Redis(八):zset/zadd/zrange/zrembyscore 命令源码解析
前面几篇文章,我们完全领略了redis的string,hash,list,set数据类型的实现方法,相信对redis已经不再神秘。
本篇我们将介绍redis的最后一种数据类型: zset 的相关实现。
本篇过后,我们对redis的各种基础功能,应该不会再有疑惑。有可能的话,我们后续将会对redis的高级功能的实现做解析。(如复制、哨兵模式、集群模式)
回归本篇主题,zset。zset 又称有序集合(sorted set),即是序版本的set。经过上篇的介绍,大家可以看到,redis的读取功能相当有限,许多是基于随机数的方式进行读取,其原因就是set是无序的。当set有序之后,查询能力就会得到极大的提升。
可以根据下标进行定位元素;
可以范围查询元素; 这是有序带来的好处。
那么,我们不妨先思考一下,如何实现有序?两种方法:1. 根据添加顺序定义,1、2、3... ; 2. 自定义排序值; 第1种方法实现简单,添加时复杂度小,但是功能受限;第2种方法相对自由,对于每次插入都可能涉及重排序问题,但是查询相对稳定,可以不必完全受限于系统实现;
同样,我们以功能列表,到数据结构,再功能实现的思路,来解析redis的zset有序集合的实现方式吧。
零、redis zset相关操作方法
zset: Redis 有序集合是string类型元素的集合,且不允许重复的成员。每个元素都会关联一个double类型的分数,通过分数来为集合中的成员进行从小到大的排序。
使用场景如: 保存任务队列,该队列由后台定时扫描; 排行榜;
从官方手册上查到相关使用方法如下:
1> ZADD key score1 member1 [score2 member2]
功能: 向有序集合添加一个或多个成员,或者更新已存在成员的分数
返回值: 添加成功的元素个数(已存在的添加不成功)2> ZCARD key
功能: 获取有序集合的成员数
返回值: 元素个数或03> ZCOUNT key min max
功能: 计算在有序集合中指定区间分数的成员数
返回值: 区间内的元素个数4> ZINCRBY key increment member
功能: 有序集合中对指定成员的分数加上增量 increment
返回值: member增加后的分数5> ZINTERSTORE destination numkeys key [key ...]
功能: 计算给定的一个或多个有序集的交集并将结果集存储在新的有序集合 key 中
返回值: 交集元素个数6> ZLEXCOUNT key min max
功能: 在有序集合中计算指定字典区间内成员数量
返回值: 区间内的元素个数7> ZRANGE key start stop [WITHSCORES]
功能: 通过索引区间返回有序集合指定区间内的成员
返回值: 区间内元素列表8> ZRANGEBYLEX key min max [LIMIT offset count]
功能: 通过字典区间返回有序集合的成员
返回值: 区间内元素列表9> ZRANGEBYSCORE key min max [WITHSCORES] [LIMIT]
功能: 通过分数返回有序集合指定区间内的成员
返回值: 区间内元素列表10> ZRANK key member
功能: 返回有序集合中指定成员的索引
返回值: member的排名或者 nil11> ZREM key member [member ...]
功能: 移除有序集合中的一个或多个成员
返回值: 成功移除的元素个数12> ZREMRANGEBYLEX key min max
功能: 移除有序集合中给定的字典区间的所有成员
返回值: 成功移除的元素个数13> ZREMRANGEBYRANK key start stop
功能: 移除有序集合中给定的排名区间的所有成员
返回值: 成功移除的元素个数14> ZREMRANGEBYSCORE key min max
功能: 移除有序集合中给定的分数区间的所有成员
返回值: 成功移除的元素个数15> ZREVRANGE key start stop [WITHSCORES]
功能: 返回有序集中指定区间内的成员,通过索引,分数从高到低
返回值: 区间内元素列表及分数16> ZREVRANGEBYSCORE key max min [WITHSCORES]
功能: 返回有序集中指定分数区间内的成员,分数从高到低排序
返回值: 区间内元素列表及分数17> ZREVRANK key member
功能: 返回有序集合中指定成员的排名,有序集成员按分数值递减(从大到小)排序
返回值: member排名或者 nil18> ZSCORE key member
功能: 返回有序集中,成员的分数值
返回值: member分数19> ZUNIONSTORE destination numkeys key [key ...]
