>();
}
...
}
HashMap构造函数有三个可选入参,这里我们都不传,这样的话返回的就是个_HashMap实例。有入参的情况下会返回另外两种_IdentityHashMap和_CustomHashMap之一,本文由于篇幅所限就 不再涉及。大家感兴趣的话可以直接去看源码。
底层结构
var _buckets = List<_HashMapEntry<K, V>?>.filled(_INITIAL_CAPACITY, null);
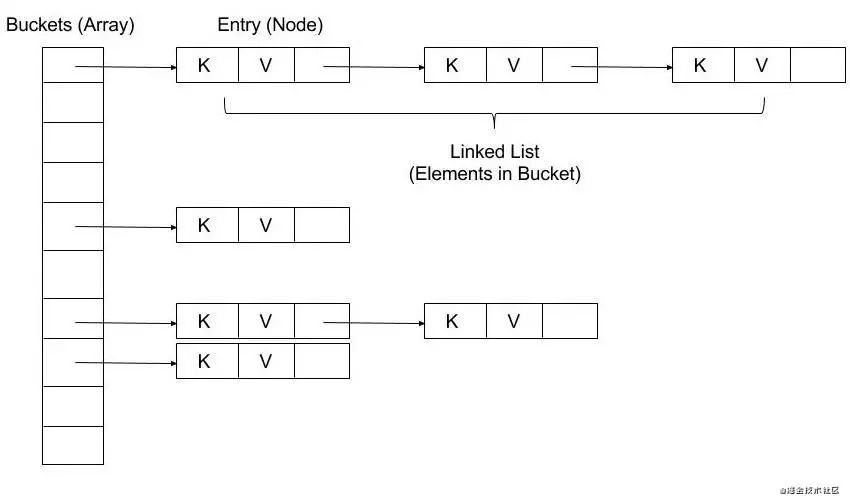
这一看就是数组+链表的形式嘛。
 初始化容量:
初始化容量:
static const int _INITIAL_CAPACITY = 8;
我们知道Java的HashMap初始化大小是16,Dart使用的是8. 虽然不同但也还是2的幂。另外貌似Dart也没有给用户提供自定义初始化大小的机会。
查找操作
V? operator [](Object? key) {
final hashCode = key.hashCode;
final buckets = _buckets;
final index = hashCode & (buckets.length - 1);
var entry = buckets[index];
while (entry != null) {
if (hashCode == entry.hashCode && entry.key == key) {
return entry.value;
}
entry = entry.next;
}
return null;
}
可见取数组下标就是直接把key的hashCode和数组长度-1做与操作。
final index = hashCode & (buckets.length - 1);
然后比较链表元素保存的哈希值以及key是否相等,不相等则找下一个链表元素,都相等则返回对应值。这里我们要注意到没有红黑树。所以dart的HashMap实现其实和jdk1.8之前的实现类似。
赋值操作
void operator []=(K key, V value) {
final hashCode = key.hashCode;
final buckets = _buckets;
final length = buckets.length;
final index = hashCode & (length - 1);
var entry = buckets[index];
while (entry != null) {
if (hashCode == entry.hashCode && entry.key == key) {
entry.value = value;
return;
}
entry = entry.next;
}
_addEntry(buckets, index, length, key, value, hashCode);
}
过程和取值操作其实差不多,键值对存在的情况下就直接赋值,不存在的情况下就调用_addEntry()做新增操作。
void _addEntry(List<_HashMapEntry<K, V>?> buckets, int index, int length,
K key, V value, int hashCode) {
final entry = new _HashMapEntry<K, V>(key, value, hashCode, buckets[index]);
buckets[index] = entry;
final newElements = _elementCount + 1;
_elementCount = newElements;
// If we end up with more than 75% non-empty entries, we
// resize the backing store.
