springboot 数据库 主从方案
点击上方 Java学习之道,选择 设为星标
作者: 神牛003
来源: cnblogs.com/wangrudong003/p/11535540.html
Part1前言
本篇分享数据库主从方案,案例采用springboot+mysql+mybatis演示;要想在代码中做主从选择,通常需要明白什么时候切换数据源,怎么切换数据源,下面以代码示例来做阐述;
搭建测试环境(1个master库2个slave库) DataSource多数据源配置 设置mybatis数据源 拦截器+注解设置master和slave库选择 选出当前请求要使用的slave从库 测试用例
Part2搭建测试环境
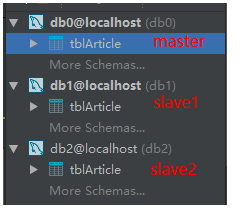
(1个master库2个slave库) 由于测试资源优先在本地模拟创建3个数据库,分别是1个master库2个slave库,里面分别都有一个tblArticle表,内容也大致相同(为了演示主从效果,我把从库中表的title列值增加了slave字样):
再来创建一个db.properties,分别配置3个数据源,格式如下:
spring.datasource0.jdbc-url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db0?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false
spring.datasource0.username=root
spring.datasource0.password=123456
spring.datasource0.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource1.jdbc-url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false
spring.datasource1.username=root
spring.datasource1.password=123456
spring.datasource1.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource2.jdbc-url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db2?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false
spring.datasource2.username=root
spring.datasource2.password=123456
spring.datasource2.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
同时我们创建具有对应关系的DbType枚举,帮助我们使代码更已读:
public class DbEmHelper {
public enum DbTypeEm {
db0(0, "db0(默认master)", -1),
db1(1, "db1", 0),
db2(2, "db2", 1);
/**
* 用于筛选从库
*
* @param slaveNum 从库顺序编号 0开始
* @return
*/
public static Optional getDbTypeBySlaveNum(int slaveNum) {
return Arrays.stream(DbTypeEm.values()).filter(b -> b.getSlaveNum() == slaveNum).findFirst();
}
DbTypeEm(int code, String des, int slaveNum) {
this.code = code;
this.des = des;
this.slaveNum = slaveNum;
}
private int code;
private String des;
private int slaveNum;
//get,set省略
}
}
Part3DataSource多数据源配置
使用上面3个库连接串信息,配置3个不同的DataSource实例,达到多个DataSource目的;由于在代码中库的实例需要动态选择,因此我们利用AbstractRoutingDataSource来聚合多个数据源;下面是生成多个DataSource代码:
@Configuration
public class DbConfig {
@Bean(name = "dbRouting")
public DataSource dbRouting() throws IOException {
//加载db配置文件
InputStream in = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("db.properties");
Properties pp = new Properties();
pp.load(in);
//创建每个库的datasource
Map targetDataSources = new HashMap<>(DbEmHelper.DbTypeEm.values().length);
Arrays.stream(DbEmHelper.DbTypeEm.values()).forEach(dbTypeEm -> {
targetDataSources.put(dbTypeEm, getDataSource(pp, dbTypeEm));
});
//设置多数据源
DbRouting dbRouting = new DbRouting();
dbRouting.setTargetDataSources(targetDataSources);
return dbRouting;
}
/**
* 创建库的datasource
*
* @param pp
* @param dbTypeEm
* @return
*/
private DataSource getDataSource(Properties pp, DbEmHelper.DbTypeEm dbTypeEm) {
DataSourceBuilder builder = DataSourceBuilder.create();
builder.driverClassName(pp.getProperty(JsonUtil.formatMsg("spring.datasource{}.driver-class-name", dbTypeEm.getCode())));
builder.url(pp.getProperty(JsonUtil.formatMsg("spring.datasource{}.jdbc-url", dbTypeEm.getCode())));
builder.username(pp.getProperty(JsonUtil.formatMsg("spring.datasource{}.username", dbTypeEm.getCode())));
builder.password(pp.getProperty(JsonUtil.formatMsg("spring.datasource{}.password", dbTypeEm.getCode())));