功能: 计算给定的一个或多个有序集的并集,并存储在新的 key 中
返回值: 存储到新key的元素个数20> ZSCAN key cursor [MATCH pattern] [COUNT count]
功能: 迭代有序集合中的元素(包括元素成员和元素分值)
返回值: 元素列表21> ZPOPMAX/ZPOPMIN/BZPOPMAX/BZPOPMIN
一、zset 相关数据结构
zset 的实现,使用了 ziplist, zskiplist 和 dict 进行实现。
/* ZSETs use a specialized version of Skiplists */typedef struct zskiplistNode {sds ele;double score;struct zskiplistNode *backward;struct zskiplistLevel {struct zskiplistNode *forward;unsigned int span;} level[];} zskiplistNode;// 跳跃链表typedef struct zskiplist {struct zskiplistNode *header, *tail;unsigned long length;int level;} zskiplist;// zset 主数据结构,dict + zskiplisttypedef struct zset {dict *dict;zskiplist *zsl;} zset;// zset 在合适场景下,将先使用 ziplist 存储数据typedef struct zlentry {unsigned int prevrawlensize, prevrawlen;unsigned int lensize, len;unsigned int headersize;unsigned char encoding;unsigned char *p;} zlentry;
二、zadd 添加成员操作
从添加实现中,我们可以完整领略数据结构的运用。
// 用法: ZADD key score1 member1 [score2 member2]// t_zset.cvoid zaddCommand(client *c) {// zadd 的多个参数变形, 使用 flags 进行区分复用zaddGenericCommand(c,ZADD_NONE);}void zaddGenericCommand(client *c, int flags) {static char *nanerr = "resulting score is not a number (NaN)";robj *key = c->argv[1];robj *zobj;sds ele;double score = 0, *scores = NULL, curscore = 0.0;int j, elements;int scoreidx = 0;/* The following vars are used in order to track what the command actually* did during the execution, to reply to the client and to trigger the* notification of keyspace change. */int added = 0; /* Number of new elements added. */int updated = 0; /* Number of elements with updated score. */int processed = 0; /* Number of elements processed, may remain zero withoptions like XX. *//* Parse options. At the end 'scoreidx' is set to the argument position* of the score of the first score-element pair. */// 从第三位置开始尝试解析特殊标识(用法规范)// 按位与到 flags 中scoreidx = 2;while(scoreidx < c->argc) {char *opt = c->argv[scoreidx]->ptr;// NX: 不更新已存在的元素,只做添加操作if (!strcasecmp(opt,"nx")) flags |= ZADD_NX;// XX: 只做更新操作,不做添加操作else if (!strcasecmp(opt,"xx")) flags |= ZADD_XX;// CH: 将返回值从添加的新元素数修改为已更改元素的总数。更改的元素是第添加的新元素以及已为其更新分数的现有元素。因此,命令行中指定的具有与过去相同分数的元素将不计算在内。注意:通常,ZADD的返回值仅计算添加的新元素的数量。else if (!strcasecmp(opt,"ch")) flags |= ZADD_CH;// INCR: 使用指定元素增加指定分数, 与 ZINCRBY 类似,此场景下,只允许操作一个元素else if (!strcasecmp(opt,"incr")) flags |= ZADD_INCR;else break;scoreidx++;}/* Turn options into simple to check vars. */int incr = (flags & ZADD_INCR) != 0;int nx = (flags & ZADD_NX) != 0;int xx = (flags & ZADD_XX) != 0;int ch = (flags & ZADD_CH) != 0;/* After the options, we expect to have an even number of args, since* we expect any number of score-element pairs. */// 把特殊标识去除后,剩下的参数列表应该2n数,即 score-element 一一配对的,否则语法错误elements = c->argc-scoreidx;if (elements % 2) {addReply(c,shared.syntaxerr);return;}elements /= 2; /* Now this holds the number of score-element pairs. *//* Check for incompatible options. */// 互斥项if (nx && xx) {addReplyError(c,"XX and NX options at the same time are not compatible");return;}// 语法检查,INCR 只能针对1个元素操作if (incr && elements > 1) {addReplyError(c,"INCR option supports a single increment-element pair");return;}/* Start parsing all the scores, we need to emit any syntax error* before executing additions to the sorted set, as the command should* either execute fully or nothing at all. */// 解析所有的 score 值为double类型,赋值到 scores 中scores = zmalloc(sizeof(double)*elements);for (j = 0; j < elements; j++) {if (getDoubleFromObjectOrReply(c,c->argv[scoreidx+j*2],&scores[j],NULL)!= C_OK) goto cleanup;}/* Lookup the key and create the sorted set if does not exist. */// 语法检查zobj = lookupKeyWrite(c->db,key);if (zobj == NULL) {if (xx) goto reply_to_client; /* No key + XX option: nothing to do. */// 创建原始key对象// 默认 zset_max_ziplist_entries=OBJ_ZSET_MAX_ZIPLIST_ENTRIES: 128// 默认 zset_max_ziplist_value=OBJ_ZSET_MAX_ZIPLIST_VALUE: 64// 所以此处默认主要是检查 第1个member的长度是大于 64if (server.zset_max_ziplist_entries == 0 ||server.zset_max_ziplist_value < sdslen(c->argv[scoreidx+1]->ptr)){// 2. 通用情况使用 dict+quicklist 型的zsetzobj = createZsetObject();} else {// 1. 元素比较小的情况下创建 ziplist 型的 zsetzobj = createZsetZiplistObject();}// 将对象添加到db中,后续所有操作针对 zobj 操作即是对db的操作 (引用传递)dbAdd(c->db,key,zobj);} else {if (zobj->type != OBJ_ZSET) {addReply(c,shared.wrongtypeerr);goto cleanup;}}// 一个个元素循环添加for (j = 0; j < elements; j++) {score = scores[j];ele = c->argv[scoreidx+1+j*2]->ptr;// 分当前zobj的编码不同进行添加 (ziplist, skiplist)// 3. ZIPLIST 编码下的zset添加操作if (zobj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) {unsigned char *eptr;// 3.1. 