if ((newElements << 2) > ((length << 1) + length)) _resize();
_modificationCount = (_modificationCount + 1) & _MODIFICATION_COUNT_MASK;
}
这里注意一下在新建_HashMapEntry的时候会传入当前数组的entry,也就是buckets[index]。然后把新的entry赋值给buckets[index]。
buckets[index] = entry;
这里我们就能猜到应该用的是头插法。另外,_modificationCount是每次有增删等操作的时候都是自增的,当我们在遍历HashMap的过程中如果有此类操作会导致Concurrent modification异常。这也就是"Fail-Fast"机制
新增操作显然会涉及到扩容的问题,从上面的注释我们可以看出,在键值对数量超过数组容量的75%的时候会做扩容,也就是它的负载因子是0.75。这点和Java也是一样的。这个75%的计算过程为了提高效率使用了位运算和加法来代替除法,等效于e4>l3 -> e/l>3/4 -> e/l>75%
扩容操作
void _resize() {
final oldBuckets = _buckets;
final oldLength = oldBuckets.length;
final newLength = oldLength << 1;
final newBuckets = new List<_HashMapEntry<K, V>?>.filled(newLength, null);
for (int i = 0; i < oldLength; i++) {
var entry = oldBuckets[i];
while (entry != null) {
final next = entry.next;
final hashCode = entry.hashCode;
final index = hashCode & (newLength - 1);
entry.next = newBuckets[index];
newBuckets[index] = entry;
entry = next;
}
}
_buckets = newBuckets;
}
扩容后的新数组长度是原长度的2倍。
final newLength = oldLength << 1;
我们知道它的初始长度是8,可见buckets数组长度始终会是2的幂。
从把entry从旧数组转移到新数组的过程我们也能看出来,这个转移的过程使用的也是头插法。
扩容这里有一个需要注意的地方就是,当键值对数量超过数组长度的75%时会发生扩容,而不是数组被占用超过75%的时候会发生扩容,这一误区在很多讨论Java HashMap的文章中也出现过。需要大家仔细体会这里面的不同。
删除操作
void _removeEntry(_HashMapEntry<K, V> entry,
_HashMapEntry<K, V>? previousInBucket, int bucketIndex) {
if (previousInBucket == null) {
_buckets[bucketIndex] = entry.next;
} else {
previousInBucket.next = entry.next;
}
}
删除就是正常的链表删除节点的过程。
遍历
void forEach(void action(K key, V value)) {
final stamp = _modificationCount;
final buckets = _buckets;
final length = buckets.length;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
var entry = buckets[i];
while (entry != null) {
action(entry.key, entry.value);
if (stamp != _modificationCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationError(this);
}
entry = entry.next;
}
}
}
遍历会从数组的第一个位置开始依次访问链表的每一项。显然这个遍历顺序是不保证和键值对的插入顺序一致的。这里我们也能看到"Fail-Fast"机制发生作用的时候了,如果遍历过程中用户对HashMap做了增删等操作的话会导致stamp和_modificationCount不相等,导致ConcurrentModificationError异常。
小结
Dart的HashMap总体而言实现的还是比较简单的。整体上和jdk1.7版本的HashMap类似。相信研究过Java实现的同学们会觉得dart的HashMap比较好理解一些。
Part4LinkedHashMap
从API文档上看,LinkedHashMap和HashMap的区别就是在遍历的时候,LinkedHashMap会保留键值对的插入顺序。在jdk中,LinkedHashMap的实现是将Node改造为双向链表以保留顺序。dart的LinkedHashMap实现则有所不同。
构造函数
@patch
class LinkedHashMap<K, V> {
@patch
factory LinkedHashMap(
{bool equals(K key1, K key2)?,
int hashCode(K key)?,
bool isValidKey(potentialKey)?}) {
if (isValidKey == null) {
if (hashCode == null) {
if (equals == null) {
return new _InternalLinkedHashMap<K, V>();
}
...
