神经网络之 CNN 与 RNN 的关系

来源:人工智能AI技术 本文约6000字,建议阅读12分钟
本文为你介绍对CNN和RNN的理解。
1、CNN介绍
1.1 Why CNN for Image
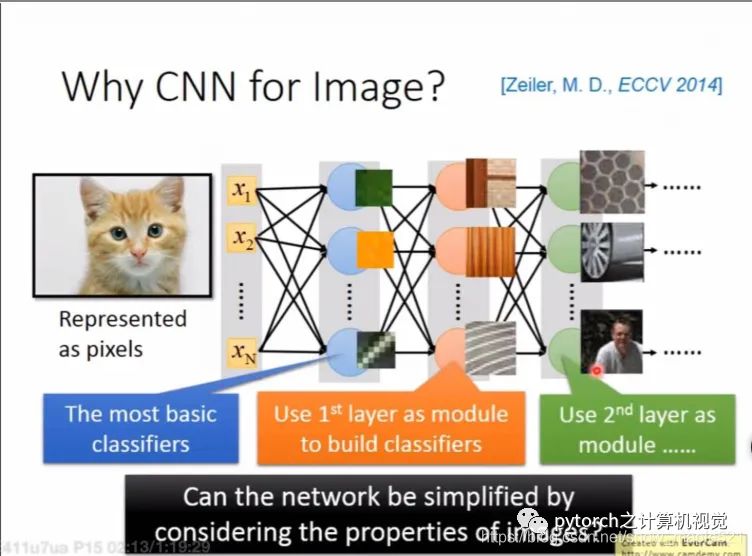
大部分的patterns要比整张图片小,一个神经元不需要去观察整个图片,只需要观察图片的一小部分就能找到一个想要的pattern,例如:给定一张图片,第一个hidden layer的某个神经元找图像中的鸟的嘴,另一个神经元找鸟的爪子。如下图只需要看红色框不需要观察整张图就可以找到鸟嘴。

不同位置的鸟嘴只需要训练一个识别鸟嘴的参数就Ok了,不需要分别训练。 我们可以采用子样品来使图片变小,子样不会改变目标图像。
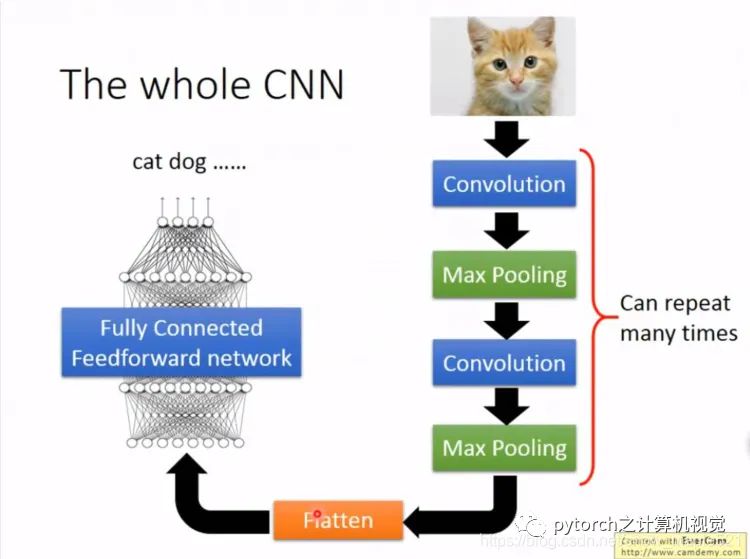
1.2 CNN架构图
1.3 卷积层
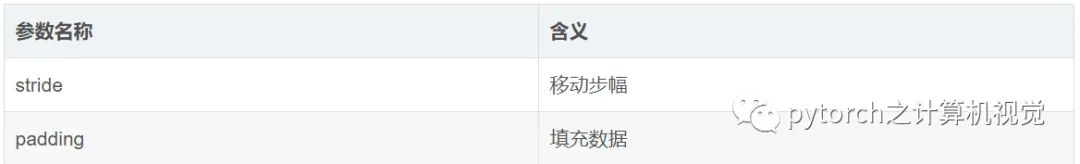
1.3.1 重要参数
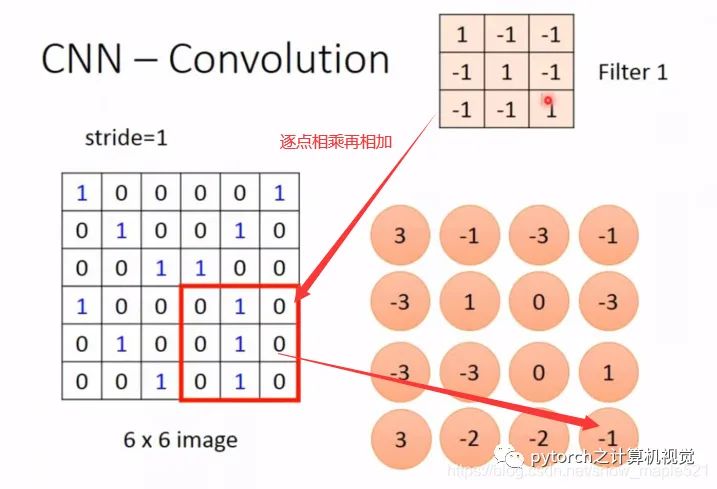
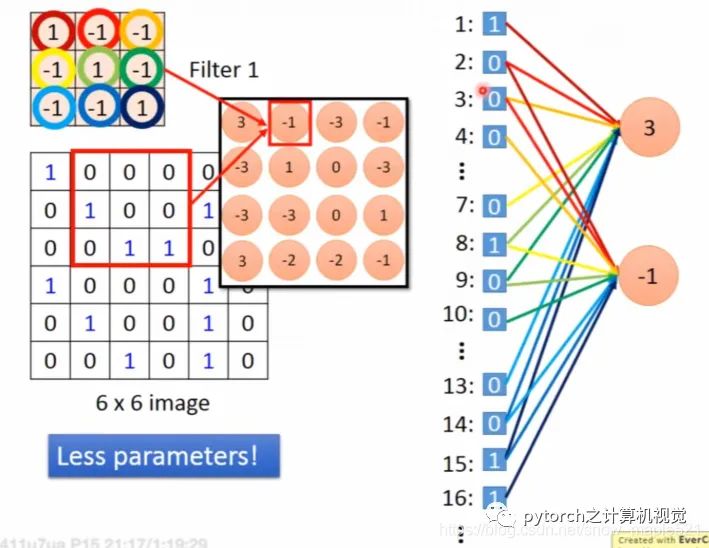
1.3.2 卷积计算
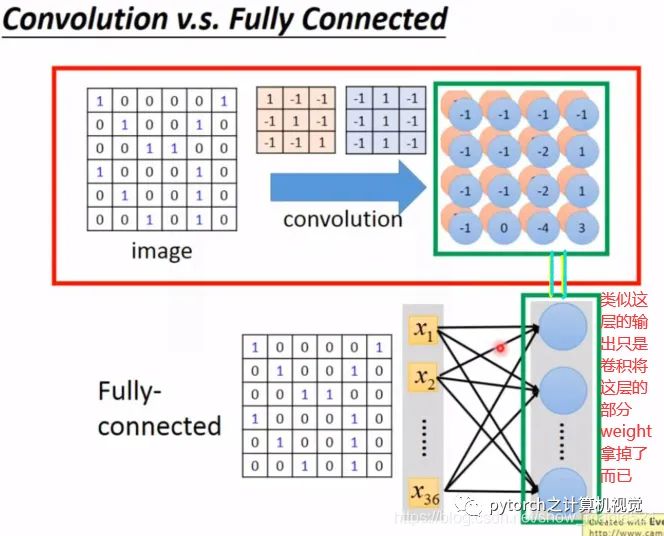
1.3.3 卷积层与全连接层的关系
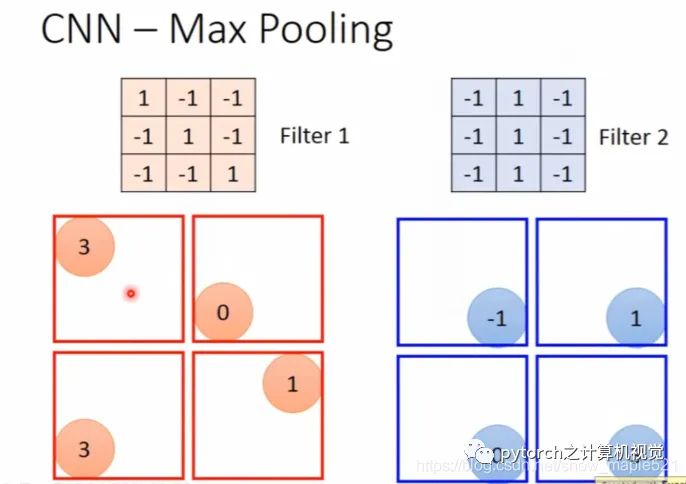
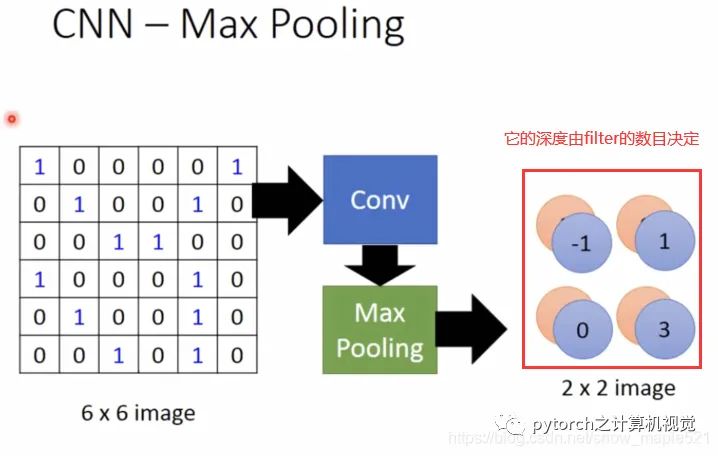
1.4 池化层
1.5 应用
torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels: int, #输入图像的通道数out_channels: int, #卷积产生的输出通道数kernel_size: Union[T, Tuple[T, T]], #卷积核大小stride: Union[T, Tuple[T, T]] = 