Java 判空新写法!干掉 if else !
user.getAddress().getProvince();
if(user!=null){
Address address = user.getAddress();
if(address!=null){
String province = address.getProvince();
}
}
API 介绍
1、Optional(T value),empty(),of(T value),ofNullable(T value)
Optional(T value),即构造函数,它是private权限的,不能由外部调用的。其余三个函数是public权限,供我们所调用。那么,Optional的本质,就是内部储存了一个真实的值,在构造的时候,就直接判断其值是否为空。好吧,这么说还是比较抽象。直接上Optional(T value)构造函数的源码,如下图所示
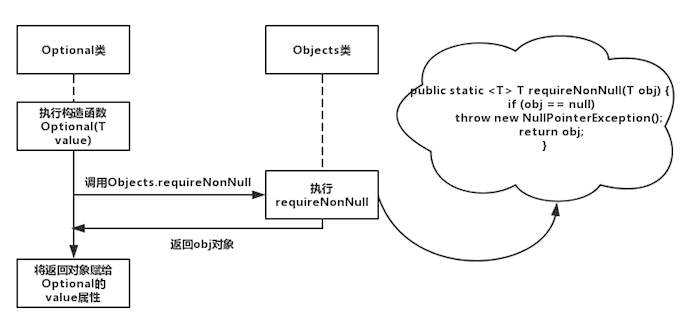
public static <T> Optional<T> of(T value) {
return new Optional<>(value);
}
-
通过 of(T value)函数所构造出的Optional对象,当Value值为空时,依然会报NullPointerException。 -
通过 of(T value)函数所构造出的Optional对象,当Value值不为空时,能正常构造Optional对象。
public final class Optional<T> {
//省略....
private static final Optional<?> EMPTY = new Optional<>();
private Optional() {
this.value = null;
}
//省略...
public static<T> Optional<T> empty() {
@SuppressWarnings(unchecked)
Optional<T> t = (Optional<T>) EMPTY;
return t;
}
}
empty()的作用就是返回EMPTY对象。
ofNullable(T value)的作用了,上源码
public static <T> Optional<T> ofNullable(T value) {
return value == null ? empty() : of(value);
}
of(T value)的区别就是,当value值为null时,of(T value)会报NullPointerException异常;ofNullable(T value)不会throw Exception,ofNullable(T value)直接返回一个EMPTY对象。
ofNullable函数而不用of函数呢?
NullPointerException。而是要立即报告,这种情况下就用Of函数。但是不得不承认,这样的场景真的很少。博主也仅在写junit测试用例中用到过此函数。
2、orElse(T other),orElseGet(Supplier other)和orElseThrow(Supplier exceptionSupplier)
orElse和orElseGet的用法如下所示,相当于value值为null时,给予一个默认值:
@Test
public void test() {
User user = null;
user = Optional.ofNullable(user).orElse(createUser());
user = Optional.ofNullable(user).orElseGet(() -> createUser());
}
public User createUser(){
User user = new User();
user.setName(zhangsan);
return user;
}
orElse函数依然会执行createUser()方法,而orElseGet函数并不会执行createUser()方法,大家可自行测试。
User user = null;
Optional.ofNullable(user).orElseThrow(()->new Exception(用户不存在));
3、map(Function mapper)和flatMap(Function> mapper)
public final class Optional<T> {
//省略....
public<U> Optional<U> map(Function<? super T, ? extends U> mapper) {
Objects.requireNonNull(mapper);
if (!isPresent())
return empty();
else {
return Optional.ofNullable(mapper.apply(value));
}
}
//省略...
public<U> Optional<U> flatMap(Function<? super T, Optional<U>> mapper) {
Objects.requireNonNull(mapper);
if (!isPresent())
return empty();
else {
return Objects.requireNonNull(mapper.apply(value));
}
}
}
Function<? super T, ? extends U>,而flapMap的入参类型为Function<? super T, Optional<U>>。
public class User {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
String city = Optional.ofNullable(user).map(u-> u.getName()).get();
public class User {
private String name;
public Optional<String> getName() {
return Optional.ofNullable(name);
}
}
String city = Optional.ofNullable(user).flatMap(u-> u.getName()).get();
4、isPresent()和ifPresent(Consumer consumer)
isPresent即判断value值是否为空,而ifPresent就是在value值不为空时,做一些操作。这两个函数的源码如下
public final class Optional<T> {
//省略....
public boolean isPresent() {
return value != null;
}
//省略...
public void ifPresent(Consumer<? super T> consumer) {
if (value != null)
consumer.accept(value);
}
}
if (user != null){
// TODO: do something
}
User user = Optional.ofNullable(user);
if (Optional.isPresent()){
// TODO: do something
}
ifPresent(Consumer<? super T> consumer),用法也很简单,如下所示
Optional.ofNullable(user).ifPresent(u->{
// TODO: do something
});
5、filter(Predicate predicate)
public final class Optional<T> {
//省略....
Objects.requireNonNull(predicate);
if (!isPresent())
return this;
else
return predicate.test(value) ? this : empty();
}
Predicate 来对 Optional 中包含的值进行过滤,如果包含的值满足条件,那么还是返回这个 Optional;否则返回 Optional.empty。
Optional<User> user1 = Optional.ofNullable(user).filter(u -> u.getName().length()<6);
实战使用
例一
public String getCity(User user) throws Exception{
if(user!=null){
if(user.getAddress()!=null){
Address address = user.getAddress();
if(address.getCity()!=null){
return address.getCity();
}
}
}
throw new Excpetion(取值错误);
}
public String getCity(User user) throws Exception{
return Optional.ofNullable(user)
.map(u-> u.getAddress())
.map(a->a.getCity())
.orElseThrow(()->new Exception(取指错误));
}
例二
if(user!=null){
dosomething(user);
}
Optional.ofNullable(user)
.ifPresent(u->{
dosomething(u);
});
例三
public User getUser(User user) throws Exception{
if(user!=null){
String name = user.getName();
if(zhangsan.equals(name)){
return user;
}
}else{
user = new User();
user.setName(zhangsan);
return user;
}
}
public User getUser(User user) {
return Optional.ofNullable(user)
.filter(u->zhangsan.equals(u.getName()))
.orElseGet(()-> {
User user1 = new User();
user1.setName(zhangsan);
return user1;
});
}
评论
