【机器学习】三大树模型实战乳腺癌预测分类
公众号:尤而小屋
作者:Peter
编辑:Peter
今天给大家带来一篇新的UCI数据集建模的文章。
本文从数据的探索分析出发,经过特征工程和样本均衡性处理,使用决策树、随机森林、梯度提升树对一份女性乳腺癌的数据集进行分析和预测建模。
关键词:相关性、决策树、随机森林、降维、独热码、乳腺癌

数据集
数据是来自UCI官网,很老的一份数据,主要是用于分类问题,可以自行下载学习
https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/breast+cancer
导入库
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
%matplotlib inline
import plotly_express as px
import plotly.graph_objects as go
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.tree import export_graphviz
from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve, auc
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
from sklearn import metrics
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
导入数据
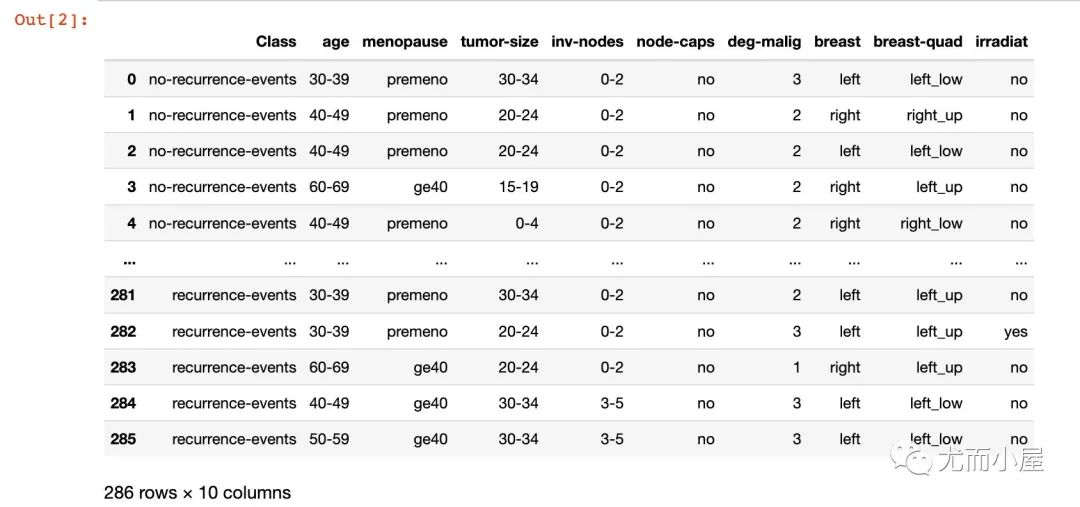
数据是来自UCI官网,下载到本地可以直接读取。只是这份数据是.data文件,没有文件头,我们需要自行指定对应的文件头(网上搜索的)
# 来自uci
df = pd.read_table("breast-cancer.data",
sep=",",
names=["Class","age","menopause","tumor-size","inv-nodes",
"node-caps","deg-malig","breast","breast-quad","irradiat"])
df
基本信息
In [3]:
df.dtypes # 字段类型
Out[3]:
全部是object类型,只有一个int64类型
Class object
age object
menopause object
tumor-size object
inv-nodes object