return builder.build();
}
}
能够看到一个DbRouting实例,其是继承了AbstractRoutingDataSource,她里面有个Map变量来存储多个数据源信息:
public class DbRouting extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
return DbContextHolder.getDb().orElse(DbEmHelper.DbTypeEm.db0);
}
}
DbRouting里面主要重写了determineCurrentLookupKey(),通过设置和存储DataSource集合的Map相同的key,以此达到选择不同DataSource的目的,这里使用ThreadLocal获取同一线程存储的key;主要看AbstractRoutingDataSource类中下面代码:
protected DataSource determineTargetDataSource() {
Assert.notNull(this.resolvedDataSources, "DataSource router not initialized");
Object lookupKey = this.determineCurrentLookupKey();
DataSource dataSource = (DataSource)this.resolvedDataSources.get(lookupKey);
if(dataSource == null && (this.lenientFallback || lookupKey == null)) {
dataSource = this.resolvedDefaultDataSource;
}
if(dataSource == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot determine target DataSource for lookup key [" + lookupKey + "]");
} else {
return dataSource;
}
}
Part4设置mybatis数据源
本次演示为了便利,这里使用mybatis的注解方式来查询数据库,我们需要给mybatis设置数据源,我们可以从上面的声明DataSource的bean方法获取:
@EnableTransactionManagement
@Configuration
public class MybaitisConfig {
@Resource(name = "dbRouting")
DataSource dataSource;
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory() throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean factoryBean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
factoryBean.setDataSource(dataSource);
// factoryBean.setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources("classpath:*"));
return factoryBean.getObject();
}
}
我们使用的mybatis注解方式来查询数据库,所以不需要加载mapper的xml文件,下面注解方式查询sql:
@Mapper
public interface ArticleMapper {
@Select("select * from tblArticle where id = #{id}")
Article selectById(int id);
}
Part5拦截器+注解来选择master和slave库
通常操作数据的业务逻辑都放在service层,我们希望service中不同方法使用不同的库;比如:添加、修改、删除、部分查询方法等,使用master主库来操作,而大部分查询操作可以使用slave库来查询;这里通过拦截器+灵活的自定义注解来实现我们的需求:
@Documented
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface DbType {
boolean isMaster() default true;
}
注解参数默认选择master库来操作业务(看具体需求吧)
@Aspect
@Component
public class DbInterceptor {
//全部service层请求都走这里,ThreadLocal才能有DbType值
private final String pointcut = "execution(* com.sm.service..*.*(..))";
@Pointcut(value = pointcut)
public void dbType() {
}
@Before("dbType()")
void before(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("before...");
MethodSignature methodSignature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
Method method = methodSignature.getMethod();
DbType dbType = method.getAnnotation(DbType.class);
//设置Db
DbContextHolder.setDb(dbType == null ? false : dbType.isMaster());
}
@After("dbType()")
void after() {
System.out.println("after...");
DbContextHolder.remove();
}
}
拦截器拦截service层的所有方法,然后获取带有自定义注解DbType的方法的isMaster值,DbContextHolder.setDb()方法判断走master还是slave库,并赋值给ThreadLocal:
public class DbContextHolder {
private static final ThreadLocal> dbTypeEmThreadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
private static final AtomicInteger atoCounter = new AtomicInteger(0);
public static void setDb(DbEmHelper.DbTypeEm dbTypeEm) {
dbTypeEmThreadLocal.set(Optional.ofNullable(dbTypeEm));
}
