SpringBoot中使用异步方法优化Service逻辑,提高接口响应速度
共 6097字,需浏览 13分钟
·
2021-11-04 19:24

阅读本文大概需要 5 分钟。
来自:blog.csdn.net/weixin_43441509/article/details/119855613
1. 为什么需要异步方法?
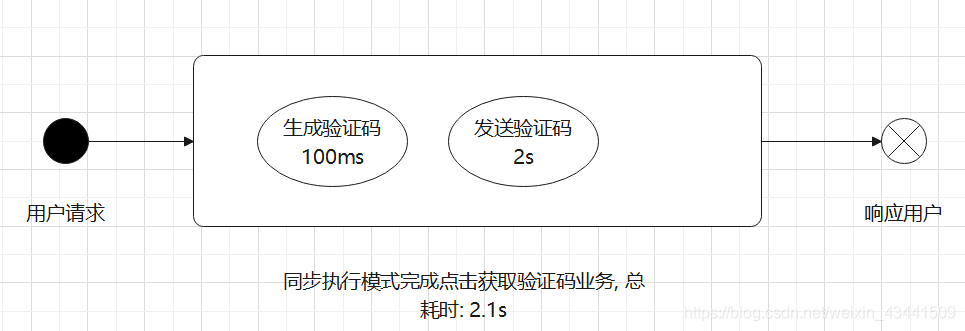
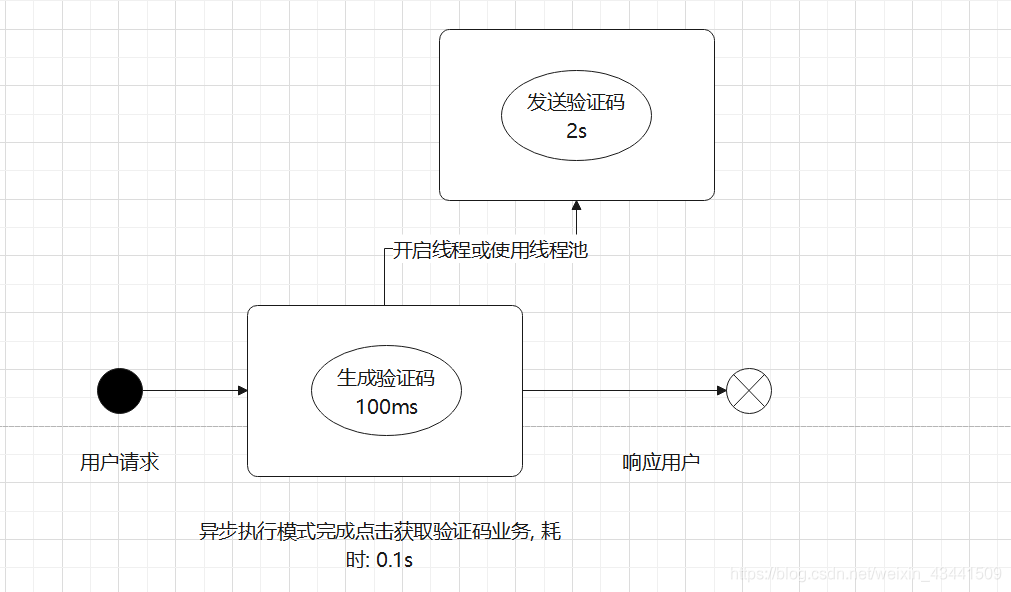
2. SpringBoot中的异步方法支持
@EnableAsync // 使用异步方法时需要提前开启(在启动类上或配置类上)
@Async // 被async注解修饰的方法由SpringBoot默认线程池(SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor)执行
@Service
public class ArticleServiceImpl {
// 查询文章
public String selectArticle() {
// TODO 模拟文章查询操作
System.out.println("查询任务线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "文章详情";
}
// 文章阅读量+1
@Async
public void updateReadCount() {
// TODO 模拟耗时操作
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("更新任务线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
@RestController
public class AsyncTestController {
@Autowired
private ArticleServiceImpl articleService;
/**
* 模拟获取文章后阅读量+1
*/
@PostMapping("/article")
public String getArticle() {
// 查询文章
String article = articleService.selectArticle();
// 阅读量+1
articleService.updateReadCount();
System.out.println("文章阅读业务执行完毕");
return article;
}
}
3. 自定义线程池执行异步方法
@EnableAsync // 开启多线程, 项目启动时自动创建
@Configuration
public class AsyncConfig {
@Bean("customExecutor")
public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor asyncOperationExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
// 设置核心线程数
executor.setCorePoolSize(8);
// 设置最大线程数
executor.setMaxPoolSize(20);
// 设置队列大小
executor.setQueueCapacity(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// 设置线程活跃时间(秒)
executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(60);
// 设置线程名前缀+分组名称
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("AsyncOperationThread-");
executor.setThreadGroupName("AsyncOperationGroup");
// 所有任务结束后关闭线程池
executor.setWaitForTasksToCompleteOnShutdown(true);
// 初始化
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
}
// 文章阅读量+1
@Async("customExecutor")
public void updateReadCount() {
// TODO 模拟耗时操作
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("更新文章阅读量线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
5. 如何捕获(无返回值的)异步方法中的异常
@EnableAsync // 开启多线程, 项目启动时自动创建
@Configuration
public class AsyncConfig implements AsyncConfigurer {
@Override
public Executor getAsyncExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
// 设置核心线程数
executor.setCorePoolSize(8);
// 设置最大线程数
executor.setMaxPoolSize(20);
