【神经网络搜索】Microsoft NNI 有关NAS的核心类
共 13478字,需浏览 27分钟
·
2021-03-12 11:06
【GiantPandaCV导语】本文介绍NNI PyTorch版实现神经网络过程搜索过程中的几个重要的类,比如LayerChoice和InputChoice,对这两个类有了初步认识以后,就可以设计自己的搜索空间。
1. Mutable类
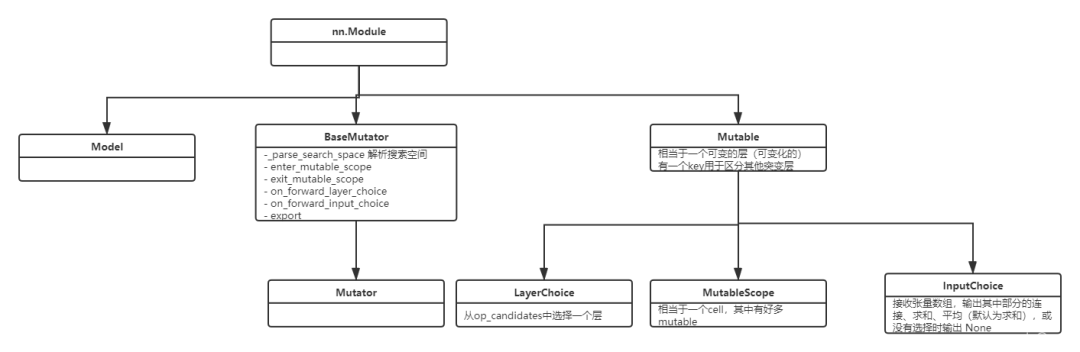
上图是NNI的有关NAS的部分类图,Mutable类表示的意思是可变的,这也是实现NAS中的核心,操作是可变动的,具体选择什么操作需要优化器,也就是tuner来决定。
Mutable被设计成一个普通层,具有所有操作的权重。
Mutator中应该包含网络架构的状态和权重,而不是层本身。
Mutable对象有一个key,用于标记mutable对象的身份。用户可以根据key来进行共享不同mutable对象之间的决定。
在Mutator的实现中,Mutator应该使用key区分不同的mutable对象。如果两个mutable对象的key是相同的,说明并不需要对其进行区分,即这两个mutable对象是相似的。
当前key的默认作用域是全局的。默认情况下,key使用counter从1开始计数,来自动生成unique id
Mutable类属于模型级别的设置,counter是程序级别的。
class Mutable(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, key=None):
super().__init__()
if key is not None:
if not isinstance(key, str):
key = str(key)
logger.warning("Warning: key \"%s\" is not string, converted to string.", key)
self._key = key
else:
self._key = self.__class__.__name__ + str(global_mutable_counting())
self.init_hook = self.forward_hook = None
在初始化的时候,需要接收key,如果没有特别设置key,那就通过global_mutable_counting()方法返回全局变量counter数量。
2. MutableScope
MutableScope代码实现非常短,如下:
class MutableScope(Mutable):
def __init__(self, key):
super().__init__(key=key)
def __call__(self, *args, **kwargs):
try:
self._check_built()
self.mutator.enter_mutable_scope(self)
return super().__call__(*args, **kwargs)
finally:
self.mutator.exit_mutable_scope(self)
MutableScope是继承了Mutable对象,也有一个key,他是比操作更高层次的抽象。类似的概念有子图,子模块,可以看作一系列操作的集合。
MutableScope可以更好的帮助Mutator做决策,将其看作略高层次的抽象。 如果没有标注为mutable scope, 那么搜索空间将会展开为一个列表。如果一个模块是在mutable scope中定义,那么将被视为sub-search-space, 子搜索空间,并且这些mutable scope之间也可以相互嵌套。 Mutator有两种方法使用mutable scope: 一种是初始化的时候,通过树的形式进行初始化搜索空间。 另一种是实现' enter_mutable_scope '和' exit_mutable_scope '两个方法 Mutable Scope也是一种Mutable对象,只不过其比较特殊,包含的内容不是普通的操作opration, 而是Mutable对象。Mutable Scope也会在搜索空间中被枚举出来,但是不应该出现在选项的字典中。
3. LayerChoice
LayerChoice类的核心功能是从候选操作中挑选一个,将该操作施加到输入得到输出结果。在特殊情况下,可以选择zero 或者选择多个操作。Layer Choice不允许嵌套。主要有以下几个参数:
op_candidates: 候选操作,可以是nn.Module列表或字典 reduction: 可以从mean, concat, sum, none几种选择。 return_mask: 决定返回结果是否包含mask key:input_choice的key
class LayerChoice(Mutable):
def __init__(self, op_candidates, reduction="sum", return_mask=False, key=None):
super().__init__(key=key)
self.names = []
if isinstance(op_candidates, OrderedDict):
for name, module in op_candidates.items():
assert name not in ["length", "reduction", "return_mask", "_key", "key", "names"], \
"Please don't use a reserved name '{}' for your module.".format(name)
self.add_module(name, module) # 添加模块进来
self.names.append(name)
elif isinstance(op_candidates, list):
for i, module in enumerate(op_candidates):
self.add_module(str(i), module)
self.names.append(str(i)) # list的画就手动添加name
else:
raise TypeError("Unsupported op_candidates type: {}".format(type(op_candidates)))
self.reduction = reduction
self.return_mask = return_mask # 是否同时return mask 和 tensor
可以看出LayerChoice就是一个类似于列表的类,其中包含了候选的操作,可以通过add_module的方式将候选操作添加到LayerChoice这个类中。
def forward(self, *args, **kwargs):
"""
Returns
-------
tuple of tensors
Output and selection mask. If ``return_mask`` is ``False``, only output is returned.