1, #卷积的步数 默认:1padding: Union[T, Tuple[T, T]] = 0, #0填充添加到输入的两边 默认:0dilation: Union[T, Tuple[T, T]] = 1, #核元素之间的间距 默认:1groups: int = 1, #从输入通道到输出通道的阻塞链接数,默认:1#groups:控制输入和输出之间的连接,输入和输出通道数必须被组整除,#当groups=1:所有输入移交给所有输出#当groups=2:相当于两个卷积层,一个看到一半的输入通道并产生一半的输出通道,将两个合并#当groups=in_channels:每个通道都有自己的一组过滤器,其大小为out_channel/in_channelbias: bool = True, #将可学习的偏差添加到输出中 默认:truepadding_mode: str = 'zeros')#注:kenerl_size,stride,padding,dilation参数类型可以是int,可以是tuple,当是tuple时,第一个int是高度维度,第二个是宽度维度。当是单个int时,高度宽度值相同# 方形核和等步幅m = nn.Conv2d(16, 33, 3, stride=2)# 非方形核和不等步幅和填充m = nn.Conv2d(16, 33, (3, 5), stride=(2, 1), padding=(4, 2))# 非方形核和不等步幅和填充和扩展m = nn.Conv2d(16, 33, (3, 5), stride=(2, 1), padding=(4, 2), dilation=(3, 1))input = torch.randn(20, 16, 50, 100)output = m(input)
import torchvision.models as modelsimport torch.nn as nnimport torchfrom torchsummary import summarydevice = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')model = models.vgg16(pretrained=True).to(device)print(model)
