翻了源码,我把 panic 与 recover 给彻底搞明白了
共 30095字,需浏览 61分钟
·
2021-03-20 17:40
点击上方“Go编程时光”,选择“加为星标”
第一时间关注Go技术干货!

0. 写在前面
今天与大家来聊一聊go语言中的"throw、try…..catch{}"。如果你之前是一名java程序员,我相信你一定吐槽过go语言错误处理方式,但是这篇文章不是来讨论好坏的,我们本文的重点是带着大家看一看panic与recover是如何实现的。上一文我们讲解了defer是如何实现的,但是没有讲解与defer紧密相连的recover,想搞懂panic与recover的实现也没那么简单,就放到这一篇来讲解了。废话不多说,直接开整。
1. 什么是`panic`、`recover`
Go 语言中 panic 关键字主要用于主动抛出异常,类似 java 等语言中的 throw 关键字。panic 能够改变程序的控制流,调用 panic 后会立刻停止执行当前函数的剩余代码,并在当前 Goroutine 中递归执行调用方的 defer;
Go 语言中 recover 关键字主要用于捕获异常,让程序回到正常状态,类似 java 等语言中的 try ... catch 。recover 可以中止 panic 造成的程序崩溃。它是一个只能在 defer 中发挥作用的函数,在其他作用域中调用不会发挥作用;
recover只能在defer中使用这个在标准库的注释中已经写明白了,我们可以看一下:
// The recover built-in function allows a program to manage behavior of a
// panicking goroutine. Executing a call to recover inside a deferred
// function (but not any function called by it) stops the panicking sequence
// by restoring normal execution and retrieves the error value passed to the
// call of panic. If recover is called outside the deferred function it will
// not stop a panicking sequence. In this case, or when the goroutine is not
// panicking, or if the argument supplied to panic was nil, recover returns
// nil. Thus the return value from recover reports whether the goroutine is
// panicking.
func recover() interface{}
这里有一个要注意的点就是recover必须要要在defer函数中使用,否则无法阻止panic。最好的验证方法是先写两个例子:
func main() {
example1()
example2()
}
func example1() {
defer func() {
if err := recover(); err !=nil{
fmt.Println(string(Stack()))
}
}()
panic("unknown")
}
func example2() {
defer recover()
panic("unknown")
}
func Stack() []byte {
buf := make([]byte, 1024)
for {
n := runtime.Stack(buf, false)
if n < len(buf) {
return buf[:n]
}
buf = make([]byte, 2*len(buf))
}
}
运行我们会发现example2()方法的panic是没有被recover住的,导致整个程序直接crash了。这里大家肯定会有疑问,为什么直接写recover()就不能阻止panic了呢。我们在详解defer实现机制(附上三道面试题,我不信你们都能做对)讲解了defer实现原理,一个重要的知识点defer将语句放入到栈中时,也会将相关的值拷贝同时入栈。所以defer recover()这种写法在放入defer栈中时就已经被执行过了,panic是发生在之后,所以根本无法阻止住panic。
2. 它们的特性
上面我们简单的介绍了一下什么是panic与recover,下面我一起来看看他们有什么特性,避免我们踩坑。
recover只有在defer函数中使用才有效,上面已经举例说明了,这里就不在赘述了。panic允许在defer中嵌套多次调用.程序多次调用panic也不会影响defer函数的正常执行,所以使用defer进行收尾工作一般来说都是安全的。写个例子验证一下:
func example3() {
defer fmt.Println("this is a example3 for defer use panic")
defer func() {
defer func() {
panic("panic defer 2")
}()
panic("panic defer 1")
}()
panic("panic example3")
}
// 运行结果
this is a example3 for defer use panic
panic: panic example3