"""
out, mask = self.mutator.on_forward_layer_choice(self, *args, **kwargs)
if self.return_mask:
return out, mask
return out
前向传播的时候,是mutator的on_forward_layer_choice函数进行控制具体的操作,return_mask控制是否同时输出mask和tensor。
一个调用的例子:
self.op_choice = LayerChoice(OrderedDict([
("conv3x3", nn.Conv2d(3, 16, 128)),
("conv5x5", nn.Conv2d(5, 16, 128)),
("conv7x7", nn.Conv2d(7, 16, 128))
]))
4. InputChoice
InputChoice是用来解决网络层与层之间连接的问题,有以下几个参数:
n_candidates: 是一个数,选择多少个作为input choose_from: 是一个装满key的列表,都是过去已经生成的mutable对象的key。也可以是InputChoice.NO_KEY代表 n_chosen: 选择的输入的个数,如果不设置,那就可以选择任何数量的组合。 reduction: 规约方式有mean, concat, sum, none。 return_mask&key同上。
综合来说,Input Choice就是从choose_from对应key中选择n_chosen个输入, 其中n_candidates决定了forward函数中,候选选项中选择的个数。
举个例子:
class Cell(MutableScope):
pass
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
self.cell1 = Cell("cell1")
self.cell2 = Cell("cell2")
self.op = LayerChoice([conv3x3(), conv5x5()], key="op")
self.input_choice = InputChoice(choose_from=["cell1", "cell2", "op", InputChoice.NO_KEY])
def forward(self, x):
x1 = max_pooling(self.cell1(x))
x2 = self.cell2(x)
x3 = self.op(x)
x4 = torch.zeros_like(x)
return self.input_choice([x1, x2, x3, x4])
InputChoice的源码实现:
class InputChoice(Mutable):
NO_KEY = ""
def __init__(self, n_candidates=None, choose_from=None, n_chosen=None,
reduction="sum", return_mask=False, key=None):
super().__init__(key=key)
# precondition check
assert n_candidates is not None or choose_from is not None, "At least one of `n_candidates` and `choose_from`" \
"must be not None."
if choose_from is not None and n_candidates is None:
n_candidates = len(choose_from) # choose_from 不为None,n_candidate就是其长度
elif choose_from is None and n_candidates is not None:
choose_from = [self.NO_KEY] * n_candidates # 将空白字符串作为key
assert n_candidates == len(choose_from), "Number of candidates must be equal to the length of `choose_from`."
assert n_candidates > 0, "Number of candidates must be greater than 0."
assert n_chosen is None or 0 <= n_chosen <= n_candidates, "Expected selected number must be None or no more " \
"than number of candidates."
self.n_candidates = n_candidates
self.choose_from = choose_from.copy()
self.n_chosen = n_chosen
self.reduction = reduction
self.return_mask = return_mask
def forward(self, optional_inputs):
# optional_inputs是一个列表,里边是所有可选的输入张量
optional_input_list = optional_inputs
if isinstance(optional_inputs, dict):
optional_input_list = [optional_inputs[tag] for tag in self.choose_from]
assert isinstance(optional_input_list, list), \
"Optional input list must be a list, not a {}.".format(type(optional_input_list))
assert len(optional_inputs) == self.n_candidates, \
"Length of the input list must be equal to number of candidates."
out, mask = self.mutator.on_forward_input_choice(self, optional_input_list)
if self.return_mask:
return out, mask
return out
前向传播的选择还是通过调用mutator的on_forward_input_choice函数来决定选择哪条路径连接。
本文主要介绍了nni中搜索空间指定最核心的几个类,通过使用这些类就可以做到构建自己的搜索空间。最近nni更新了2.1版本retiarii等新的功能特性, 允许用户以高度的灵活性表达各种搜索空间,重用许多前沿搜索算法,更加易用,准备踩坑。
- END -
欢迎添加笔者加入交流群或者进行学术交流合作