}
类似的,LinkedHashMap构造函数有三个可选入参,这里我们都不传,这样的话返回的就是个_InternalLinkedHashMap实例。有入参的情况下会返回另外两种_CompactLinkedIdentityHashMap和_CompactLinkedCustomHashMap之一,本文也不再涉及。
底层结构
我们直接看_InternalLinkedHashMap。
_InternalLinkedHashMap构造函数:
_InternalLinkedHashMap() {
_index = new Uint32List(_HashBase._INITIAL_INDEX_SIZE);
_hashMask = _HashBase._indexSizeToHashMask(_HashBase._INITIAL_INDEX_SIZE);
_data = new List.filled(_HashBase._INITIAL_INDEX_SIZE, null);
_usedData = 0;
_deletedKeys = 0;
}
可见_InternalLinkedHashMap底层有两个数组,_index和_data。_index数组以哈希码为下标记录对应键值对在_data数组中的位置。_data数组按插入顺序依次保存key和value。
用图来表示就是下面这个样子:
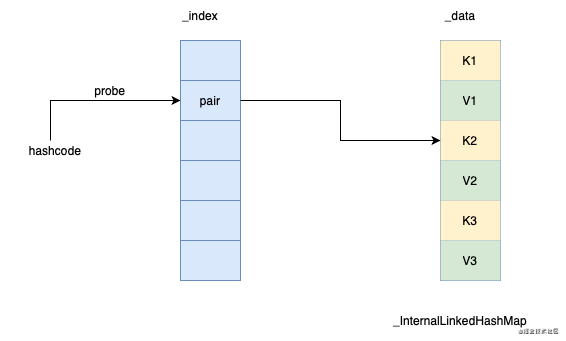
两个数组的初始化长度都是_INITIAL_INDEX_SIZE。通过以下代码可见其值为16。_data数组存放的是键值对,那最多的话只能存放8个键值对了。也就是说LinkedHashMap初始容量其实是8。
abstract class _HashBase implements _HashVMBase {
...
static const int _INITIAL_INDEX_BITS = 3;
static const int _INITIAL_INDEX_SIZE = 1 << (_INITIAL_INDEX_BITS + 1);
}
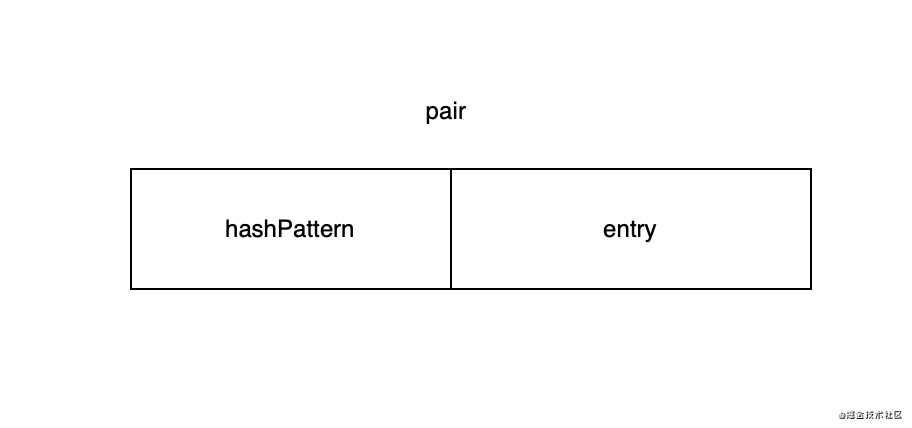
LinkedHashMap底层其实是用线性探测法实现的。数组_index里保存的是叫pair的一个整数。之所以叫pair是因为它是由高位和低位两部分组成的,高位叫hashPattern, 低位叫entry。entry指向_data数组对应的键值对。从hashcode到真正键值对的查找过程的关键点其实就是这个entry。
同时pair也用来表示_index数组对应位置的状态。0(_UNUSED_PAIR)表示当前未使用,1(_DELETED_PAIR)表示当前位置处于删除状态:
abstract class _HashBase implements _HashVMBase {
...
static const int _UNUSED_PAIR = 0;
static const int _DELETED_PAIR = 1;
...
}
查找操作
V? operator [](Object? key) {
var v = _getValueOrData(key);
return identical(_data, v) ? null : internal.unsafeCast<V>(v);
}
查找最终会调用到_getValueOrData
Object? _getValueOrData(Object? key) {
final int size = _index.length;
final int sizeMask = size - 1;
final int maxEntries = size >> 1;
final int fullHash = _hashCode(key);
final int hashPattern = _HashBase._hashPattern(fullHash, _hashMask, size);
int i = _HashBase._firstProbe(fullHash, sizeMask);
int pair = _index[i];
while (pair != _HashBase._UNUSED_PAIR) {
if (pair != _HashBase._DELETED_PAIR) {
final int entry = hashPattern ^ pair;
if (entry < maxEntries) {
final int d = entry << 1;
if (_equals(key, _data[d])) {
return _data[d + 1];
}
}
}
i = _HashBase._nextProbe(i, sizeMask);
pair = _index[i];
}
return _data;
}
从这个函数中我们就能了解到线性探测的过程了。首先通过调用_HashBase._firstProbe()来拿到首个地址:
static int _firstProbe(int fullHash, int sizeMask) {
final int i = fullHash & sizeMask;
// Light, fast shuffle to mitigate bad hashCode (e.g., sequential).