查找是否存在要添加的元素 (确定添加或更新)if ((eptr = zzlFind(zobj->ptr,ele,&curscore)) != NULL) {if (nx) continue;if (incr) {score += curscore;if (isnan(score)) {addReplyError(c,nanerr);goto cleanup;}}/* Remove and re-insert when score changed. */if (score != curscore) {// 3.2. 元素更新操作,先删再插入zobj->ptr = zzlDelete(zobj->ptr,eptr);zobj->ptr = zzlInsert(zobj->ptr,ele,score);server.dirty++;updated++;}processed++;} else if (!xx) {/* Optimize: check if the element is too large or the list* becomes too long *before* executing zzlInsert. */zobj->ptr = zzlInsert(zobj->ptr,ele,score);// 5. 超过一条件后,做 ziplist->skiplist 转换// 默认 元素个数>128, 当前元素>64// 这两个判断不会重复吗??两个原因: 1. 转换函数内部会重新判定; 2. 下一次循环时不会再走当前逻辑;if (zzlLength(zobj->ptr) > server.zset_max_ziplist_entries)zsetConvert(zobj,OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST);if (sdslen(ele) > server.zset_max_ziplist_value)zsetConvert(zobj,OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST);server.dirty++;added++;processed++;}}// 4. skiplist 下的zset元素添加else if (zobj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST) {zset *zs = zobj->ptr;zskiplistNode *znode;dictEntry *de;// 判断ele是否已存在,使用hash查找,快速de = dictFind(zs->dict,ele);if (de != NULL) {if (nx) continue;curscore = *(double*)dictGetVal(de);if (incr) {score += curscore;if (isnan(score)) {addReplyError(c,nanerr);/* Don't need to check if the sorted set is empty* because we know it has at least one element. */goto cleanup;}}/* Remove and re-insert when score changes. */// 先删再插入 skiplistif (score != curscore) {zskiplistNode *node;serverAssert(zslDelete(zs->zsl,curscore,ele,&node));znode = zslInsert(zs->zsl,score,node->ele);/* We reused the node->ele SDS string, free the node now* since zslInsert created a new one. */node->ele = NULL;zslFreeNode(node);/* Note that we did not removed the original element from* the hash table representing the sorted set, so we just* update the score. */// 更新dict中的分数引用dictGetVal(de) = &znode->score; /* Update score ptr. */server.dirty++;updated++;}processed++;} else if (!xx) {ele = sdsdup(ele);znode = zslInsert(zs->zsl,score,ele);// 添加skiplist的同时,也往 dict 中添加一份数据,因为hash的查找永远是最快的serverAssert(dictAdd(zs->dict,ele,&znode->score) == DICT_OK);server.dirty++;added++;processed++;}} else {serverPanic("Unknown sorted set encoding");}}reply_to_client:if (incr) { /* ZINCRBY or INCR option. */if (processed)addReplyDouble(c,score);elseaddReply(c,shared.nullbulk);} else { /* ZADD. */addReplyLongLong(c,ch ? added+updated : added);}cleanup:zfree(scores);if (added || updated) {signalModifiedKey(c->db,key);notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_ZSET,incr ? "zincr" : "zadd", key, c->db->id);}}// 1. 元素比较小的情况下创建 ziplist 型的 zset// object.c, 创建ziplist 的zsetrobj *createZsetZiplistObject(void) {unsigned char *zl = ziplistNew();robj *o = createObject(OBJ_ZSET,zl);o->encoding = OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST;return o;}// 2. 创建通用的 zset 实例// object.crobj *createZsetObject(void) {zset *zs = zmalloc(sizeof(*zs));robj *o;// zsetDictType 稍有不同zs->dict = dictCreate(&zsetDictType,NULL);// 首次遇到 skiplist, 咱去瞅瞅是如何创建的zs->zsl = zslCreate();o = createObject(OBJ_ZSET,zs);o->encoding = OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST;return o;}// server.c, zset创建时使用的dict类型,与hash有不同/* Sorted sets hash (note: a skiplist is used in addition to the hash table) */dictType zsetDictType = {dictSdsHash, /* hash function */NULL, /* key dup */NULL, /* val dup */dictSdsKeyCompare, /* key compare */NULL, /* Note: SDS string shared & freed by skiplist */NULL /* val destructor */};// 创建 skiplist 对象/* Create a new skiplist. */zskiplist *zslCreate(void) {int j;zskiplist *zsl;zsl = zmalloc(sizeof(*zsl));zsl->level = 1;zsl->length = 0;// 创建header节点,ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL 32zsl->header = zslCreateNode(ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL,0,NULL);// 初始化headerfor (j = 0; j < ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL; j++) {zsl->header->level[j].forward = NULL;zsl->header->level[j].span = 0;}zsl->header->backward = NULL;zsl->tail = NULL;return zsl;}/* Create a skiplist node with the specified number of levels.