panic: panic defer 1
panic: panic defer 2
.......... 省略
通过运行结果可以看出panic不会影响defer函数的使用,所以他是安全的。
panic只会对当前Goroutine的defer有效,还记得我们上一文分析的deferproc函数吗?在newdefer中分配_defer结构体对象的时,会把分配到的对象链入当前goroutine的_defer链表的表头,也就是把延迟调用函数与调用方所在的Goroutine进行关联。因此当程序发生panic时只会调用当前 Goroutine 的延迟调用函数是没有问题的。写个例子验证一下:
func main() {
go example4()
go example5()
time.Sleep(10 * time.Second)
}
func example4() {
fmt.Println("goroutine example4")
defer func() {
fmt.Println("test defer")
}()
panic("unknown")
}
func example5() {
defer fmt.Println("goroutine example5")
time.Sleep(5 * time.Second)
}
// 运行结果
goroutine example4
test defer
panic: unknown
............. 省略部分代码
这里我开了两个协程,一个协程会发生panic,导致程序崩溃,但是只会执行自己所在Goroutine的延迟函数,所以正好验证了多个 Goroutine 之间没有太多的关联,一个 Goroutine 在 panic 时也不应该执行其他 Goroutine 的延迟函数。
3. 典型应用
其实我们在实际项目开发中,经常会遇到panic问题, Go 的 runtime 代码中很多地方都调用了 panic 函数,对于不了解 Go 底层实现的新人来说,这无疑是挖了一堆深坑。我们在实际生产环境中总会出现panic,但是我们的程序仍能正常运行,这是因为我们的框架已经做了recover,他已经为我们兜住底,比如gin,我们看一看他是怎么做的。
先看代码部分吧:
func Default() *Engine {
debugPrintWARNINGDefault()
engine := New()
engine.Use(Logger(), Recovery())
return engine
}
// Recovery returns a middleware that recovers from any panics and writes a 500 if there was one.
func Recovery() HandlerFunc {
return RecoveryWithWriter(DefaultErrorWriter)
}
// RecoveryWithWriter returns a middleware for a given writer that recovers from any panics and writes a 500 if there was one.
func RecoveryWithWriter(out io.Writer) HandlerFunc {
var logger *log.Logger
if out != nil {
logger = log.New(out, "\n\n\x1b[31m", log.LstdFlags)
}
return func(c *Context) {
defer func() {
if err := recover(); err != nil {
// Check for a broken connection, as it is not really a
// condition that warrants a panic stack trace.
...................// 省略
}
}()
c.Next()
}
}
我们在使用gin时,第一步会初始化一个Engine实例,调用Default方法会把recovery middleware附上,recovery中使用了defer函数,通过recover来阻止panic,当发生panic时,会返回500错误码。这里有一个需要注意的点是只有主程序中的panic是会被自动recover的,协程中出现panic会导致整个程序crash。还记得我们上面讲的第三个特性嘛,一个协程会发生panic,导致程序崩溃,但是只会执行自己所在Goroutine的延迟函数,所以正好验证了多个 Goroutine 之间没有太多的关联,一个 Goroutine 在 panic 时也不应该执行其他 Goroutine 的延迟函数。 这就能解释通了吧, 所以为了程序健壮性,我们应该自己主动检查我们的协程程序,在我们的协程函数中添加recover是很有必要的,比如这样:
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
r.GET("/asong/test/go-panic", func(ctx *gin.Context) {
go func() {
defer func() {
if err := recover();err != nil{
fmt.Println(err)
}
}()
panic("panic")
}()
})
r.Run()
}
如果使用的Gin框架,切记要检查协程中是否会出现panic,否则线上将付出沉重的代价。非常危险!!!