return ((i << 1) + i) & sizeMask;
}
首次探测就是把hashcode和数组长度取模,注意还有一步,是把i乘以3以后再取模。从注释上看是为了使hashcode分布更均匀一些。大家可以思考一下其中的原因。
首次探测以后拿到pair,如果这个pair是未占用状态说明键值对不存在,按约定直接返回_data数组。如果是删除状态就接着做二次探测。如果是正常占用状态,就将pair和hashPattern做异或,从前面的图可知,这样就得到了entry。检查entry未越界的话,将其乘以2就是key在_data数组中的位置了,最后判断key相等,则返回_data的下一个元素,即value。
二次探测会调用_HashBase._nextProbe()
static int _nextProbe(int i, int sizeMask) => (i + 1) & sizeMask;
源码可见就是挨个去试下一个地址。
赋值操作
void operator []=(K key, V value) {
final int size = _index.length;
final int fullHash = _hashCode(key);
final int hashPattern = _HashBase._hashPattern(fullHash, _hashMask, size);
final int d = _findValueOrInsertPoint(key, fullHash, hashPattern, size);
if (d > 0) {
_data[d] = value;
} else {
final int i = -d;
_insert(key, value, hashPattern, i);
}
}
赋值时会先调用_findValueOrInsertPoint()来寻找已存在的键值对,其逻辑和函数_getValueOrData类似。键值对存在则直接返回对应value在_data中的位置,然后直接赋值就完了。如果不存在的话,就会返回一个负数,这个负数其实就是经过探测以后在_index数组中的可用位置。有了这个位置就可以调用_insert()来做插入操作了。
void _insert(K key, V value, int hashPattern, int i) {
if (_usedData == _data.length) {
_rehash();
this[key] = value;
} else {
assert(1 <= hashPattern && hashPattern < (1 << 32));
final int index = _usedData >> 1;
assert((index & hashPattern) == 0);
_index[i] = hashPattern | index;
_data[_usedData++] = key;
_data[_usedData++] = value;
}
}
插入之前先判断_data数组是否已占满。满了的话就要调用_rehash()做扩容了。未满的话就是简单的赋值操作了,将_data的下一个空位除以2以后和hashPattern做或运算,然后放入_index数组,再将key和value紧挨着放入_data数组。
扩容操作
void _rehash() {
if ((_deletedKeys << 2) > _usedData) {
_init(_index.length, _hashMask, _data, _usedData);
} else {
_init(_index.length << 1, _hashMask >> 1, _data, _usedData);
}
}
扩容之前先看数组中是否有超过一半的元素是处于删除状态,是的话扩容长度和原数组长度是一样的,否则新数组长度为原长的2倍。为什么这么操作,我们接着看_ininit()函数。
void _init(int size, int hashMask, List? oldData, int oldUsed) {
_index = new Uint32List(size);
_hashMask = hashMask;
_data = new List.filled(size, null);
_usedData = 0;
_deletedKeys = 0;
if (oldData != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < oldUsed; i += 2) {
var key = oldData[i];
if (!_HashBase._isDeleted(oldData, key)) {
this[key] = oldData[i + 1];
}
}
}
}
这里会按新的长度新建_index和_data数组。接着会做拷贝,如果是已删除状态的键值对是不会被拷贝的。所以和原数组一样长的"扩容"过程其实就是把被删除的元素真正删除了。
删除操作
V? remove(Object? key) {
final int size = _index.length;
final int sizeMask = size - 1;
final int maxEntries = size >> 1;