node-caps object
deg-malig int64
breast object
breast-quad object
irradiat object
dtype: object
In [4]:
df.isnull().sum() # 缺失值
Out[4]:
数据比较完整,没有缺失值
Class 0
age 0
menopause 0
tumor-size 0
inv-nodes 0
node-caps 0
deg-malig 0
breast 0
breast-quad 0
irradiat 0
dtype: int64
In [5]:
## 字段解释
columns = df.columns.tolist()
columns
Out[5]:
['Class',
'age',
'menopause',
'tumor-size',
'inv-nodes',
'node-caps',
'deg-malig',
'breast',
'breast-quad',
'irradiat']
下面是每个字段的含义和具体的取值范围:
| 属性名 | 含义 | 取值范围 |
|---|---|---|
| Class | 是否复发 | no-recurrence-events, recurrence-events |
| age | 年龄 | 10-19, 20-29, 30-39, 40-49, 50-59, 60-69, 70-79, 80-89, 90-99 |
| menopause | 绝经情况 | lt40(40岁之前绝经), ge40(40岁之后绝经), premeno(还未绝经) |
| tumor-size | 肿瘤大小 | 0-4, 5-9, 10-14, 15-19, 20-24, 25-29, 30-34, 35-39, 40-44, 45-49, 50-54, 55-59 |
| inv-nodes | 受侵淋巴结数 | 0-2, 3-5, 6-8, 9-11, 12-14, 15-17, 18-20, 21-23, 24-26, 27-29, 30-32, 33-35, 36-39 |
| node-caps | 有无结节帽 | yes, no |
| deg-malig | 恶性肿瘤程度 | 1, 2, 3 |
| breast | 肿块位置 | left, right |
| breast-quad | 肿块所在象限 | left-up, left-low, right-up, right-low, central |
| irradiat | 是否放疗 | yes,no |
去除缺失值
In [6]:
两个字段中的?就是本数据中的缺失值,我们直接选择非缺失值值的数据
df = df[(df["node-caps"] != "?") & (df["breast-quad"] != "?")]
len(df)
Out[6]:
277
字段处理
In [7]:
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
年龄段-age
In [8]:
age = df["age"].value_counts().reset_index()
age.columns = ["年龄段", "人数"]
age

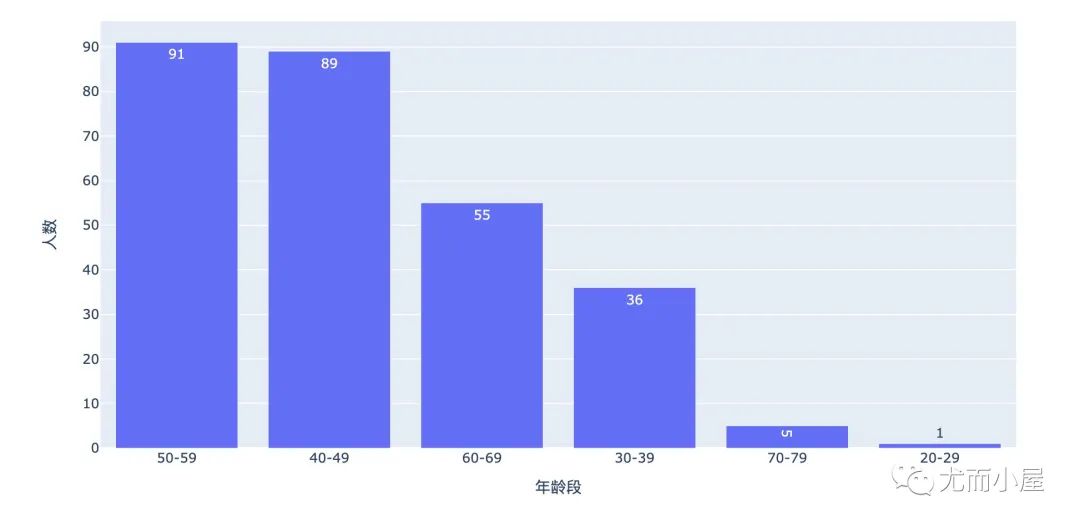
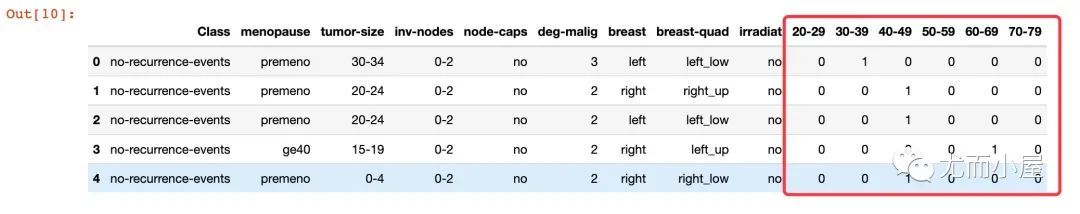
可以看到数据中大部分的用户集中在40-59岁。对年龄段执行独热码:
df = df.join(pd.get_dummies(df["age"]))
df.drop("age", axis=1, inplace=True)
df.head()
绝经-menopause
In [11]:
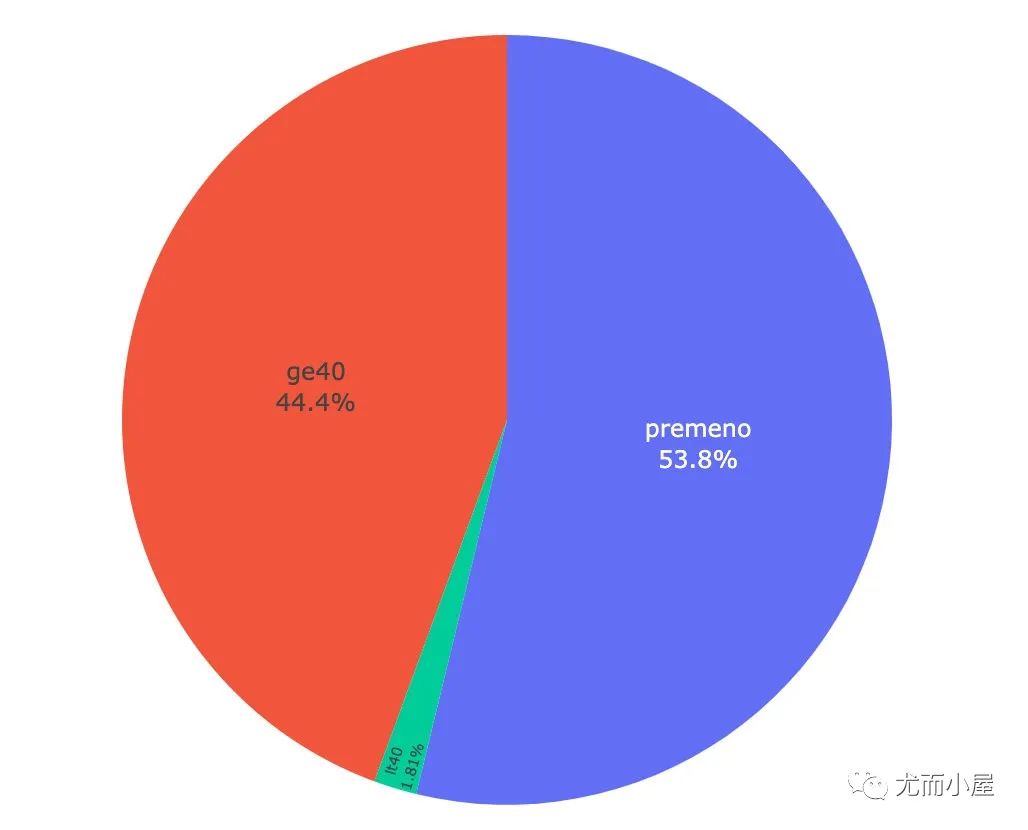
menopause = df["menopause"].value_counts().reset_index()
menopause
Out[11]:
| index | menopause | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | premeno | 149 |
| 1 | ge40 | 123 |
| 2 | lt40 | 5 |
In [12]:
fig = px.pie(menopause,names="index",values="menopause")
fig.update_traces(
textposition='inside',
textinfo='percent+label')
fig.show()
df = df.join(pd.get_dummies(df["menopause"])) # 独热码
df.drop("menopause",axis=1, inplace=True)
肿瘤大小-tumor-size
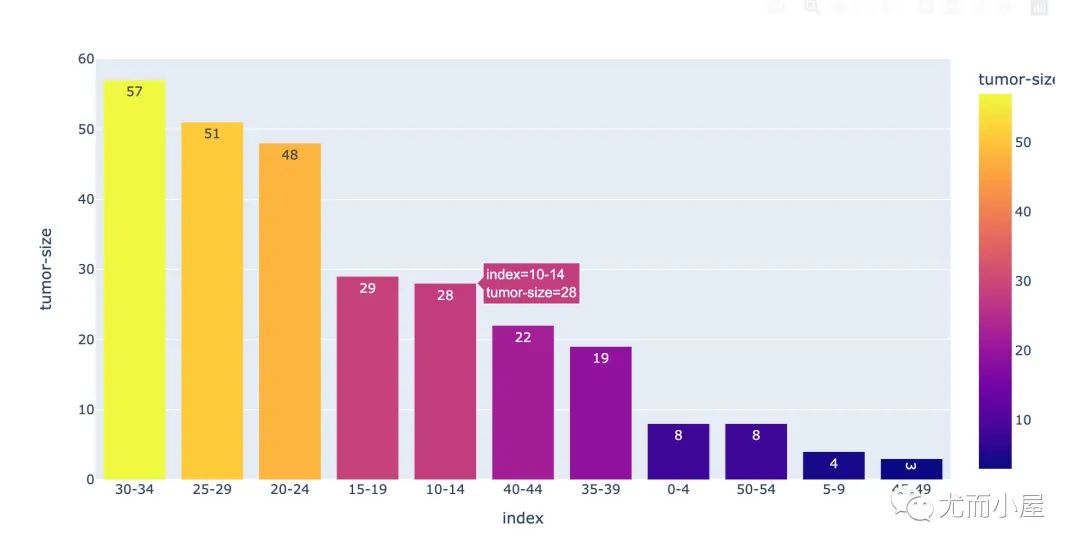
In [14]:
tumor_size = df["tumor-size"].value_counts().reset_index()
tumor_size
Out[14]:
| index | tumor-size | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 30-34 | 57 |
| 1 | 25-29 | 51 |
| 2 | 20-24 | 48 |
| 3 | 15-19 | 29 |
| 4 | 10-14 | 28 |
| 5 | 40-44 | 22 |
| 6 | 35-39 | 19 |
| 7 | 0-4 | 8 |
| 8 | 50-54 | 8 |
| 9 | 5-9 | 4 |
| 10 | 45-49 | 3 |
In [15]:
fig = px.bar(tumor_size,
x="index",
y="tumor-size",
color="tumor-size",
text="tumor-size")
fig.show()
df = df.join(pd.get_dummies(df["tumor-size"]))
df.drop("tumor-size",axis=1, inplace=True)
In [18]:
df = df.join(pd.get_dummies(df["inv-nodes"]))
df.drop("inv-nodes",axis=1, inplace=True)
有无结节帽-node-caps
In [19]:
df["node-caps"].value_counts()
Out[19]:
no 221
yes 56
Name: node-caps, dtype: int64
In [20]:
df = df.join(pd.get_dummies(df["node-caps"]).rename(columns={"no":"node_capes_no", "yes":"node_capes_yes"}))
df.drop("node-caps",axis=1, inplace=True)
恶性肿瘤程度-deg-malig
In [21]:
df["deg-malig"].value_counts()
Out[21]:
2 129
3 82
1 66
Name: deg-malig, dtype: int64
肿块位置-breast
In [22]:
df["breast"].value_counts()
Out[22]:
left 145
right 132
Name: breast, dtype: int64
In [23]:
df = df.join(pd.get_dummies(df["breast"]))
df.drop("breast",axis=1, inplace=True)
...