4. 源码解析
go-version: 1.15.3
我们先来写个简单的代码,看看他的汇编调用:
func main() {
defer func() {
if err:= recover();err != nil{
fmt.Println(err)
}
}()
panic("unknown")
}
执行go tool compile -N -l -S main.go就可以看到对应的汇编码了,我们截取部分片段分析:
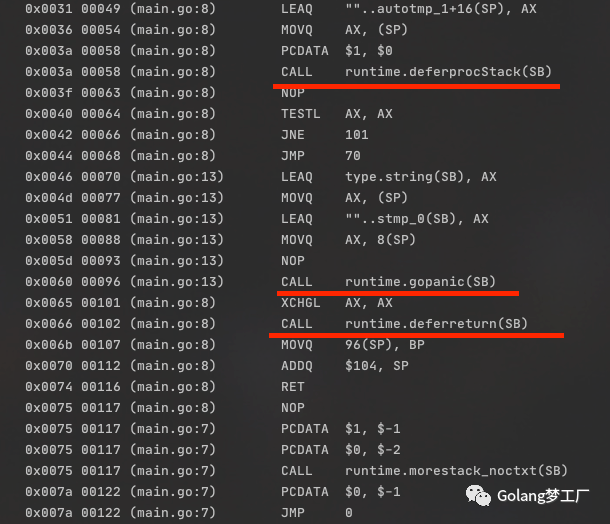
上面重点部分就是画红线的三处,第一步调用runtime.deferprocStack创建defer对象,这一步大家可能会有疑惑,我上一文忘记讲个这个了,这里先简单概括一下,defer总共有三种模型,编译一个函数里只会有一种defer模式
第一种,堆上分配(deferproc),基本是依赖运行时来分配"_defer"对象并加入延迟参数。在函数的尾部插入
deferreturn方法来消费deferlink。第二种,栈上分配(deferprocStack),基本上跟堆差不多,只是分配方式改为在栈上分配,压入的函数调用栈存有
_defer记录,编译器在ssa过程中会预留defer空间。第三种,开放编码模式(open coded),不过是有条件的,默认open-coded最多支持8个defer,超过则取消。在构建ssa时如发现gcflags有N禁止优化的参数 或者 return数量 * defer数量超过了 15不适用open-coded模式。并不能处于循环中。
按理说我们的版本是1.15+,应该使用开放编码模式呀,但是这里怎么还会在栈上分配?注意看呀,伙计们,我在汇编处理时禁止了编译优化,那肯定不会走开放编码模式呀,这个不是重点,我们接着分析上面的汇编。
第二个红线在程序发生panic时会调用runtime.gopanic,现在程序处于panic状态,在函数返回时调用runtime.deferreturn,也就是调用延迟函数处理。上面这一步是主程序执行部分,下面我们在看一下延迟函数中的执行:
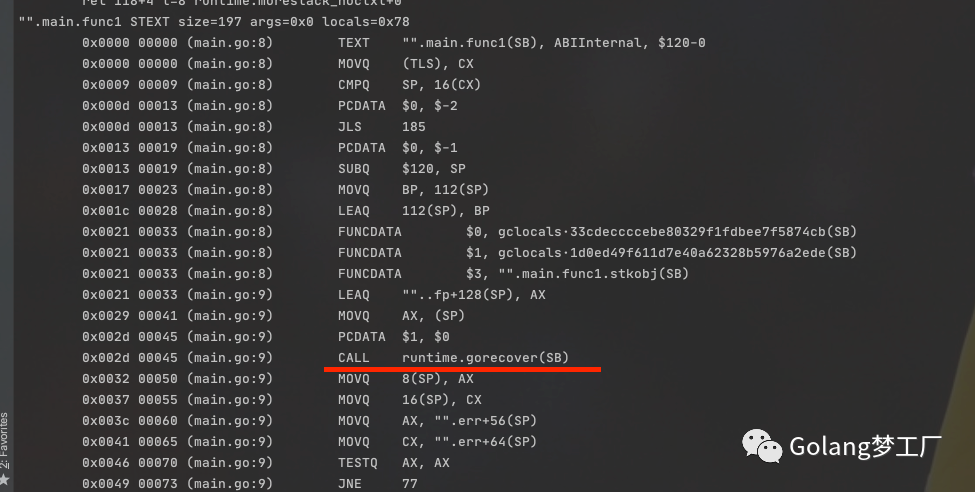
这里最重点的就只有一个,调用runtime.gorecover,也就是在这一步,对主程序中的panic进行了恢复了,这就是panic与recover的执行过程,接下来我们就仔细分析一下runtime.gopanic、runtime.gorecover这两个方法是如何实现的!