* The SDS string 'ele' is referenced by the node after the call. */zskiplistNode *zslCreateNode(int level, double score, sds ele) {zskiplistNode *zn =zmalloc(sizeof(*zn)+level*sizeof(struct zskiplistLevel));zn->score = score;zn->ele = ele;return zn;}// 3. ZIPLIST 编码下的zset添加操作// 3.1. 查找是否存在要添加的元素 (确定添加或更新)// t_zset.c, 查找指定eleunsigned char *zzlFind(unsigned char *zl, sds ele, double *score) {unsigned char *eptr = ziplistIndex(zl,0), *sptr;// 遍历所有ziplist// 可见,此时的ziplist并没有表现出有序啊while (eptr != NULL) {// eptr 相当于是 key// sptr 相当于scoresptr = ziplistNext(zl,eptr);serverAssert(sptr != NULL);if (ziplistCompare(eptr,(unsigned char*)ele,sdslen(ele))) {/* Matching element, pull out score. */// 找到相应的 key 后,解析下一值,即 scoreif (score != NULL) *score = zzlGetScore(sptr);return eptr;}/* Move to next element. */// 移动两次对象,才会到下一元素(因为存储是 key-score 相邻存储)eptr = ziplistNext(zl,sptr);}return NULL;}// t_zset.c, 获取元素的scoredouble zzlGetScore(unsigned char *sptr) {unsigned char *vstr;unsigned int vlen;long long vlong;char buf[128];double score;serverAssert(sptr != NULL);serverAssert(ziplistGet(sptr,&vstr,&vlen,&vlong));// 带小数点不带小数点if (vstr) {memcpy(buf,vstr,vlen);buf[vlen] = '\0';// 做类型转换score = strtod(buf,NULL);} else {score = vlong;}return score;}// 3.2. 元素更新操作,先删再插入// t_zset.c/* Delete (element,score) pair from ziplist. Use local copy of eptr because we* don't want to modify the one given as argument. */unsigned char *zzlDelete(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char *eptr) {unsigned char *p = eptr;/* TODO: add function to ziplist API to delete N elements from offset. */zl = ziplistDelete(zl,&p);zl = ziplistDelete(zl,&p);return zl;}// 添加 ele-score 到 ziplist 中/* Insert (element,score) pair in ziplist. This function assumes the element is* not yet present in the list. */unsigned char *zzlInsert(unsigned char *zl, sds ele, double score) {unsigned char *eptr = ziplistIndex(zl,0), *sptr;double s;// 在上面查找时,我们看到ziplist也是遍历,以为是无序的ziplist// 然而实际上,插入时是维护了顺序的哟while (eptr != NULL) {sptr = ziplistNext(zl,eptr);serverAssert(sptr != NULL);s = zzlGetScore(sptr);// 找到第一个比score大的位置,在其前面插入 ele-scoreif (s > score) {/* First element with score larger than score for element to be* inserted. This means we should take its spot in the list to* maintain ordering. */zl = zzlInsertAt(zl,eptr,ele,score);break;} else if (s == score) {/* Ensure lexicographical ordering for elements. */// 当分数相同时,按字典顺序排列if (zzlCompareElements(eptr,(unsigned char*)ele,sdslen(ele)) > 0) {zl = zzlInsertAt(zl,eptr,ele,score);break;}}/* Move to next element. */eptr = ziplistNext(zl,sptr);}/* Push on tail of list when it was not yet inserted. */// 以上遍历完成都没有找到相应位置,说明当前score是最大值,将其插入尾部if (eptr == NULL)zl = zzlInsertAt(zl,NULL,ele,score);return zl;}// 在eptr的前面插入 ele-scoreunsigned char *zzlInsertAt(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char *eptr, sds ele, double score) {unsigned char *sptr;char scorebuf[128];int scorelen;size_t offset;scorelen = d2string(scorebuf,sizeof(scorebuf),score);if (eptr == NULL) {// 直接插入到尾部zl = ziplistPush(zl,(unsigned char*)ele,sdslen(ele),ZIPLIST_TAIL);zl = ziplistPush(zl,(unsigned char*)scorebuf,scorelen,ZIPLIST_TAIL);} else {/* Keep offset relative to zl, as it might be re-allocated. */offset = eptr-zl;// 直接在 eptr 位置添加 ele, 其他元素后移zl = ziplistInsert(zl,eptr,(unsigned char*)ele,sdslen(ele));eptr = zl+offset;/* Insert score after the element. */// 此时的 eptr 已经插入ele之后的位置,后移一位后,就可以找到 score 的存储位置serverAssert((sptr = ziplistNext(zl,eptr)) != NULL);zl = ziplistInsert(zl,sptr,(unsigned char*)scorebuf,scorelen);}return zl;}// 4. skiplist 下的zset元素添加// 4.1. 添加元素// t_zset.c, 添加 ele-score 到 skiplist 中/* Insert a new node in the skiplist. Assumes the element does not already* exist (up to the caller to enforce that). The skiplist takes ownership* of the passed SDS string 'ele'. */zskiplistNode *zslInsert(zskiplist *zsl, double score, sds ele) {// ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL 32zskiplistNode *update[ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL], *x;unsigned int rank[ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL];int i, level;serverAssert(!isnan(score));x = zsl->header;// 初始 zsl->level = 1// 从header的最高层开始遍历for (i = zsl->level-1; i >= 0; i--) {/* store rank that is crossed to reach the insert position */// 计算出每层可以插入的位置rank[i] = i == (zsl->level-1) ? 