是否复发-Class
这个是最终预测的因变量,我们需要将文本信息转成0-1的数值信息
In [29]:
dic = {"no-recurrence-events":0, "recurrence-events":1}
df["Class"] = df["Class"].map(dic) # 实施转换
df
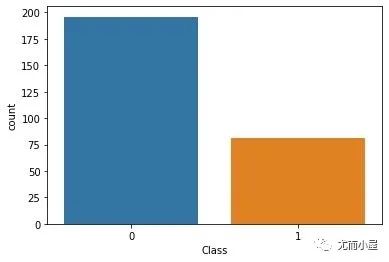
复发和非复发的统计:
sns.countplot(df['Class'],label="Count")
plt.show()
样本不均衡处理
In [31]:
# 样本量分布
df["Class"].value_counts()
Out[31]:
0 196
1 81
Name: Class, dtype: int64
In [32]:
from imblearn.over_sampling import SMOTE
In [33]:
X = df.iloc[:,1:]
y = df.iloc[:,0]
y.head()
Out[33]:
0 0
1 0
2 0
3 0
4 0
Name: Class, dtype: int64
In [34]:
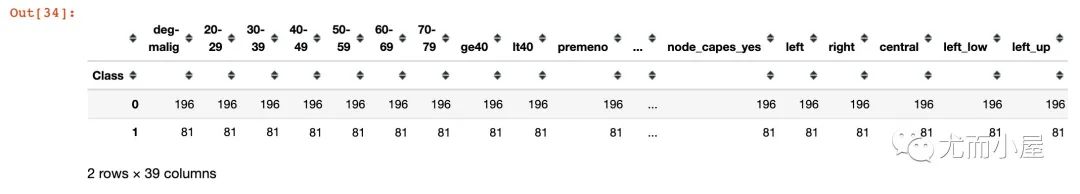
groupby_df = df.groupby('Class').count()
# 输出原始数据集样本分类分布
groupby_df
model_smote = SMOTE()
x_smote_resampled, y_smote_resampled = model_smote.fit_resample(X, y)
x_smoted = pd.DataFrame(x_smote_resampled,
columns=df.columns.tolist()[1:])
y_smoted = pd.DataFrame(y_smote_resampled,
columns=['Class'])
df_smoted = pd.concat([x_smoted, y_smoted],axis=1)
建模
相关性
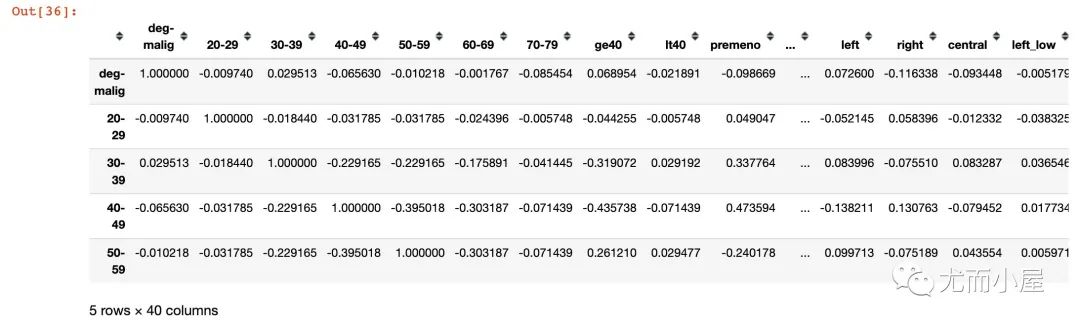
分析每个新字段和因变量之间的相关性
In [36]:
corr = df_smoted.corr()
corr.head()
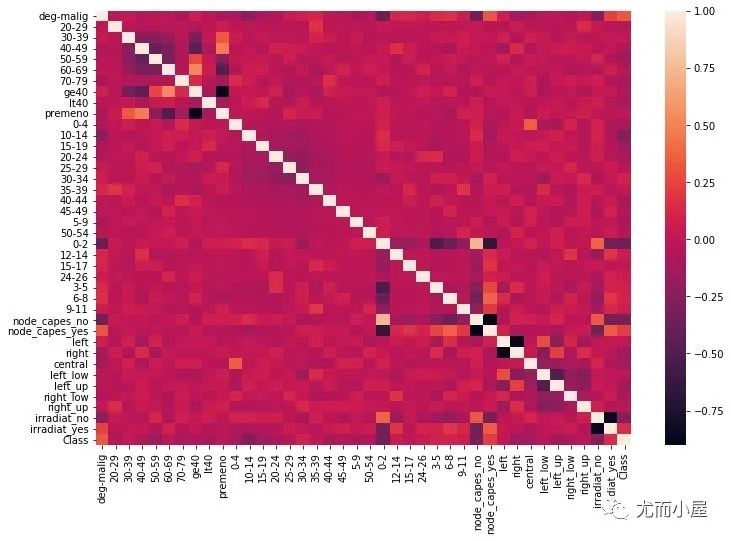
绘制相关性热力图:
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12,8))
sns.heatmap(corr)
plt.show()
数据集划分
In [38]:
X = df_smoted.iloc[:,:-1]
y = df_smoted.iloc[:,-1]
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(X,y,
test_size=0.20,
random_state=123)
决策树
In [39]:
dt = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=5)
dt.fit(X_train, y_train)
Out[39]:
DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=5)
In [40]:
# 预测
y_prob = dt.predict_proba(X_test)[:,1]
# 预测的概率转成0-1分类
y_pred = np.where(y_prob > 0.5, 1, 0)
dt.score(X_test, y_pred)
