给 SpringBoot 服务添加健康检查
引子
公司的后端服务基于 SpringBoot 开发,部署在 K8S 集群中。在平时开发过程中,由于部署频繁,经常导致服务队对外表现为 502 不可用,非常影响前端开发体验。
如果服务长时间不可用,那么前端只能启用 mock 模式进行开发了。具体做法可以参见《前后端分离开发中前端需要克服的挑战》一文。
尽管前端有办法,但是作为后端服务,还是得保证服务的可用性,不能随意找借口搪塞。
实际上,公司的 dev 环境也在 AWS 集群上,配置并不低,而且需要的话可以继续调高配置。在部署时,观察 pod 的状态,的确是滚动更新的。
之所以在部署时服务会不可用,是因为没有配置服务就绪探针,K8S 没有办法获取 pod 里应用的状态,只能检查 pod 的状态。只要 pod 起来了,流量就会路由给它,但这时如果应用并未启动完毕,就会导致对外表现为 502 Bad Gateway。
因此,要解决这个问题,实现服务无宕机更新,就只需要配置好探针就行了。
给 SpringBoot 应用添加 actuator
测试
第一步,先把测试写好,文档化我们期待的行为:
import org.junit.Test;import org.junit.runner.RunWith;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.boot.availability.ApplicationAvailability;import org.springframework.boot.availability.AvailabilityChangeEvent;import org.springframework.boot.availability.LivenessState;import org.springframework.boot.availability.ReadinessState;import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.AutoConfigureMockMvc;import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;import org.springframework.test.context.ActiveProfiles;import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.assertThat;import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders.get;import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath;import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.status;@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)@ActiveProfiles("test")@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)@AutoConfigureMockMvcpublic class HealthCheckControllerTest {@Autowiredprivate ApplicationAvailability applicationAvailability;@Autowiredprivate MockMvc mockMvc;@Autowired private ApplicationContext context;@Testpublic void testHealthCheck() throws Exception {assertThat(applicationAvailability.getLivenessState()).isEqualTo(LivenessState.CORRECT);mockMvc.perform(get("/healthz/liveness")).andExpect(status().isOk()).andExpect(jsonPath("$.status.code").value("UP"));AvailabilityChangeEvent.publish(context, ReadinessState.REFUSING_TRAFFIC);assertThat(applicationAvailability.getReadinessState()).isEqualTo(ReadinessState.REFUSING_TRAFFIC);mockMvc.perform(get("/healthz/readiness")).andExpect(status().isServiceUnavailable()).andExpect(jsonPath("$.status.code").value("OUT_OF_SERVICE"));}}
添加依赖
以 maven 项目为例,在 pom 文件中添加:
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuatorartifactId>dependency>
配置项目
可以在 bootstrap.yml 中增加这样的配置:
management:endpoint:health:probes:enabled: truelivenessState:enabled: truereadinessState:enabled: trueendpoints:web:: /:health: healthz
这时测试可以通过了。也可以本地启动进行手动端到端验证。先启动:
mvn clean install && mvn spring-boot:run -pl your-representation-layer执行:
curl http://localhost:your-port/healthz/liveness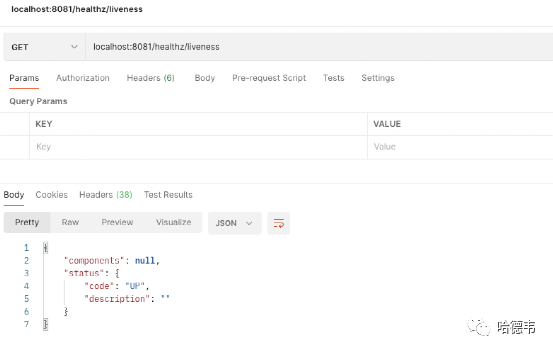
curl http://localhost:your-port/healthz/readiness
在 deployment 文件里配置探针
在 deployment 文件中增加如下配置项:
readinessProbe:httpGet:path: /healthz/readinessport: 8080initialDelaySeconds: 30timeoutSeconds: 10livenessProbe:httpGet:path: /healthz/livenessport: 8080initialDelaySeconds: 130timeoutSeconds: 10
大功告成,提交本次改动,后面的服务更新就不会影响前端开发了。当然,这只从运维层解决了服务的可用。对于开发层面,一定要注意,作为服务提供者,对于接口的修改,必须保证向前兼容。永远不要假设和要求前端和你同时更新(根本做不到,比如对于微信小程序,发布后,仍然有最长 24 小时的更新延迟;如果是原生 APP,用户不一定自动更新的)。
总结
监控和可观测性对于分布式系统至关重要,这两点要求系统在运行时提供健康检查机制。假如现有的系统没有这个机制,那么可以参考《利用 Vector 从日志创建指标来提高系统的可观测性》一文,从日志的角度来弥补。然而,正如本文开头提到的,这依然会影响平时的开发体验,所以,本文详细介绍了如何在 SpringBoot 应用中增加健康检查机制,一来解决了开发体验问题,二来为后续捕获有用的健康指标从而与流行的工具集成以提高系统的可观测性打下了基础。