5.1 _panic结构
在讲defer实现机制时,我们一起看过defer的结构,其中有一个字段就是_panic,是触发defer的作用,我们来看看的panic的结构:
type _panic struct {
argp unsafe.Pointer // pointer to arguments of deferred call run during panic; cannot move - known to liblink
arg interface{} // argument to panic
link *_panic // link to earlier panic
pc uintptr // where to return to in runtime if this panic is bypassed
sp unsafe.Pointer // where to return to in runtime if this panic is bypassed
recovered bool // whether this panic is over
aborted bool // the panic was aborted
goexit bool
}
简单介绍一下上面的字段:
argp是指向defer调用时参数的指针。arg是我们调用panic时传入的参数link指向的是更早调用runtime._panic结构,也就是说painc可以被连续调用,他们之间形成链表recovered表示当前runtime._panic是否被recover恢复aborted表示当前的panic是否被强行终止
上面的pc、sp、goexit我们单独讲一下,runtime包中有一个Goexit方法,Goext能够终止调用它的goroutine,其他的goroutine是不受影响的,goexit也会在终止goroutine之前运行所有延迟调用函数,Goexit不是一个panic,所以这些延迟函数中的任何recover调用都将返回nil。如果我们在主函数中调用了Goexit会终止该goroutine但不会返回func main。由于func main没有返回,因此程序将继续执行其他gorountine,直到所有其他goroutine退出,程序才会crash。写个简单的例子:
func main() {
go func() {
defer func() {
if err := recover(); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
}()
runtime.Goexit()
}()
go func() {
for true {
fmt.Println("test")
}
}()
runtime.Goexit()
fmt.Println("main")
select {
}
}
运行上面的例子你就会发现,即使在主goroutine中调用了runtime.Goexit,其他goroutine是没有任何影响的。所以结构中的pc、sp、goexit三个字段都是为了修复runtime.Goexit,这三个字段就是为了保证该函数的一定会生效,因为如果在defer中发生panic,那么goexit函数就会被取消,所以才有了这三个字段做保护。看这个例子:
func main() {
maybeGoexit()
}
func maybeGoexit() {
defer func() {
fmt.Println(recover())
}()
defer panic("cancelled Goexit!")
runtime.Goexit()
}
英语好的可以看一看这个:https://github.com/golang/go/issues/29226,这就是上面的一个例子,这里就不过多解释了,了解就好。
下面就开始我们的重点吧~。
5.2 gopanic
gopanic的代码有点长,我们一点一点来分析:
第一部分,判断
panic类型:
gp := getg()
if gp.m.curg != gp {
print("panic: ")
printany(e)
print("\n")
throw("panic on system stack")
}
if gp.m.mallocing != 0 {
print("panic: ")
printany(e)
print("\n")
throw("panic during malloc")
}
if gp.m.preemptoff != "" {
print("panic: ")
printany(e)
print("\n")
print("preempt off reason: ")
print(gp.m.preemptoff)
print("\n")
throw("panic during preemptoff")
}
if gp.m.locks != 0 {
print("panic: ")
printany(e)
print("\n")
throw("panic holding locks")
}
根据不同的类型判断当前发生panic错误,这里没什么多说的,接着往下看。
第二部分,确保每个
recover都试图恢复当前协程中最新产生的且尚未恢复的panic
var p _panic // 声明一个panic结构
p.arg = e // 把panic传入的值赋给`arg`
p.link = gp._panic // 指向runtime.panic结构
gp._panic = (*_panic)(noescape(unsafe.Pointer(&p)))
atomic.Xadd(&runningPanicDefers, 1)
// By calculating getcallerpc/getcallersp here, we avoid scanning the
// gopanic frame (stack scanning is slow...)
addOneOpenDeferFrame(gp, getcallerpc(), unsafe.Pointer(getcallersp()))
for {
d := gp._defer // 获取当前gorourine的 defer
if d == nil {
break // 如果没有defer直接退出了
}
// If defer was started by earlier panic or Goexit (and, since we're back here, that triggered a new panic),
// take defer off list. An earlier panic will not continue running, but we will make sure below that an
// earlier Goexit does continue running.
if d.started {
if d._panic != nil {
d._panic.aborted = true
}
d._panic = nil
if !d.openDefer {
// For open-coded defers, we need to process the
// defer again, in case there are any other defers
// to call in the frame (not including the defer
// call that caused the panic).
d.fn = nil
gp._defer = d.link
freedefer(d)
continue
}
}
// Mark defer as started, but keep on list, so that traceback
// can find and update the defer's argument frame if stack growth
// or a garbage collection happens before reflectcall starts executing d.fn.
d.started = true
// Record the panic that is running the defer.