VGG((features): Sequential((0): Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))(1): ReLU(inplace)(2): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))(3): ReLU(inplace)(4): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)(5): Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))(6): ReLU(inplace)(7): Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))(8): ReLU(inplace)(9): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)(10): Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))(11): ReLU(inplace)(12): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))(13): ReLU(inplace)(14): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))(15): ReLU(inplace)(16): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)(17): Conv2d(256, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))(18): ReLU(inplace)(19): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))(20): ReLU(inplace)(21): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))(22): ReLU(inplace)(23): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)(24): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))(25): ReLU(inplace)(26): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))(27): ReLU(inplace)(28): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))(29): ReLU(inplace)(30): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False))(classifier): Sequential((0): Linear(in_features=25088, out_features=4096, bias=True)(1): ReLU(inplace)(2): Dropout(p=0.5)(3): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=4096, bias=True)(4): ReLU(inplace)(5): Dropout(p=0.5)(6): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=1000, bias=True)))model.classifier = nn.Sequential(*list(model.classifier.children())[:-1]) # remove last fc layerprint(model)summary(model,(3,224,224))
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #================================================================Conv2d-1 [-1, 64, 224, 224] 1,792ReLU-2 [-1, 64, 224, 224] 0Conv2d-3 [-1, 64, 224, 224] 36,928ReLU-4 [-1, 64, 224, 224] 0MaxPool2d-5 [-1, 64, 112, 112] 0Conv2d-6 [-1, 128, 112, 112] 73,856ReLU-7 [-1, 128, 112, 112] 0Conv2d-8 [-1, 128, 112, 112] 147,584ReLU-9 [-1, 128, 112, 112] 0MaxPool2d-10 [-1, 128, 56, 56] 0Conv2d-11 [-1, 256, 56, 56] 295,168ReLU-12 [-1, 256, 56, 56] 0Conv2d-13 [-1, 256, 56, 56] 590,080ReLU-14 [-1, 256, 56, 56] 0Conv2d-15 [-1, 256, 56, 56] 590,080ReLU-16 [-1, 256, 56, 56] 0MaxPool2d-17 [-1, 256, 28, 28] 0Conv2d-18 [-1, 512, 28, 28] 1,180,160ReLU-19 [-1, 512, 28, 28] 0Conv2d-20 [-1, 512, 28, 