Out[40]:
1.0
In [41]:
# 混淆矩阵
confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
Out[41]:
array([[29, 8],
[19, 23]])
In [42]:
# 分类得分报告
print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred))
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.60 0.78 0.68 37
1 0.74 0.55 0.63 42
accuracy 0.66 79
macro avg 0.67 0.67 0.66 79
weighted avg 0.68 0.66 0.65 79
In [43]:
# roc
metrics.roc_auc_score(y_test, y_pred)
Out[43]:
0.6657014157014157
In [44]:
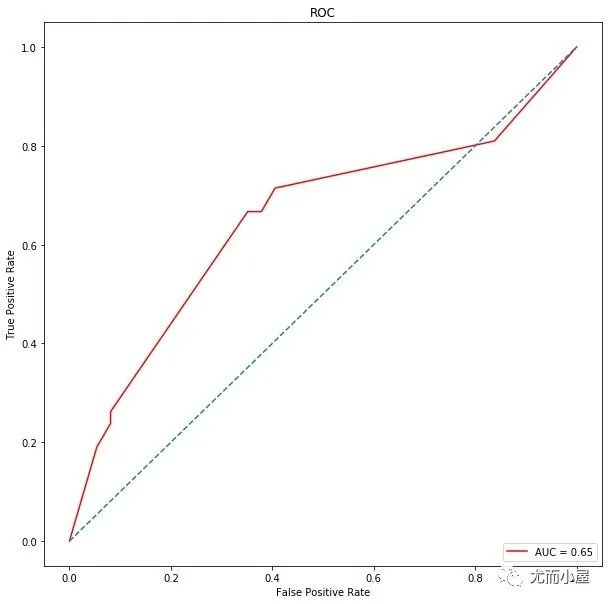
# roc曲线
from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve, auc
false_positive_rate, true_positive_rate, thresholds = roc_curve(y_test, y_prob)
roc_auc = auc(false_positive_rate, true_positive_rate)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.figure(figsize=(10,10)) # 画布
plt.title('ROC') # 标题
plt.plot(false_positive_rate, # 绘图
true_positive_rate,
color='red',
label = 'AUC = %0.2f' % roc_auc)
plt.legend(loc = 'lower right') # 图例位置
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1],linestyle='--') # 正比例直线
plt.axis('tight')
plt.xlabel('False Positive Rate')
plt.ylabel('True Positive Rate')
plt.show()
随机森林
In [45]:
rf = RandomForestClassifier(max_depth=5)
rf.fit(X_train, y_train)
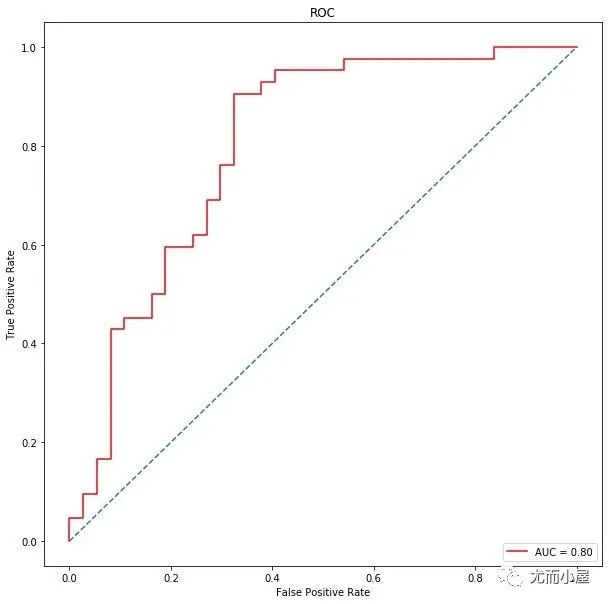
梯度提升树
In [50]:
from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingClassifier
In [51]:
gbc = GradientBoostingClassifier(loss='deviance',
learning_rate=0.1,
n_estimators=5,
subsample=1,
min_samples_split=2,
min_samples_leaf=1,
max_depth=3)
gbc.fit(X_train, y_train)
Out[51]:
GradientBoostingClassifier(n_estimators=5, subsample=1)
In [55]:
# roc曲线
from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve, auc
false_positive_rate, true_positive_rate, thresholds = roc_curve(y_test, y_prob)
roc_auc = auc(false_positive_rate, true_positive_rate)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.figure(figsize=(10,10)) # 画布
plt.title('ROC') # 标题
plt.plot(false_positive_rate, # 绘图
true_positive_rate,
color='red',
label = 'AUC = %0.2f' % roc_auc)
plt.legend(loc = 'lower right') # 图例位置
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1],linestyle='--') # 正比例直线
plt.axis('tight')
plt.xlabel('False Positive Rate')
plt.ylabel('True Positive Rate')
plt.show()
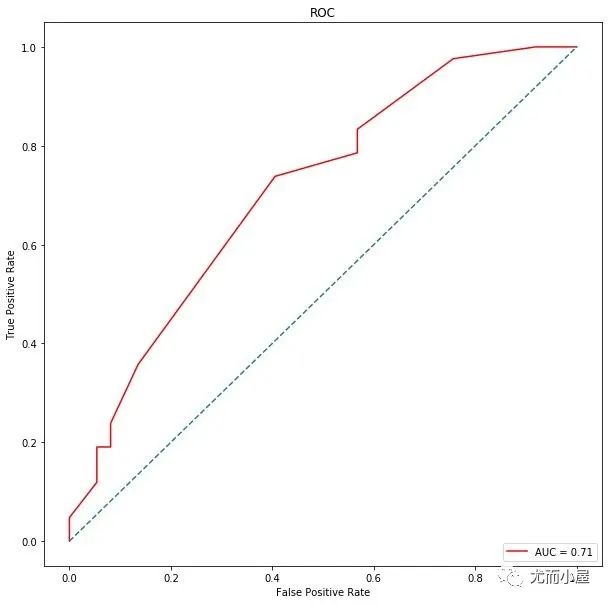
PCA降维
降维过程
In [56]:
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
pca = PCA(n_components=17)
pca.fit(X)
#返回所保留的17个成分各自的方差百分比
print(pca.explained_variance_ratio_)
[0.17513053 0.12941834 0.11453698 0.07323991 0.05889187 0.05690304
0.04869476 0.0393374 0.03703477 0.03240863 0.03062932 0.02574137
0.01887462 0.0180381 0.01606983 0.01453912 0.01318003]
In [57]:
sum(pca.explained_variance_ratio_)
Out[57]:
0.9026686181152915
降维后数据
In [58]:
X_NEW = pca.transform(X)
X_NEW
Out[58]:
array([[ 1.70510215e-01, 5.39929099e-01, -1.04314303e+00, ...,
-2.26541223e-01, -6.39332871e-02, -8.97923150e-02],
[-9.01105403e-01, 8.01693088e-01, 5.92260258e-01, ...,
9.66299251e-02, 1.40755806e-03, -2.74626972e-01],
[-6.05200264e-01, 6.08455330e-01, -1.00524376e+00, ...,
4.11416630e-02, 4.15705282e-02, -8.46941345e-02],
...,
[ 1.40652211e-02, 5.35906106e-01, 5.64150123e-02, ...,
1.70834934e-01, 7.11616391e-02, -1.72250445e-01],
[-4.41363597e-01, 9.11950641e-01, -4.22184256e-01, ...,