// If there is a new panic during the deferred call, that panic
// will find d in the list and will mark d._panic (this panic) aborted.
d._panic = (*_panic)(noescape(unsafe.Pointer(&p)))
上面的代码不太好说的部分,我添加了注释,就不在这解释一遍了,直接看 d.Started部分,这里的意思是如果defer是由先前的panic或Goexit启动的(循环处理回到这里,这触发了新的panic),将defer从列表中删除。早期的panic将不会继续运行,但我们将确保早期的Goexit会继续运行,代码中的if d._panic != nil{d._panic.aborted =true}就是确保将先前的panic终止掉,将aborted设置为true,在下面执行recover时保证goexit不会被取消。
第三部分,
defer内联优化调用性能
if !d.openDefer {
// For open-coded defers, we need to process the
// defer again, in case there are any other defers
// to call in the frame (not including the defer
// call that caused the panic).
d.fn = nil
gp._defer = d.link
freedefer(d)
continue
}
done := true
if d.openDefer {
done = runOpenDeferFrame(gp, d)
if done && !d._panic.recovered {
addOneOpenDeferFrame(gp, 0, nil)
}
} else {
p.argp = unsafe.Pointer(getargp(0))
reflectcall(nil, unsafe.Pointer(d.fn), deferArgs(d), uint32(d.siz), uint32(d.siz))
}
上面的代码都是截图片段,这些部分都是为了判断当前defer是否可以使用开发编码模式,具体怎么操作的就不展开了。
第四部分,
gopanic中执行程序恢复
在第三部分进行defer内联优化选择时会执行调用延迟函数(reflectcall就是这个作用),也就是会调用runtime.gorecover把recoverd = true,具体这个函数的操作留在下面讲,因为runtime.gorecover函数并不包含恢复程序的逻辑,程序的恢复是在gopanic中执行的。先看一下代码:
if p.recovered { // 在runtime.gorecover中设置为true
gp._panic = p.link
if gp._panic != nil && gp._panic.goexit && gp._panic.aborted {
// A normal recover would bypass/abort the Goexit. Instead,
// we return to the processing loop of the Goexit.
gp.sigcode0 = uintptr(gp._panic.sp)
gp.sigcode1 = uintptr(gp._panic.pc)
mcall(recovery)
throw("bypassed recovery failed") // mcall should not return
}
atomic.Xadd(&runningPanicDefers, -1)
if done {
// Remove any remaining non-started, open-coded
// defer entries after a recover, since the
// corresponding defers will be executed normally
// (inline). Any such entry will become stale once
// we run the corresponding defers inline and exit
// the associated stack frame.
d := gp._defer
var prev *_defer
for d != nil {
if d.openDefer {
if d.started {
// This defer is started but we
// are in the middle of a
// defer-panic-recover inside of
// it, so don't remove it or any
// further defer entries
break
}
if prev == nil {
gp._defer = d.link
} else {
prev.link = d.link
}
newd := d.link
freedefer(d)
d = newd
} else {
prev = d
d = d.link
}
}
}
gp._panic = p.link
// Aborted panics are marked but remain on the g.panic list.
// Remove them from the list.
for gp._panic != nil && gp._panic.aborted {
gp._panic = gp._panic.link
}
if gp._panic == nil { // must be done with signal
gp.sig = 0
}
// Pass information about recovering frame to recovery.
gp.sigcode0 = uintptr(sp)
gp.sigcode1 = pc
mcall(recovery)
throw("recovery failed") // mcall should not return
}
这段代码有点长,主要就是分为两部分:
第一部分主要是这个判断if gp._panic != nil && gp._panic.goexit && gp._panic.aborted { ... },正常recover是会绕过Goexit的,所以为了解决这个,添加了这个判断,这样就可以保证Goexit也会被recover住,这里是通过从runtime._panic中取出了程序计数器pc和栈指针sp并且调用runtime.recovery函数触发goroutine的调度,调度之前会准备好 sp、pc 以及函数的返回值。
第二部分主要是做panic的recover,这也与上面的流程基本差不多,他是从runtime._defer中取出了程序计数器pc和栈指针sp并调用recovery函数触发Goroutine,跳转到recovery函数是通过runtime.call进行的,我们看一下其源码(src/runtime/asm_amd64.s 289行):
// func mcall(fn func(*g))
// Switch to m->g0's stack, call fn(g).