28] 2,359,808ReLU-21 [-1, 512, 28, 28] 0Conv2d-22 [-1, 512, 28, 28] 2,359,808ReLU-23 [-1, 512, 28, 28] 0MaxPool2d-24 [-1, 512, 14, 14] 0Conv2d-25 [-1, 512, 14, 14] 2,359,808ReLU-26 [-1, 512, 14, 14] 0Conv2d-27 [-1, 512, 14, 14] 2,359,808ReLU-28 [-1, 512, 14, 14] 0Conv2d-29 [-1, 512, 14, 14] 2,359,808ReLU-30 [-1, 512, 14, 14] 0MaxPool2d-31 [-1, 512, 7, 7] 0Linear-32 [-1, 4096] 102,764,544ReLU-33 [-1, 4096] 0Dropout-34 [-1, 4096] 0Linear-35 [-1, 4096] 16,781,312ReLU-36 [-1, 4096] 0Dropout-37 [-1, 4096] 0================================================================Total params: 134,260,544Trainable params: 134,260,544Non-trainable params: 0----------------------------------------------------------------Input size (MB): 0.57Forward/backward pass size (MB): 218.58Params size (MB): 512.16Estimated Total Size (MB): 731.32
2、RNN介绍
2.1 引言
I would like to arrive Taipei on November 2nd;这里的Taipei就是Destination,November 2nd就是time of arrival;

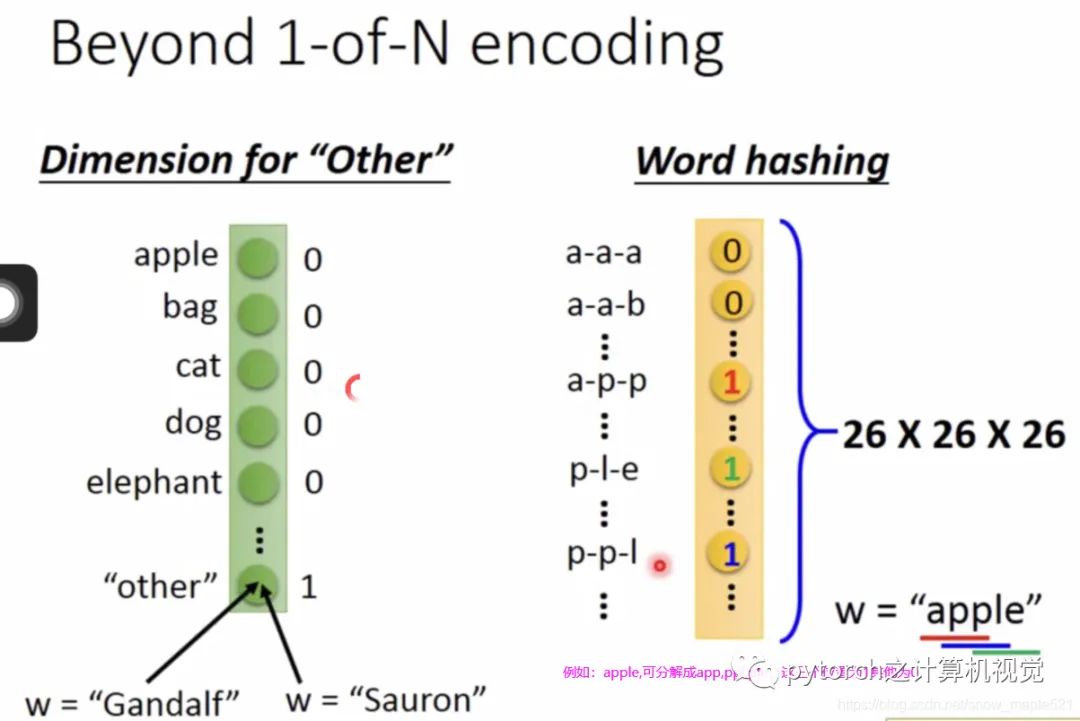
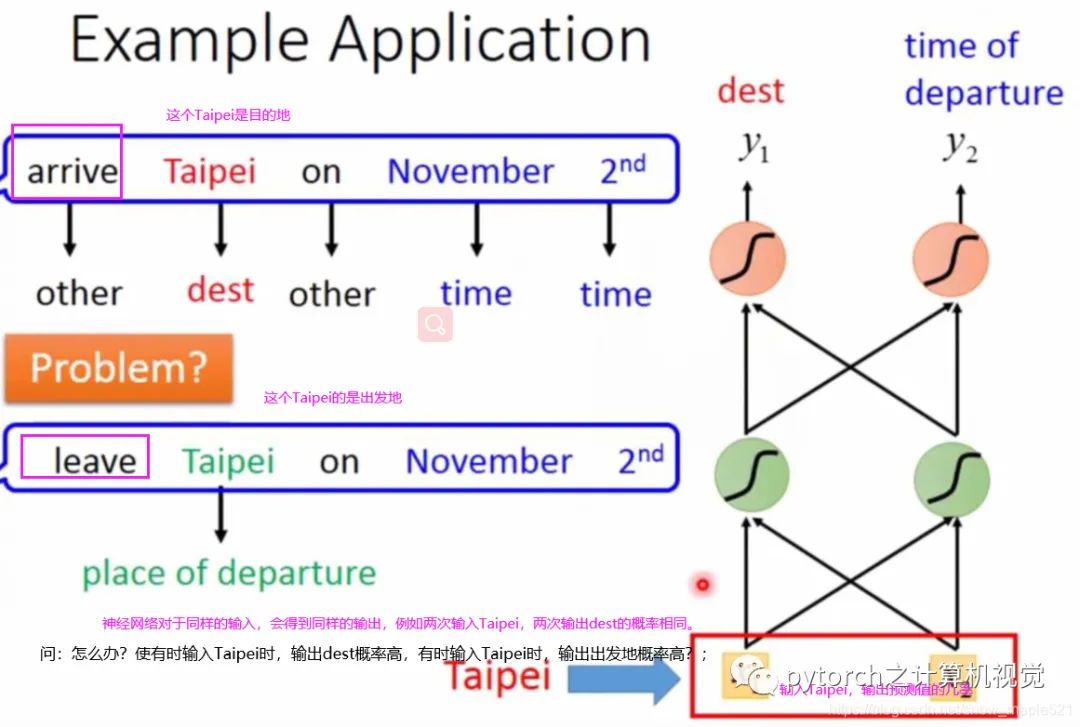
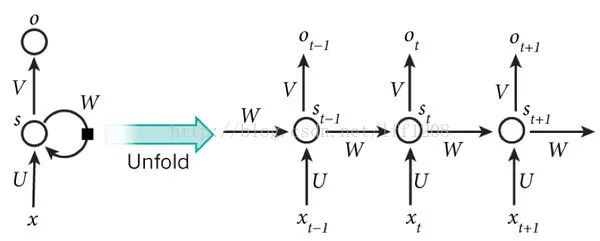
2.2 RNN简介
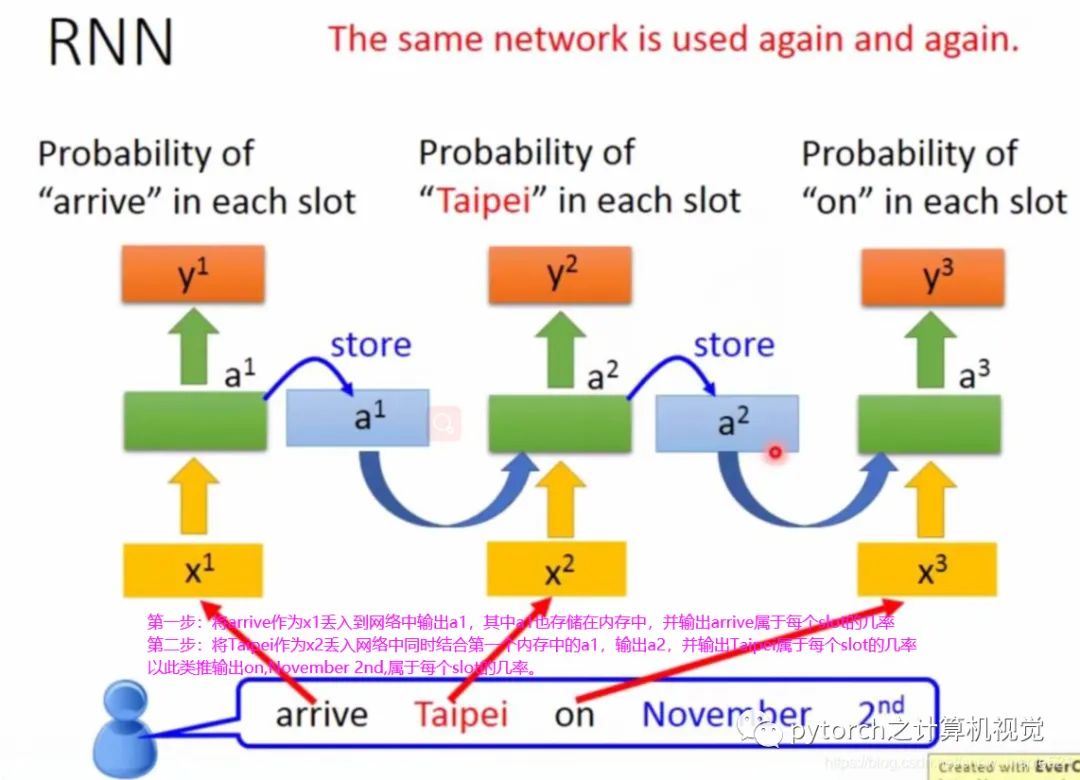
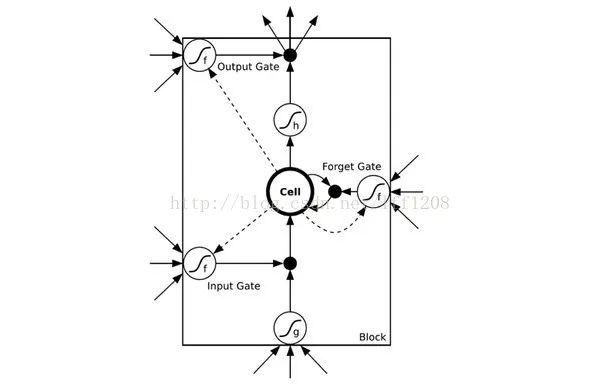
2.3 RNN之LSTM
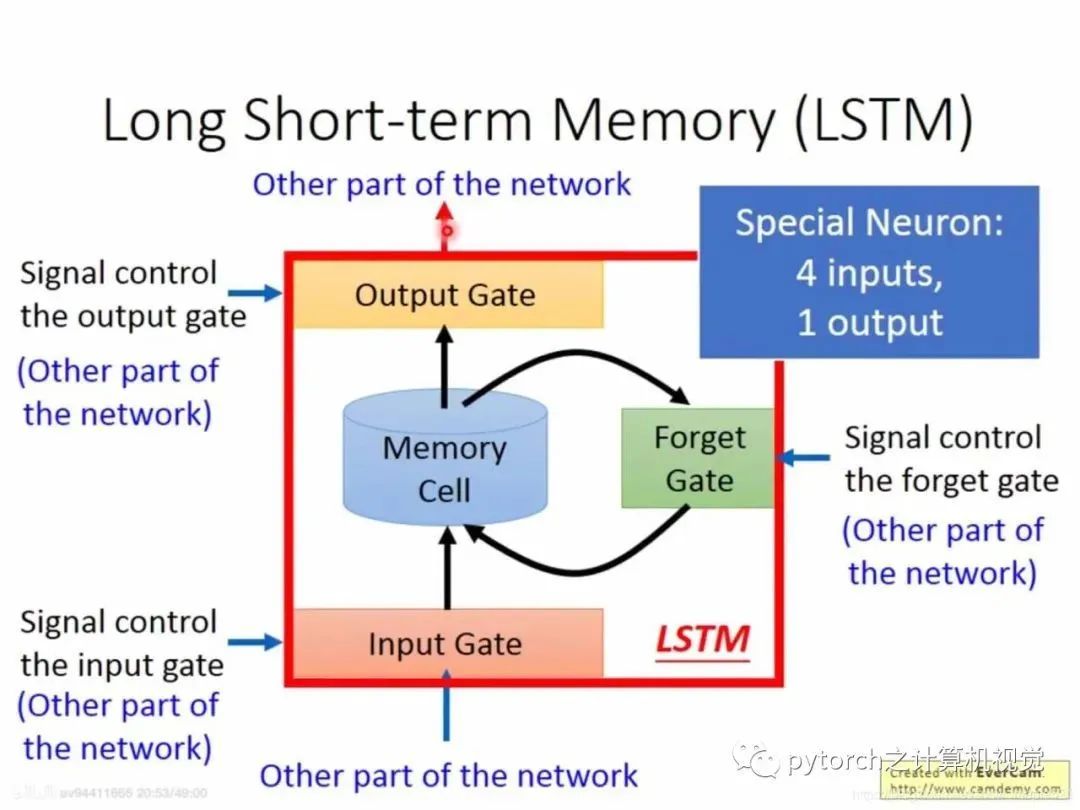
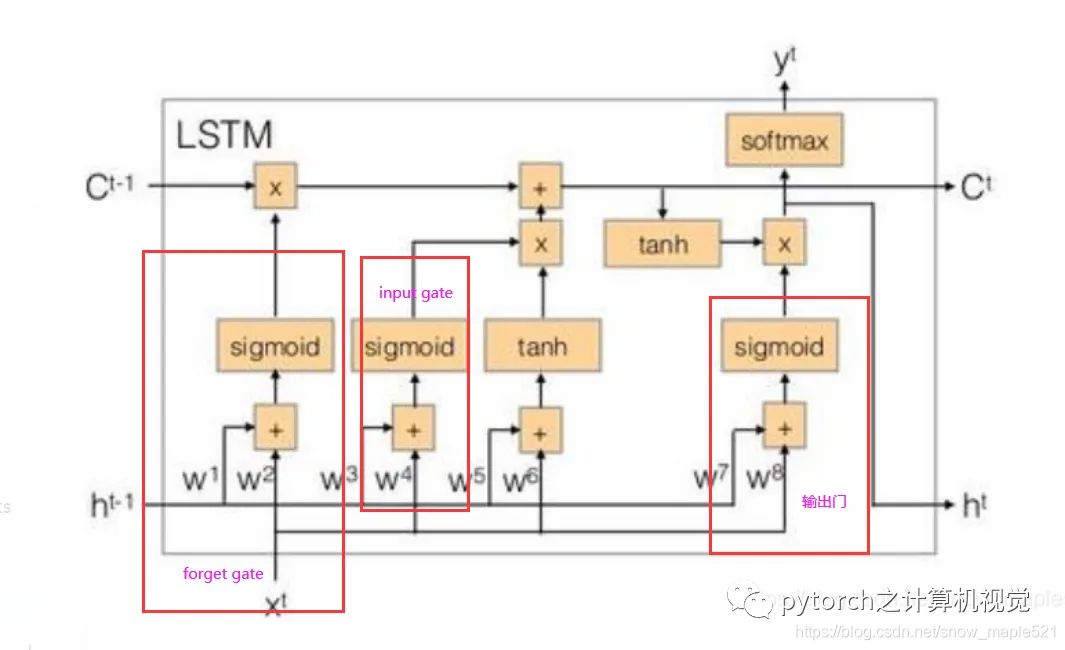
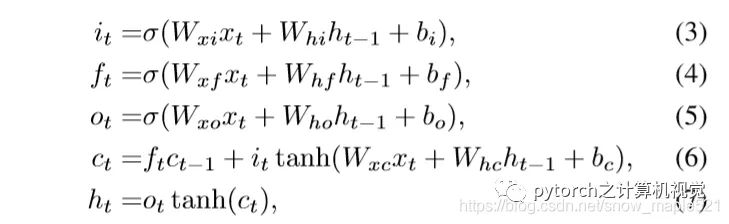
2.4 LSTM例子
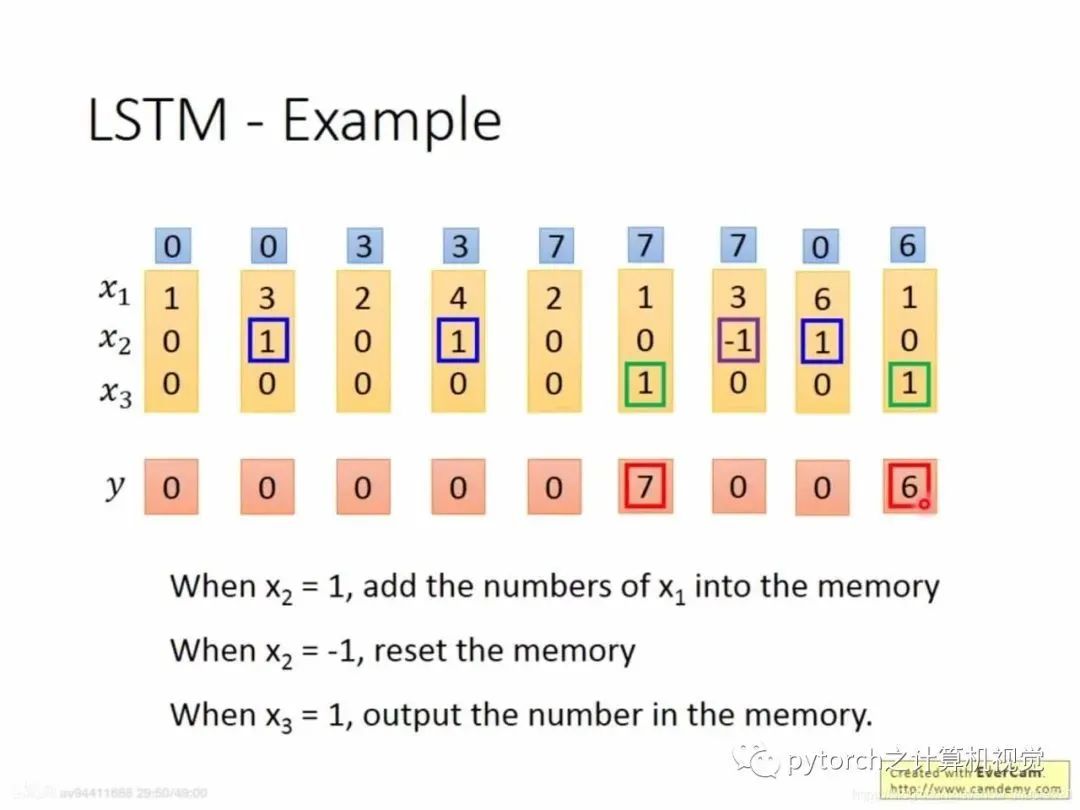
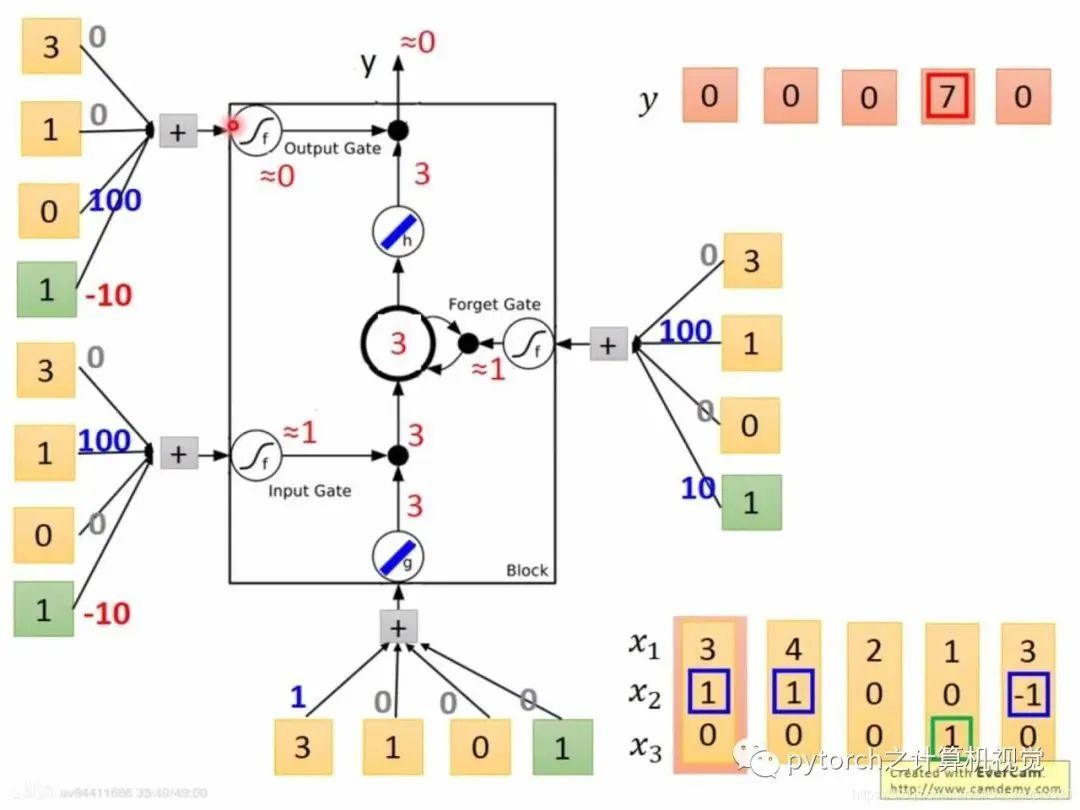
2.5 LSTM实战
class QstEncoder(nn.Module):def __init__(self, qst_vocab_size, word_embed_size, embed_size, num_layers, hidden_size):super(QstEncoder, self).__init__()self.word2vec = nn.Embedding(qst_vocab_size, word_embed_size)self.tanh = nn.Tanh()self.lstm = nn.LSTM(word_embed_size, hidden_size, num_layers)self.fc = nn.Linear(2*num_layers*hidden_size, embed_size) # 2 for hidden