// 设置队列大小
executor.setQueueCapacity(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// 设置线程活跃时间(秒)
executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(60);
// 设置线程名前缀+分组名称
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("AsyncOperationThread-");
executor.setThreadGroupName("AsyncOperationGroup");
// 所有任务结束后关闭线程池
executor.setWaitForTasksToCompleteOnShutdown(true);
// 初始化
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
@Override
public AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler getAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler() {
return new CustomAsyncExceptionHandler();
}
}
public class CustomAsyncExceptionHandler implements AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler {
@Override
public void handleUncaughtException(Throwable throwable, Method method, Object... obj) {
System.out.println("异常捕获---------------------------------");
System.out.println("Exception message - " + throwable.getMessage());
System.out.println("Method name - " + method.getName());
for (Object param : obj) {
System.out.println("Parameter value - " + param);
}
System.out.println("异常捕获---------------------------------");
}
}
5. 如何获取(有返回值)异步方法的返回值
无返回值的异步方法抛出异常不会影响Controller的主要业务逻辑
有返回值的异步方法抛出异常会影响Controller的主要业务逻辑
// 异步方法---------------------------------------------------------------------
@Async
public CompletableFuture updateReadCountHasResult() {
// TODO 模拟耗时操作
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("更新文章阅读量线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(100 + 1);
}
// Controller调用---------------------------------------------------------------------
@GetMapping("/article")
public String getArticle() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
// 查询文章
String article = articleService.selectArticle();
// 阅读量+1
CompletableFuture future = articleService.updateReadCountHasResult();
int count = 0;
// 循环等待异步请求结果
while (true) {
if(future.isCancelled()) {
System.out.println("异步任务取消");
break;
}
if (future.isDone()) {
count = future.get();
System.out.println(count);
break;
}
}
System.out.println("文章阅读业务执行完毕");
return article + count;
}
6. 异步方法带来的问题/拓展
异步方法只能声明在Service方法中在Controller直接调用才会生效, 异步方法被同级Service方法调用不会生效, 很奇怪?
异步方法 + 事务能顺利执行吗? 或许事务操作应该和异步操作分离开, 被Controller层调用时事务操作在前, 异步操作在后
异步方法执行失败后对Controller前半部分的非异步操作无影响, 因此说异步方法在整个业务逻辑中不是100%可靠的, 对于强一致性的业务来说不适用
还是消息中间件更为强大, RabbitMQ, Kafka…
推荐阅读:
朕已阅