// Fn must never return. It should gogo(&g->sched)
// to keep running g.
TEXT runtime·mcall(SB), NOSPLIT, $0-8
MOVQ fn+0(FP), DI
get_tls(CX)
MOVQ g(CX), AX // save state in g->sched
MOVQ 0(SP), BX // caller's PC
MOVQ BX, (g_sched+gobuf_pc)(AX)
LEAQ fn+0(FP), BX // caller's SP
MOVQ BX, (g_sched+gobuf_sp)(AX)
MOVQ AX, (g_sched+gobuf_g)(AX)
MOVQ BP, (g_sched+gobuf_bp)(AX)
// switch to m->g0 & its stack, call fn
MOVQ g(CX), BX
MOVQ g_m(BX), BX
MOVQ m_g0(BX), SI
CMPQ SI, AX // if g == m->g0 call badmcall
JNE 3(PC)
MOVQ $runtime·badmcall(SB), AX
JMP AX
MOVQ SI, g(CX) // g = m->g0
MOVQ (g_sched+gobuf_sp)(SI), SP // sp = m->g0->sched.sp
PUSHQ AX
MOVQ DI, DX
MOVQ 0(DI), DI
CALL DI
POPQ AX
MOVQ $runtime·badmcall2(SB), AX
JMP AX
RET
因为go语言中的runtime环境是有自己的堆栈和goroutine,recovery函数也是在runtime环境执行的,所以要调度到m->g0来执行recovery函数,我们在看一下recovery函数:
// Unwind the stack after a deferred function calls recover
// after a panic. Then arrange to continue running as though
// the caller of the deferred function returned normally.
func recovery(gp *g) {
// Info about defer passed in G struct.
sp := gp.sigcode0
pc := gp.sigcode1
// d's arguments need to be in the stack.
if sp != 0 && (sp < gp.stack.lo || gp.stack.hi < sp) {
print("recover: ", hex(sp), " not in [", hex(gp.stack.lo), ", ", hex(gp.stack.hi), "]\n")
throw("bad recovery")
}
// Make the deferproc for this d return again,
// this time returning 1. The calling function will
// jump to the standard return epilogue.
gp.sched.sp = sp
gp.sched.pc = pc
gp.sched.lr = 0
gp.sched.ret = 1
gogo(&gp.sched)
}
在recovery 函数中,利用 g 中的两个状态码回溯栈指针 sp 并恢复程序计数器 pc 到调度器中,并调用 gogo 重新调度 g ,将 g 恢复到调用 recover 函数的位置, goroutine 继续执行,recovery在调度过程中会将函数的返回值设置为1。这个有什么作用呢?在deferproc函数中找到了答案:
//go:nosplit
func deferproc(siz int32, fn *funcval) { // arguments of fn follow fn
............ 省略
// deferproc returns 0 normally.
// a deferred func that stops a panic
// makes the deferproc return 1.
// the code the compiler generates always
// checks the return value and jumps to the
// end of the function if deferproc returns != 0.
return0()
// No code can go here - the C return register has
// been set and must not be clobbered.
}
当延迟函数中recover了一个panic时,就会返回1,当 runtime.deferproc 函数的返回值是 1 时,编译器生成的代码会直接跳转到调用方函数返回之前并执行 runtime.deferreturn,跳转到runtime.deferturn函数之后,程序就已经从panic恢复了正常的逻辑。
第五部分,如果没有遇到
runtime.gorecover就会依次遍历所有的runtime._defer,在最后调用fatalpanic中止程序,并打印panic参数返回错误码2。
// fatalpanic implements an unrecoverable panic. It is like fatalthrow, except
// that if msgs != nil, fatalpanic also prints panic messages and decrements
// runningPanicDefers once main is blocked from exiting.
