图算法系列之计算图中最短路径
共 9588字,需浏览 20分钟
·
2021-05-13 17:59
吐血整理程序员必读书单:https://github.com/silently9527/ProgrammerBooks
微信公众号:贝塔学Java
前言
在前面两篇中我们通过深度优先搜索可以从图中找出一条通过顶点v到顶点w的路径,但是深度优先搜索与顶点的输入有很大的关系,找出来的路径也不一定是最短的,通常情况下我们很多时候需要找出图中的最短路径,比如:地图功能。这里我们就需要使用到广度优先搜索算法
广度优先搜索
依然使用之前定义的寻找路径的API
public class Paths {
Paths(Graph graph, int s);
boolean hasPathTo(int v); //判断出从s->v是否存在路径
Iterable<Integer> pathTo(int v); //如果存在路径,返回路径
}
在广度优先搜索中,为了找出最短路径,我们需要按照起点的顺序来遍历所有的顶点,而不在是使用递归来实现;算法的思路:
使用队列来保存已经被标记过但是邻接表还未被遍历过的顶点 取出队列中的下一个顶点v并标记它 将v相邻的所有未被标记的顶点加入到队列
在该算法中,为了保存路径,我们依然需要使用一个边的数组edgeTo[],用一颗父链树来表示根节点到所有连通顶点的最短路径。
public class BreadthFirstPaths {
private boolean marked[];
private int[] edgeTo;
private int s;
private Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedListQueue<>();
public BreadthFirstPaths(Graph graph, int s) {
this.s = s;
this.marked = new boolean[graph.V()];
this.edgeTo = new int[graph.V()];
bfs(graph, s);
}
private void bfs(Graph graph, int s) {
this.marked[s] = true;
this.queue.enqueue(s);
while (!this.queue.isEmpty()) {
Integer v = this.queue.dequeue();
for (int w : graph.adj(v)) {
if (!this.marked[w]) {
this.marked[w] = true;
this.edgeTo[w] = v;
this.queue.enqueue(w);
}
}
}
}
public boolean hasPathTo(int v) {
return this.marked[v];
}
public Iterable<Integer> pathTo(int v) {
if (!hasPathTo(v)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("s不能到达v");
}
Stack<Integer> stack = new LinkedListStack<>();
stack.push(v);
while (edgeTo[v] != s) {
stack.push(edgeTo[v]);
v = edgeTo[v];
}
stack.push(s);
return stack;
}
}
以下图为列,来看看广度优先搜索的运行轨迹
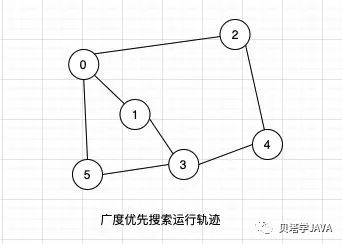

单元测试的代码:
@Test
public void test() {
Graph graph = new Graph(8);
graph.addEdge(0, 1);
graph.addEdge(0, 2);
graph.addEdge(0, 5);
graph.addEdge(1, 3);
graph.addEdge(2, 4);
graph.addEdge(4, 3);
graph.addEdge(5, 3);
graph.addEdge(6, 7);
BreadthFirstPaths paths = new BreadthFirstPaths(graph, 0);
System.out.println(paths.hasPathTo(5));
System.out.println(paths.hasPathTo(2));
System.out.println(paths.hasPathTo(6));
paths.pathTo(5).forEach(System.out::print);
System.out.println();
paths.pathTo(4).forEach(System.out::print);
System.out.println();
paths.pathTo(2).forEach(System.out::print);
System.out.println();
paths.pathTo(3).forEach(System.out::print);
}
执行的结果与我们分析的运行轨迹一致

符号图
最近几篇文章一起学习到的图算法都是以数字作为了顶点,是因为数字来实现这些算法会非常的简洁方便,但是在实际的场景中,通常都是使用的字符作为顶点而非数字,比如:地图上的位置、电影与演员的关系。
为了满足实际的场景,我们只需要在数字与字符串的关系做一个映射,此时我们会想到之前文章实现的map(通过二叉树实现map、红黑树实现map、哈希表实现map等等,有兴趣的同学可以去翻翻),使用Map来维护字符串和数字的映射关系。
public interface SymbolGraph {
boolean contains(String key); //判断是否存在顶点
int index(String key); //通过名称返回对应的数字顶点
String name(int v); //通过数字顶点返回对应的字符名称
Graph graph();
}
实现的思路:
使用Map来保存字符串-数字的映射,key为字符串,value为数字 使用一个数组来反向映射数字-字符串,数组的下标对应数字顶点,值对应字符串名称
假设构造图的顶点与边是通过字符串来表示的,如:a,b,c,d\nb,a,h,l,p\ng,s,z 使用\n分隔的每段第一个字符串表示顶点v,后面的表示与顶点v相连的相邻顶点;
实际的过程可以根据具体情况来确定,不一定非得这种字符串,可以来源于数据库,也可以来源于网路的请求。
代码实现如下:
public class SymbolGraph {
private Map<String, Integer> map = new RedBlack23RedBlackTreeMap<>();
private String[] keys;
private Graph graph;
public SymbolGraph(String text) {
Arrays.stream(text.split("\n")).forEach(line -> {
String[] split = line.split(",");
for (int i = 0; i < split.length; i++) {
map.put(split[i], i);
}
});
this.keys = new String[map.size()];
map.keys().forEach(key -> {
this.keys[this.map.get(key)] = key;
});
this.graph = new Graph(this.keys.length);
Arrays.stream(text.split("\n")).forEach(line -> {
String[] split = line.split(",");
int v = this.map.get(split[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < split.length; i++) {
this.graph.addEdge(v, this.map.get(split[i]));
}
});
}
public boolean contains(String key) {
return map.contains(key);
}
public int index(String key) {
return map.get(key);
}
public String name(int index) {
return this.keys[index];
}
public Graph graph() {
return this.graph;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString("323\n2323".split("\n")));
}
}
文中所有源码已放入到了github仓库:https://github.com/silently9527/JavaCore
最后(点关注,不迷路)
文中或许会存在或多或少的不足、错误之处,有建议或者意见也非常欢迎大家在评论交流。
最后,写作不易,请不要白嫖我哟,希望朋友们可以点赞评论关注三连,因为这些就是我分享的全部动力来源🙏