0 : rank[i+1];// 当前level的score小于需要添加的元素时,往前推进skiplistwhile (x->level[i].forward &&(x->level[i].forward->score < score ||(x->level[i].forward->score == score &&sdscmp(x->level[i].forward->ele,ele) < 0))){rank[i] += x->level[i].span;x = x->level[i].forward;}update[i] = x;}/* we assume the element is not already inside, since we allow duplicated* scores, reinserting the same element should never happen since the* caller of zslInsert() should test in the hash table if the element is* already inside or not. */// 得到一随机的level, 决定要写的节点数// 如果当前的level过小,则变更level, 重新初始化大的levellevel = zslRandomLevel();if (level > zsl->level) {for (i = zsl->level; i < level; i++) {rank[i] = 0;update[i] = zsl->header;update[i]->level[i].span = zsl->length;}zsl->level = level;}// 构建新的 skiplist 节点,为每一层节点添加同样的数据x = zslCreateNode(level,score,ele);for (i = 0; i < level; i++) {// 让i层的节点与x关联x->level[i].forward = update[i]->level[i].forward;update[i]->level[i].forward = x;/* update span covered by update[i] as x is inserted here */x->level[i].span = update[i]->level[i].span - (rank[0] - rank[i]);update[i]->level[i].span = (rank[0] - rank[i]) + 1;}/* increment span for untouched levels */// 如果当前level较小,则存在有的level未赋值情况,需要主动+1for (i = level; i < zsl->level; i++) {update[i]->level[i].span++;}// 关联好header后,设置backward指针x->backward = (update[0] == zsl->header) ? NULL : update[0];if (x->level[0].forward)x->level[0].forward->backward = x;else// 同有后继节点,说明是尾节点,赋值tailzsl->tail = x;zsl->length++;return x;}
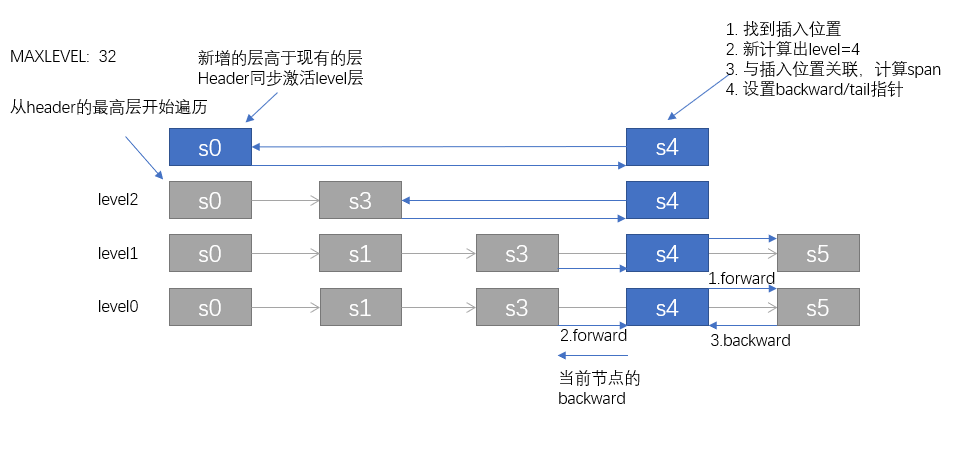
ziplist添加没啥好说的,skiplist可以稍微提提,大体步骤为四步:
1. 找位置, 从最高层开始, 判断是否后继节点小,如果小则直接在本层迭代,否则转到下一层迭代; (每一层都要迭代至相应的位置)
2. 计算得到一新的随机level,用于决定当前节点的层级;
3. 依次对每一层与原跳表做关联;
4. 设置backward指针;(双向链表)
相对说,skiplist 还是有点抽象,我们画个图来描述下上面的操作:
// 补充,我们看一下随机level的计算算法// t_zset.c/* Returns a random level for the new skiplist node we are going to create.* The return value of this function is between 1 and ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL* (both inclusive), with a powerlaw-alike distribution where higher* levels are less likely to be returned. */int zslRandomLevel(void) {int level = 1;// n次随机值得到 level, ZSKIPLIST_P:0.25// 按随机概率,应该是有1/4的命中概率(如果不是呢??)while ((random()&0xFFFF) < (ZSKIPLIST_P * 0xFFFF))level += 1;return (level<ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL) ? level : ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL;}
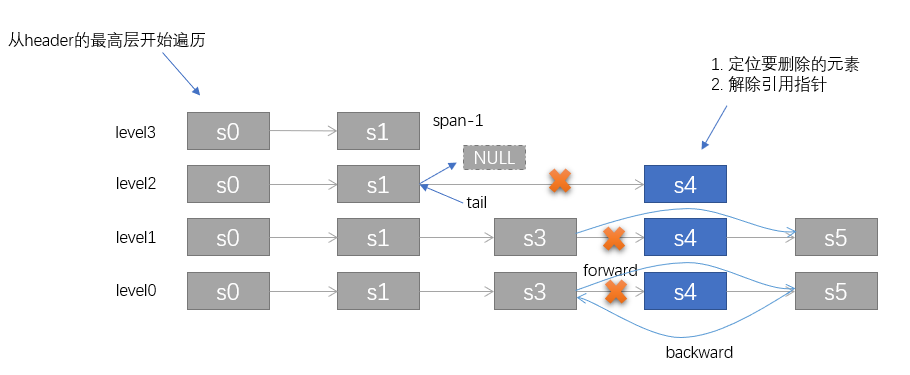
先看插入过程的目的,主要是为了先理解 skiplist 的构造过程。而在zset的更新过程,是先删除原节点,再进行插入的这么个过程。所以咱们还是有必要再来看看 skiplist 的删除节点过程。
// t_zset.c, 删除skiplist的指定节点/* Delete an element with matching score/element from the skiplist.* The function returns 1 if the node was found and deleted, otherwise* 0 is returned.** If 'node' is NULL the deleted node is freed by zslFreeNode(), otherwise* it is not freed (but just unlinked) and *node is set to the node pointer,* so that it is possible for the caller to reuse the node (including the* referenced SDS string at node->ele). */int zslDelete(zskiplist *zsl, double score, sds ele, zskiplistNode **node) {zskiplistNode *update[ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL], *x;int i;x = zsl->header;// 与添加时查找对应位置一样,先进行遍历,找到最每个层级最接近 node 的位置for (i = zsl->level-1; i >= 0; i--) {while (x->level[i].forward &&(x->level[i].forward->score < score ||(x->level[i].forward->score == score &&sdscmp(x->level[i].forward->ele,ele) < 0))){x = x->level[i].forward;}update[i] = x;}/* We may have multiple elements with the same score, what we need* is to find the element with both the right score and object. */// 进行精确比对,相同才进行删除x = x->level[0].forward;if (x && score == x->score && sdscmp(x->ele,ele) == 0) {// 执行删除动作zslDeleteNode(zsl, x, update);if (!node)zslFreeNode(x);else*node = x;return 1;}return 0; /* not found */}// 删除 x对应的节点// update 是node的每一层级对应的前驱节点/* Internal function used by zslDelete, zslDeleteByScore and zslDeleteByRank */void zslDeleteNode(zskiplist *zsl, zskiplistNode *x, zskiplistNode **update) {int i;for (i = 0; i < zsl->level; i++) {if (update[i]->level[i].forward == x) {update[i]->level[i].span += x->level[i].span - 1;update[i]->level[i].forward = x->level[i].forward;} else {// 不相等说明该层不存在指向 x 的引用update[i]->level[i].span -= 1;}}// 更新第0层尾节点指针if (x->level[0].forward) {x->level[0].forward->backward = x->backward;} else {zsl->tail = x->backward;}// 降低 skiplist 的层级,直到第一个非空的节点为止while(zsl->level > 1 && zsl->header->level[zsl->level-1].forward == NULL)zsl->level--;zsl->length--;}
skiplist 删除过程的示意图如下:
最后,我们再来看另一种情况,即zset发生编码转换时,是如何做的。即如何从 ziplist 转换到 skiplist 中呢?
