据悉,深圳某工程师沦为C语言笔试枪手
事情是这样的,昨晚晚上,有个网友发消息给我,说他有几道C语言笔试题不会写,所以,就出现了解题的这一幕。
文章中,我只讲解了一部分,有一些题目觉得没必要讲,然后我在pdf上做了注释,想看的在公众号留言「20201227」获取pdf文档。
1、第一题
#include "stdio.h"
int x = 2;
int y = 0;
int main()
{
if(x){
y++;
}
printf("%d\n",y);
getchar();
return 0;
}
这是送分题,就没有怎么好说的了,答案 1 .
2、解析一道比较有坑的。
#include "stdio.h"
#include "string.h"
int a()
{
static int i =0;
if(i>=1)
{
return --i;
}
return i++;
}
int main()
{
int A1 = 0;
int A2 = 0;
int A3 = 0;
A1 = a();
A2 = a();
A3 = a();
printf("%d,%d,%d\n",A1,A2,A3);
getchar();
return 0;
}
这个题目,主要要搞清楚,return i++ ,是先return i 再++,那就问题不大了。
3、这题应该好好说一下
#include "stdio.h"
int arg[] = {0,1,2,3};
int *p = &arg[1];
int v = 0;
int w = 0;
int main()
{
int i;
*(p++)+= 5;
v = *p;
*p = *p +5;
w=*p;
printf("v:%d\n",v);
printf("w:%d\n",w);
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
printf("arg[%d]=%d\n",i,arg[i]);
getchar();
return 0;
}
这题乍一看其实没有什么难度,但是实际写的时候,容易出问题,特意拿出来说一下。
核心在这行代码 *(p++)+= 5;
分解出来就是 取得p指向的值,然后 +=5 ,再让p指向下一个位置。
反汇编代码是这样的
mov rax,QWORD PTR [rip+0x2f0f] # 404040
lea rdx,[rax+0x4] //这是让指针指向下一个位置保存的寄存器
mov QWORD PTR [rip+0x2f04],rdx # 404040
mov edx,DWORD PTR [rax] //这是用来也 5 运算的寄存器
add edx,0x5
mov DWORD PTR [rax],edx
如果知道了这点,其他的就容易很多了。
int i;
*(p++)+= 5; //arg[1] = 6 p指向arg[2]
v = *p; //v = arg[2] = 2
*p = *p +5; //arg[2] = 2+5 = 7
w=*p; //w = 7
printf("v:%d\n",v);
printf("w:%d\n",w);
大家可以自己试试,如果把 *(p++)+= 5 改成 *(++p)+= 5 结果如何呢?
4、链表编程题
下面的题目我只写了第一题,后面的一题没有继续下,写链表的题目,我建议画一张链表的连接图,这样写代码的时候就会特别清晰了。
大家有不懂的,可以尽管问,另一个题目,欢迎留言写出来,我觉得这样的题目简单,但是也比较考验思维能力。
题目:

链表图形
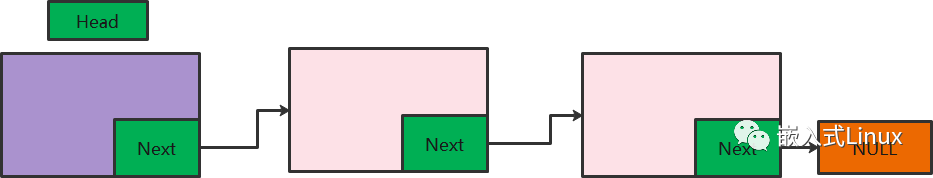
直接上代码吧
#include "stdio.h"
#include "string.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
typedef struct _STUDENT_INFO
{
int IDx;
char Name[32];
struct _STUDENT_INFO *Next;
} STUDENT_INFO_DEF;
STUDENT_INFO_DEF * creat(void)
{
STUDENT_INFO_DEF * h = (STUDENT_INFO_DEF *)malloc(sizeof(STUDENT_INFO_DEF));
h->Next = NULL;
return h;
}
int InsertStu(STUDENT_INFO_DEF *head,STUDENT_INFO_DEF stu)
{
if(head == NULL){
printf("head NULL\n");
return -1;
}
STUDENT_INFO_DEF * temp = head;
STUDENT_INFO_DEF * new = (STUDENT_INFO_DEF *)malloc(sizeof(STUDENT_INFO_DEF));
new->IDx = stu.IDx;
strncpy(new->Name,stu.Name,strlen(stu.Name));
new->Next = NULL;
while (temp->Next != NULL) {temp=temp->Next;}
temp->Next = new;
printf("[InsertStu] IDx:%d Name:%s Ok\n",new->IDx,new->Name);
return (0);
}
/*遍历链表*/
int TraverseStu(STUDENT_INFO_DEF *head)
{
STUDENT_INFO_DEF * temp = head;
if(head == NULL){
printf("head NULL\n");
return -1;
}
while(temp->Next!=NULL)
{
temp = temp->Next;
printf("[TraverseStu]IDx:%d Name:%s\n",temp->IDx,temp->Name);
}
return (0);
}
int FindAndDelete(STUDENT_INFO_DEF *head,STUDENT_INFO_DEF stu)
{
STUDENT_INFO_DEF * temp = head;
STUDENT_INFO_DEF * temp1 = NULL;
if(head == NULL){
printf("head NULL\n");
return -1;
}
while(temp->Next!=NULL)
{
temp = temp->Next;
if(temp->IDx == stu.IDx) break;
}
temp1 = temp->Next;
temp->Next = NULL;
while(temp1!=NULL)
{
free(temp1);
temp1 = temp1->Next;
}
printf("[FindAndDelete]\n");
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int i;
/*创建链表头*/
STUDENT_INFO_DEF *head;
STUDENT_INFO_DEF stu;
head=creat();
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
{
stu.IDx = i+1;
snprintf(stu.Name, strlen("student")+2, "student%d", i+1);
InsertStu(head,stu);
}
TraverseStu(head);
stu.IDx = 2;
FindAndDelete(head,stu);
TraverseStu(head);
getchar();
return 0;
}
代码输出
weiqifa@bsp-ubuntu1804:~/c/mianshi$ gcc lianbiao.c && ./a.out
[InsertStu] IDx:1 Name:student1 Ok
[InsertStu] IDx:2 Name:student2 Ok
[InsertStu] IDx:3 Name:student3 Ok
[InsertStu] IDx:4 Name:student4 Ok
[InsertStu] IDx:5 Name:student5 Ok
[TraverseStu]IDx:1 Name:student1
[TraverseStu]IDx:2 Name:student2
[TraverseStu]IDx:3 Name:student3
[TraverseStu]IDx:4 Name:student4
[TraverseStu]IDx:5 Name:student5
[FindAndDelete]
[TraverseStu]IDx:1 Name:student1
[TraverseStu]IDx:2 Name:student2

评论