//
//go:nosplit
func fatalpanic(msgs *_panic) {
pc := getcallerpc()
sp := getcallersp()
gp := getg()
var docrash bool
// Switch to the system stack to avoid any stack growth, which
// may make things worse if the runtime is in a bad state.
systemstack(func() {
if startpanic_m() && msgs != nil {
// There were panic messages and startpanic_m
// says it's okay to try to print them.
// startpanic_m set panicking, which will
// block main from exiting, so now OK to
// decrement runningPanicDefers.
atomic.Xadd(&runningPanicDefers, -1)
printpanics(msgs)
}
docrash = dopanic_m(gp, pc, sp)
})
if docrash {
// By crashing outside the above systemstack call, debuggers
// will not be confused when generating a backtrace.
// Function crash is marked nosplit to avoid stack growth.
crash()
}
systemstack(func() {
exit(2)
})
*(*int)(nil) = 0 // not reached
}
在这里runtime.fatalpanic实现了无法被恢复的程序崩溃,它在中止程序之前会通过 runtime.printpanics 打印出全部的 panic 消息以及调用时传入的参数。
好啦,至此整个gopanic方法就全部看完了,接下来我们再来看一看gorecover方法。
5.3 gorecover
这个函数就简单很多了,代码量比较少,先看一下代码吧:
// The implementation of the predeclared function recover.
// Cannot split the stack because it needs to reliably
// find the stack segment of its caller.
//
// TODO(rsc): Once we commit to CopyStackAlways,
// this doesn't need to be nosplit.
//go:nosplit
func gorecover(argp uintptr) interface{} {
// Must be in a function running as part of a deferred call during the panic.
// Must be called from the topmost function of the call
// (the function used in the defer statement).
// p.argp is the argument pointer of that topmost deferred function call.
// Compare against argp reported by caller.
// If they match, the caller is the one who can recover.
gp := getg()
p := gp._panic
if p != nil && !p.goexit && !p.recovered && argp == uintptr(p.argp) {
p.recovered = true
return p.arg
}
return nil
}
首先获取当前所在的Goroutine,如果当前Goroutine没有调用panic,那么该函数会直接返回nil,是否能recover住该panic的判断条件必须四个都吻合,p.Goexit判断当前是否是goexit触发的,如果是则无法revocer住,上面讲过会在gopanic中执行进行recover。argp是最顶层延迟函数调用的实参指针,与调用者的argp进行比较,如果匹配说明调用者是可以recover,直接将recovered字段设置为true就可以了。这里主要的作用就是判断当前panic是否可以recover,具体的恢复逻辑还是由gopanic函数负责的。
5. 流程总结
上面看了一篇源码,肯定也是一脸懵逼吧~。这正常,毕竟文字诉说,只能到这个程度了,还是要自己结合带去去看,这里只是起一个辅助作用,最后做一个流程总结吧。
在程序执行过程中如果遇到
panic,那么会调用runtime.gopanic,然后取当前Goroutine的defer链表依次执行。在调用
defer函数是如果有recover就会调用runtime.gorecover,在gorecover中会把runtime._panic中的recoved标记为true,这里只是标记的作用,恢复逻辑仍在runtime.panic中。在
gopanic中会执行defer内联优化、程序恢复逻辑。在程序恢复逻辑中,会进行判断,如果是触发是runtime.Goexit,也会进行recovery。panic也会进行recovery,主要逻辑是runtime.gopanic会从runtime._defer结构体中取出程序计数器pc和栈指针sp并调用runtime.recovery函数恢复程序。runtime.recvoery函数中会根据传入的pc和sp在gogo中跳转回runtime.deferproc,如果返回值为1,就会调用runtime.deferreturn恢复正常流程。在
gopanic执行完所有的_defer并且也没有遇到recover,那么就会执行runtime.fatalpanic终止程序,并返回错误码2.
这就是这个逻辑流程,累死我了,如果文章对你有帮助,还请不吝点赞转发~
-- END --
⬇⬇⬇