// t_zset.c, 编码类型转换void zsetConvert(robj *zobj, int encoding) {zset *zs;zskiplistNode *node, *next;sds ele;double score;// 编码相同,直接返回if (zobj->encoding == encoding) return;// ziplist -> skiplist 转换if (zobj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) {unsigned char *zl = zobj->ptr;unsigned char *eptr, *sptr;unsigned char *vstr;unsigned int vlen;long long vlong;if (encoding != OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST)serverPanic("Unknown target encoding");zs = zmalloc(sizeof(*zs));zs->dict = dictCreate(&zsetDictType,NULL);zs->zsl = zslCreate();eptr = ziplistIndex(zl,0);serverAssertWithInfo(NULL,zobj,eptr != NULL);sptr = ziplistNext(zl,eptr);serverAssertWithInfo(NULL,zobj,sptr != NULL);while (eptr != NULL) {score = zzlGetScore(sptr);serverAssertWithInfo(NULL,zobj,ziplistGet(eptr,&vstr,&vlen,&vlong));if (vstr == NULL)ele = sdsfromlonglong(vlong);elseele = sdsnewlen((char*)vstr,vlen);// 依次插入 skiplist 和 dict 中即可node = zslInsert(zs->zsl,score,ele);serverAssert(dictAdd(zs->dict,ele,&node->score) == DICT_OK);// zzlNext 封装了同时迭代 eptr 和 sptr 方法zzlNext(zl,&eptr,&sptr);}zfree(zobj->ptr);zobj->ptr = zs;zobj->encoding = OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST;}// skiplist -> ziplist 逆向转换else if (zobj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST) {unsigned char *zl = ziplistNew();if (encoding != OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST)serverPanic("Unknown target encoding");/* Approach similar to zslFree(), since we want to free the skiplist at* the same time as creating the ziplist. */zs = zobj->ptr;dictRelease(zs->dict);node = zs->zsl->header->level[0].forward;zfree(zs->zsl->header);zfree(zs->zsl);// 正向迭代转换while (node) {zl = zzlInsertAt(zl,NULL,node->ele,node->score);next = node->level[0].forward;zslFreeNode(node);node = next;}zfree(zs);zobj->ptr = zl;zobj->encoding = OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST;} else {serverPanic("Unknown sorted set encoding");}}// 基于ziplist, 同时迭代 ele-score/* Move to next entry based on the values in eptr and sptr. Both are set to* NULL when there is no next entry. */void zzlNext(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char **eptr, unsigned char **sptr) {unsigned char *_eptr, *_sptr;serverAssert(*eptr != NULL && *sptr != NULL);_eptr = ziplistNext(zl,*sptr);if (_eptr != NULL) {_sptr = ziplistNext(zl,_eptr);serverAssert(_sptr != NULL);} else {/* No next entry. */_sptr = NULL;}*eptr = _eptr;*sptr = _sptr;}
至此,整个添加过程结束。本身是不太复杂的,主要针对 ziplist 和 skiplist 的分别处理(注意有逆向编码)。但为了讲清整体关系,稍显杂乱。
三、zrange 范围查询
范围查询功能,redis提供了好几个,zrange/zrangebyscore/zrangebylex... 应该说查询方式都不太一样,不过我们也不必纠结这些,只管理会大概就行。就挑一个以 下标进行范围查询的实现讲解下就行。
// 用法: ZRANGE key start stop [WITHSCORES]// t_zset.cvoid zrangeCommand(client *c) {zrangeGenericCommand(c,0);}void zrangeGenericCommand(client *c, int reverse) {robj *key = c->argv[1];robj *zobj;int withscores = 0;long start;long end;int llen;int rangelen;if ((getLongFromObjectOrReply(c, c->argv[2], &start, NULL) != C_OK) ||(getLongFromObjectOrReply(c, c->argv[3], &end, NULL) != C_OK)) return;if (c->argc == 5 && !strcasecmp(c->argv[4]->ptr,"withscores")) {withscores = 1;} else if (c->argc >= 5) {addReply(c,shared.syntaxerr);return;}if ((zobj = lookupKeyReadOrReply(c,key,shared.emptymultibulk)) == NULL|| checkType(c,zobj,OBJ_ZSET)) return;/* Sanitize indexes. */// 小于0,则代表反向查询,但实际的输出顺序不是按此值运算的(提供了 reverse 方法)llen = zsetLength(zobj);if (start < 0) start = llen+start;if (end < 0) end = llen+end;if (start < 0) start = 0;/* Invariant: start >= 0, so this test will be true when end < 0.* The range is empty when start > end or start >= length. */if (start > end || start >= llen) {addReply(c,shared.emptymultibulk);return;}if (end >= llen) end = llen-1;rangelen = (end-start)+1;/* Return the result in form of a multi-bulk reply */addReplyMultiBulkLen(c, withscores ? (rangelen*2) : rangelen);// 同样,分 ZIPLIST 和 SKIPLIST 编码分别实现if (zobj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) {unsigned char *zl = zobj->ptr;unsigned char *eptr, *sptr;unsigned char *vstr;unsigned int vlen;long long vlong;// ziplist 以 ele-score 方式存储,所以步长是 2if (reverse)eptr = ziplistIndex(zl,-2-(2*start));elseeptr = ziplistIndex(zl,2*start);serverAssertWithInfo(c,zobj,eptr != NULL);sptr = ziplistNext(zl,eptr);// 依次迭代输出while (rangelen--) {serverAssertWithInfo(c,zobj,eptr != NULL && sptr != NULL);serverAssertWithInfo(c,zobj,ziplistGet(eptr,&vstr,&vlen,&vlong));if (vstr == NULL)addReplyBulkLongLong(c,vlong);elseaddReplyBulkCBuffer(c,vstr,vlen);if (withscores)addReplyDouble(c,zzlGetScore(sptr));// ziplist 提供正向迭代,返回迭代功能,其实就是 offset的加减问题if (reverse)zzlPrev(zl,&eptr,&sptr);elsezzlNext(zl,&eptr,&sptr);}} else if (zobj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST) {zset *zs = zobj->ptr;zskiplist *zsl = zs->zsl;zskiplistNode *ln;sds ele;/* Check if starting point is trivial, before doing log(N) lookup. */// 反向使用 tail 迭代,否则使用header迭代if (reverse) {ln = zsl->tail;if (start > 0)// 获取下标元素应该只是一个迭代循环问题,不过还是稍微细看一下skiplist实现ln = zslGetElementByRank(zsl,llen-start);} else {ln = zsl->header->level[0].forward;if (start > 0)ln = zslGetElementByRank(zsl,start+1);}while(rangelen--) {serverAssertWithInfo(c,zobj,ln != NULL);ele = ln->ele;addReplyBulkCBuffer(c,ele,sdslen(ele));if (withscores)addReplyDouble(c,ln->score);// 直接正向或反向迭代即可ln = reverse ? ln->backward : ln->level[0].forward;}} else {serverPanic("Unknown sorted set encoding");}}// 根据排名查找元素/* Finds an element by its rank. The rank argument needs to be 1-based. */zskiplistNode* zslGetElementByRank(zskiplist *zsl, unsigned long rank) {zskiplistNode *x;unsigned long traversed = 0;int i;x = zsl->header;// 好像没有相像中的简单哦// 请仔细品for (i = zsl->level-1; i >= 0; i--) {while (x->level[i].forward && (traversed + x->level[i].span) <= rank){// span 的作用??traversed += x->level[i].span;x = x->level[i].forward;}if (traversed == rank) {return x;}}return NULL;}
根据范围查找元素,整体是比较简单,迭代输出而已。只是 skiplist 的span维护,得好好想想。
四、zrembyscore 根据分数删除元素
zrembyscore, 首先这是个删除命令,其实它是根据分数查询,我们可以同时解析这两种情况。
// t_zset.c,void zremrangebyscoreCommand(client *c) {// 几个范围删除,都复用 zremrangeGenericCommand// ZRANGE_RANK/ZRANGE_SCORE/ZRANGE_LEXzremrangeGenericCommand(c,ZRANGE_SCORE);}void zremrangeGenericCommand(client *c, int rangetype) {robj *key = c->argv[1];robj *zobj;int keyremoved = 0;unsigned long deleted = 0;// score 存储使用另外的数据结构zrangespec range;zlexrangespec lexrange;long start, end, llen;/* Step 1: Parse the range. */// 解析参数,除了 rank 方式的查询,其他两个都使用 另外的专门数据结构存储参数if (rangetype == ZRANGE_RANK) {if ((getLongFromObjectOrReply(c,c->argv[2],&start,NULL) != C_OK) ||(getLongFromObjectOrReply(c,c->argv[3],&end,NULL) != C_OK))return;} else if (rangetype == ZRANGE_SCORE) {if (zslParseRange(c->argv[2],c->argv[3],&range) != C_OK) {addReplyError(c,"min or max is not a float");return;}} else if (rangetype == ZRANGE_LEX) {if (zslParseLexRange(c->argv[2],c->argv[3],&lexrange) != C_OK) {addReplyError(c,"min or max not valid string range item");return;}}/* Step 2: Lookup & range sanity checks if needed. */if ((zobj = lookupKeyWriteOrReply(c,key,shared.czero)) == NULL ||checkType(c,zobj,OBJ_ZSET)) goto cleanup;if (rangetype == ZRANGE_RANK) {/* Sanitize indexes. */llen = zsetLength(zobj);if (start < 0) start = llen+start;if (end < 0) end = llen+end;if (start < 0) start = 0;/* Invariant: start >= 0, so this test will be true when end < 0.* The range is empty when start > end or start >= length. */if (start > end || start >= llen) {addReply(c,shared.czero);goto cleanup;}if (end >= llen) end = llen-1;}/* Step 3: Perform the range deletion operation. */if (zobj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) {// 针对不同的删除类型,使用不同的删除方法// 所以,这段代码的复用体现在哪里呢???switch(rangetype) {case ZRANGE_RANK:zobj->ptr = zzlDeleteRangeByRank(zobj->ptr,start+1,end+1,&deleted);break;case ZRANGE_SCORE:// 3.1. 我们只看 score 的删除 --ziplistzobj->ptr = zzlDeleteRangeByScore(zobj->ptr,&range,&deleted);break;case ZRANGE_LEX:zobj->ptr = zzlDeleteRangeByLex(zobj->ptr,&lexrange,&deleted);break;}if (zzlLength(zobj->ptr) == 0) {dbDelete(c->db,key);keyremoved = 1;}} else if (zobj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST) {zset *zs = zobj->ptr;switch(rangetype) {case ZRANGE_RANK:deleted = zslDeleteRangeByRank(zs->zsl,start+1,end+1,zs->dict);break;case ZRANGE_SCORE:// 3.2. skiplist 的删除rangeByScore 方法deleted = zslDeleteRangeByScore(zs->zsl,&range,zs->dict);break;case ZRANGE_LEX:deleted = zslDeleteRangeByLex(zs->zsl,&lexrange,zs->dict);break;}if (htNeedsResize(zs->dict)) dictResize(zs->dict);if (dictSize(zs->dict) == 0) {dbDelete(c->db,key);keyremoved = 1;}} else {serverPanic("Unknown sorted set encoding");}/* Step 4: Notifications and reply. */if (deleted) {char *event[3] = {"zremrangebyrank","zremrangebyscore","zremrangebylex"};signalModifiedKey(c->db,key);notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_ZSET,event[rangetype],key,c->db->id);if (keyremoved)notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_GENERIC,"del",key,c->db->id);}server.dirty += deleted;addReplyLongLong(c,deleted);cleanup:if (rangetype == ZRANGE_LEX) zslFreeLexRange(&lexrange);}// server.h, 范围查询参数存储/* Struct to hold a inclusive/exclusive range spec by score comparison. */typedef struct {double min, max;int minex, maxex; /* are min or max exclusive? */} zrangespec;// 3.1. ziplist 的删除range方法// t_zset.cunsigned char *zzlDeleteRangeByScore(unsigned char *zl, zrangespec *range, unsigned long *deleted) {unsigned char *eptr, *sptr;double score;unsigned long num = 0;if (deleted != NULL) *deleted = 0;// 找到首个在范围内的指针,进行迭代eptr = zzlFirstInRange(zl,range);if (eptr == NULL) return zl;/* When the tail of the ziplist is deleted, eptr will point to the sentinel* byte and ziplistNext will return NULL. */while ((sptr = ziplistNext(zl,eptr)) != NULL) {score = zzlGetScore(sptr);// 肯定是比 min 大的,所以只需确认比 max 小即可if (zslValueLteMax(score,range)) {/* Delete both the element and the score. */zl = ziplistDelete(zl,&eptr);zl = ziplistDelete(zl,&eptr);num++;} else {/* No longer in range. */break;}}if (deleted != NULL) *deleted = num;return zl;}/* Find pointer to the first element contained in the specified range.* Returns NULL when no element is contained in the range. */unsigned char *zzlFirstInRange(unsigned char *zl, zrangespec *range) {unsigned char *eptr = ziplistIndex(zl,0), *sptr;double score;/* If everything is out of range, return early. */// 比较第1个元素和最后 一个元素,即可确认是否在范围内if (!zzlIsInRange(zl,range)) return NULL;while (eptr != NULL) {sptr = ziplistNext(zl,eptr);serverAssert(sptr != NULL);score = zzlGetScore(sptr);// score >= minif (zslValueGteMin(score,range)) {/* Check if score <= max. */if (zslValueLteMax(score,range))return eptr;return NULL;}/* Move to next element. */eptr = ziplistNext(zl,sptr);}return NULL;}// 检查zl是否在range范围内// 检查第1个分数和最后一个数即可/* Returns if there is a part of the zset is in range. Should only be used* internally by zzlFirstInRange and zzlLastInRange. */int zzlIsInRange(unsigned char *zl, zrangespec *range) {unsigned char *p;double score;/* Test for ranges that will always be empty. */if (range->min > range->max ||(range->min == range->max && (range->minex || range->maxex)))return 0;p = ziplistIndex(zl,-1); /* Last score. */if (p == NULL) return 0; /* Empty sorted set */score = zzlGetScore(p);// scoreMax >= minif (!zslValueGteMin(score,range))return 0;p = ziplistIndex(zl,1); /* First score. */serverAssert(p != NULL);score = zzlGetScore(p);// scoreMin <= maxif (!zslValueLteMax(score,range))return 0;return 1;}// 3.2. 删除 skiplist 中的range元素/* Delete all the elements with score between min and max from the skiplist.* Min and max are inclusive, so a score >= min || score <= max is deleted.* Note that this function takes the reference to the hash table view of the* sorted set, in order to remove the elements from the hash table too. */unsigned long zslDeleteRangeByScore(zskiplist *zsl, zrangespec *range, dict *dict) {zskiplistNode *update[ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL], *x;unsigned long removed = 0;int i;x = zsl->header;// 找出每层小于 range->min 的元素for (i = zsl->level-1; i >= 0; i--) {while (x->level[i].forward && (range->minex ?x->level[i].forward->score <= range->min :x->level[i].forward->score < range->min))x = x->level[i].forward;update[i] = x;}/* Current node is the last with score < or <= min. */x = x->level[0].forward;// 从第0层开始,依次删除引用,删除元素// 同有找到符合条件的元素时,一次循环也不会成立/* Delete nodes while in range. */while (x &&(range->maxex ? x->score < range->max : x->score <= range->max)){// 保留下一次迭代zskiplistNode *next = x->level[0].forward;zslDeleteNode(zsl,x,update);// 同步删除 dict 数据dictDelete(dict,x->ele);zslFreeNode(x); /* Here is where x->ele is actually released. */removed++;x = next;}return removed;}
删除的逻辑比较清晰,ziplist和skiplist分开处理。大体思路相同是:找到第一个符合条件的元素,然后迭代,直到第一个不符合条件的元素为止。
set虽然从定义上与zset有很多相通之处,然而在实现上却是截然不同的。由于很多东西和之前介绍的知识有重合的地方,也没啥好特别说的。zset 的解析差不多就到这里了。
你觉得zset还有什么有意思的实现呢?欢迎讨论。

腾讯、阿里、滴滴后台面试题汇总总结 — (含答案)
面试:史上最全多线程面试题 !
最新阿里内推Java后端面试题
JVM难学?那是因为你没认真看完这篇文章

关注作者微信公众号 —《JAVA烂猪皮》
了解更多java后端架构知识以及最新面试宝典

看完本文记得给作者点赞+在看哦~~~大家的支持,是作者源源不断出文的动力
作者:等你归去来
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/yougewe/p/12253982.html