-4.13385344e-02, -7.64405982e-02, 1.04686148e-01],
[ 1.98533663e+00, -4.74547396e-01, -1.52557494e-01, ...,
2.72194184e-02, 5.71553613e-02, 1.78074886e-01]])
In [59]:
X_NEW.shape
Out[59]:
(392, 17)
重新划分数据
In [60]:
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(X_NEW,y,test_size=0.20,random_state=123)
再用随机森林
In [61]:
rf = RandomForestClassifier(max_depth=5)
rf.fit(X_train, y_train)
Out[61]:
RandomForestClassifier(max_depth=5)
In [62]:
# 预测
y_prob = rf.predict_proba(X_test)[:,1]
# 预测的概率转成0-1分类
y_pred = np.where(y_prob > 0.5, 1, 0)
rf.score(X_test, y_pred)
Out[62]:
1.0
In [63]:
# 混淆矩阵
confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
Out[63]:
array([[26, 11],
[13, 29]])
In [64]:
# roc
metrics.roc_auc_score(y_test, y_pred)
Out[64]:
0.6965894465894465
In [65]:
# roc曲线
from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve, auc
false_positive_rate, true_positive_rate, thresholds = roc_curve(y_test, y_prob)
roc_auc = auc(false_positive_rate, true_positive_rate)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))
plt.title('ROC')
plt.plot(false_positive_rate,
true_positive_rate,
color='red',
label = 'AUC = %0.2f' % roc_auc)
plt.legend(loc = 'lower right')
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1],linestyle='--')
plt.axis('tight')
plt.xlabel('False Positive Rate')
plt.ylabel('True Positive Rate')
plt.show()
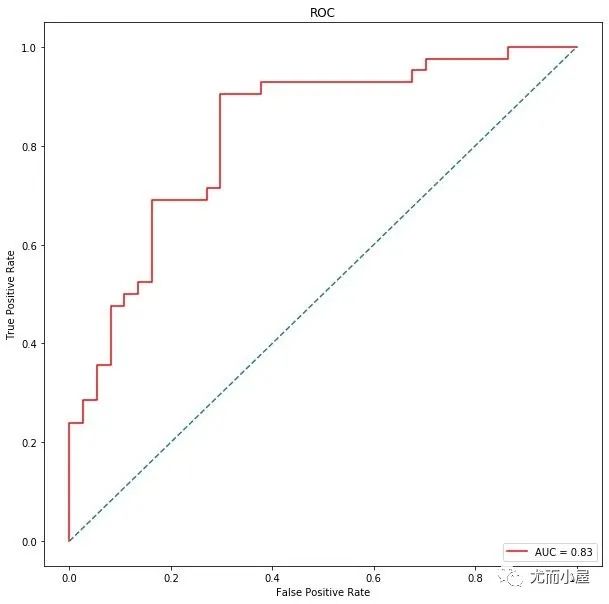
总结
从数据预处理和特征工程出发,建立不同的树模型表现来看,随机森林表现的最好,AUC值高达0.81,在经过对特征简单的降维之后,我们选择前17个特征,它们的重要性超过90%,再次建模,此时AUC值达到0.83。
往期精彩回顾
适合初学者入门人工智能的路线及资料下载 (图文+视频)机器学习入门系列下载 中国大学慕课《机器学习》(黄海广主讲) 机器学习及深度学习笔记等资料打印 《统计学习方法》的代码复现专辑 机器学习交流qq群955171419,加入微信群请扫码