final int fullHash = _hashCode(key);
final int hashPattern = _HashBase._hashPattern(fullHash, _hashMask, size);
int i = _HashBase._firstProbe(fullHash, sizeMask);
int pair = _index[i];
while (pair != _HashBase._UNUSED_PAIR) {
if (pair != _HashBase._DELETED_PAIR) {
final int entry = hashPattern ^ pair;
if (entry < maxEntries) {
final int d = entry << 1;
if (_equals(key, _data[d])) {
_index[i] = _HashBase._DELETED_PAIR;
_HashBase._setDeletedAt(_data, d);
V value = _data[d + 1];
_HashBase._setDeletedAt(_data, d + 1);
++_deletedKeys;
return value;
}
}
}
i = _HashBase._nextProbe(i, sizeMask);
pair = _index[i];
}
return null;
}
删除过程首先也是做线性探测。找到了的话就做两件事,首先将_index数组对应位置置为_HashBase._DELETED_PAIR。然后将_data数组对应位置置为_data。
遍历
我们知道,LinkedHashMap则会保证遍历顺序和插入顺序相同。那通过上面介绍我们了解到插入的键值对都按顺序保存在_data数组中了。那么遍历的时候只需要遍历_data数组自然就能按插入顺序遍历LinkedHashMap了。
bool moveNext() {
if (_table._isModifiedSince(_data, _checkSum)) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationError(_table);
}
do {
_offset += _step;
} while (_offset < _len && _HashBase._isDeleted(_data, _data[_offset]));
if (_offset < _len) {
_current = internal.unsafeCast<E>(_data[_offset]);
return true;
} else {
_current = null;
return false;
}
}
如果是删除状态的键值对是会被跳过的。
小结
Dart的LinkedHashMap实现和jdk的是不同的,大家初次接触的话可能会比较陌生,需要仔细研究一下源码来看看具体实现,也是能学到一些东西的。
Part5总结
总体来说Dart的HashMap和LinkedHashMap实现还是比较简单的,并没有像jdk一样做一些细致的优化工作,这可能有待于Dart/Flutter的进一步发展吧。但我们也能看到不论是何种语言,一些基础的数据结构其设计思想都是相通的。掌握源码背后的设计思路就可以举一反三,不论是哪种新语言,新架构都可以快速掌握,最后,我把最开始的那几个问题连带粗浅的答案一起放在下面:
HashMap和LinkedHashMap有什么区别?
从API角度,HashMap遍历的时候不保证和插入顺序相同,而LinkedHashMap则会保证遍历顺序和插入顺序相同。
这个表达式final map = Map();得到的map是上面两种Map的那一种?
是LinkedHashMap。
HashMap底层的数据结构是什么样的?
数组+链表。
HashMap默认大小是多大?
8。
HashMap如何处理hash冲突?
链地址法。
HashMap何时扩容?如何扩容?
当键值对数量超过数组长度的75%时会发生扩容,而不是数组被占用超过75%的时候会发生扩容。扩容后的新数组长度将会是原数组长度的2倍,扩容过程采用头插法。
LinkedHashMap底层的数据结构是什么样的?
两个数组:_index和_data, _index数组以哈希码为下标记录对应键值对在_data数组中的位置。_data数组按插入顺序依次保存key和value。
LinkedHashMap如何处理hash冲突?
线性探测法。
LinkedHashMap何时扩容?如何扩容?
_data数组满时扩容,扩容之前先看数组中是否有超过一半的元素是处于删除状态,是的话扩容长度和原数组长度是一样的,否则新数组长度为原长的2倍。
系统:全书分为基础、进阶、拓展和实战四大篇,体系化讲解Java高并发编程技术
深入:深度剖析Java并发包、Dubbo等框架源码设计,领略大咖的代码设计艺术
实战:分布式系统设计理论与项目实战相结合,懂理论,能落地,手把手教你吃透高并发项目核心技术
资源:附赠全书案例源代码,知其然更知其所以然,快速上手不用愁
免费获取方法:
6月9日前,公众号后台回复 【 并发学习 】即可参与活动!!!
▲扫码回复「并发学习」抽奖品
没加小编微信的建议先加一下小编微信,方便中奖之后安排发货和领