public static Optional getDb() {
return dbTypeEmThreadLocal.get();
}
public static void remove() {
dbTypeEmThreadLocal.remove();
}
/**
* 设置主从库
*
* @param isMaster
*/
public static void setDb(boolean isMaster) {
if (isMaster) {
//主库
setDb(DbEmHelper.DbTypeEm.db0);
} else {
//从库
setSlave();
}
}
private static void setSlave() {
//累加值达到最大时,重置
if (atoCounter.get() >= 100000) {
atoCounter.set(0);
}
//排除master,选出当前线程请求要使用的db从库 - 从库算法
int slaveNum = atoCounter.getAndIncrement() % (DbEmHelper.DbTypeEm.values().length - 1);
Optional dbTypeEm = DbEmHelper.DbTypeEm.getDbTypeBySlaveNum(slaveNum);
if (dbTypeEm.isPresent()) {
setDb(dbTypeEm.get());
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("从库未匹配");
}
}
}
这一步骤很重要,通过拦截器来到达选择master和slave目的,当然也有其他方式的;
Part6选出当前请求要使用的slave从库
上面能选择出master和slave走向了,但是往往slave至少有两个库存在;我们需要知道怎么来选择多个slave库,目前最常用的方式通过计数器取余的方式来选择:
private static void setSlave() {
//累加值达到最大时,重置
if (atoCounter.get() >= 100000) {
atoCounter.set(0);
}
//排除master,选出当前线程请求要使用的db从库 - 从库算法
int slaveNum = atoCounter.getAndIncrement() % (DbEmHelper.DbTypeEm.values().length - 1);
Optional dbTypeEm = DbEmHelper.DbTypeEm.getDbTypeBySlaveNum(slaveNum);
if (dbTypeEm.isPresent()) {
setDb(dbTypeEm.get());
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("从库未匹配");
}
}
这里根据余数来匹配对应DbType枚举,选出DataSource的Map需要的key,并且赋值到当前线程ThreadLocal中;
/**
* 用于筛选从库4 * @param slaveNum 从库顺序编号 0开始
* @return
*/
public static Optional getDbTypeBySlaveNum(int slaveNum) {
return Arrays.stream(DbTypeEm.values()).filter(b -> b.getSlaveNum() == slaveNum).findFirst();
}
Part7测试用例
完成上面操作后,我们搭建个测试例子,ArticleService中分别如下3个方法,不同点在于@DbType注解的标记:
@Service
public class ArticleService {
@Autowired
ArticleMapper articleMapper;
@DbType
public Article selectById01(int id) {
Article article = articleMapper.selectById(id);
System.out.println(JsonUtil.formatMsg("selectById01:{} --- title:{}", DbContextHolder.getDb().get(), article.getTitle()));
return article;
}
@DbType(isMaster = false)
public Article selectById02(int id) {
Article article = articleMapper.selectById(id);
System.out.println(JsonUtil.formatMsg("selectById02:{} --- title:{}", DbContextHolder.getDb().get(), article.getTitle()));
return article;
}
public Article selectById(int id) {
Article article = articleMapper.selectById(id);
System.out.println(JsonUtil.formatMsg("selectById:{} --- title:{}", DbContextHolder.getDb().get(), article.getTitle()));
return article;
}
}
在同一个Controller层接口方法中去调用这3个service层方法,按照正常逻辑来讲,不出意外得到的结果是这样: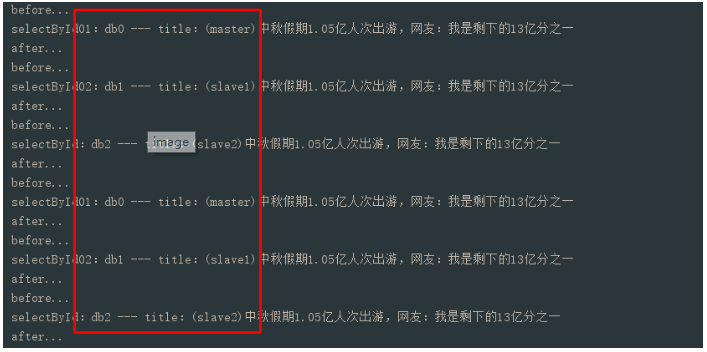 请求了两次接口,得到结果是:selectById01方法:标记了@DbType,但默认走isMaster=true,实际走了db0(master)库
selectById02方法:标记了@DbType(isMaster = false),实际走了db1(slave1)库
selectById方法:没有标记了@DbType,实际走了db2(slave2)库,因为拦截器中没有找到DbType注解,让其走了slave方法;因为selectById02执行过一次slave方法,计数器+1了,因此余数也变了所以定位到了slave2库(如果是基数调用,selectById02和selectById方法来回切换走不同slave库);
请求了两次接口,得到结果是:selectById01方法:标记了@DbType,但默认走isMaster=true,实际走了db0(master)库
selectById02方法:标记了@DbType(isMaster = false),实际走了db1(slave1)库
selectById方法:没有标记了@DbType,实际走了db2(slave2)库,因为拦截器中没有找到DbType注解,让其走了slave方法;因为selectById02执行过一次slave方法,计数器+1了,因此余数也变了所以定位到了slave2库(如果是基数调用,selectById02和selectById方法来回切换走不同slave库);
-  | 更多精彩文章 -
| 更多精彩文章 -
▽加我微信,交个朋友 长按/扫码添加↑↑↑