and cell statesdef forward(self, question):qst_vec = self.word2vec(question) # [batch_size, max_qst_length=30, word_embed_size=300]qst_vec = self.tanh(qst_vec)qst_vec = qst_vec.transpose(0, 1) # [max_qst_length=30, batch_size, word_embed_size=300]_, (hidden, cell) = self.lstm(qst_vec) # [num_layers=2, batch_size, hidden_size=512]qst_feature = torch.cat((hidden, cell), 2) # [num_layers=2, batch_size, 2*hidden_size=1024]qst_feature = qst_feature.transpose(0, 1) # [batch_size, num_layers=2, 2*hidden_size=1024]qst_feature = qst_feature.reshape(qst_feature.size()[0], -1) # [batch_size, 2*num_layers*hidden_size=2048]qst_feature = self.tanh(qst_feature)qst_feature = self.fc(qst_feature) # [batch_size, embed_size]return qst_feature
3、CNN与RNN的区别
CNN与RNN区别链接如下,引用了这个博客作者总结,(https://blog.csdn.net/lff1208/article/details/77717149)具体如下。
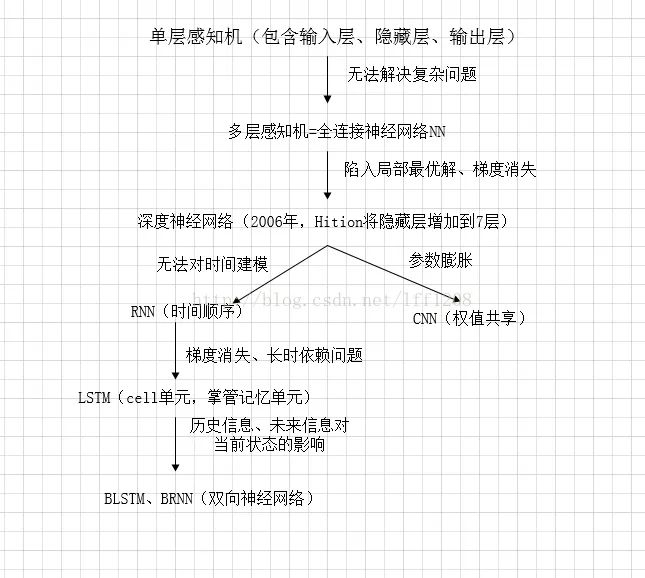
DNN形成
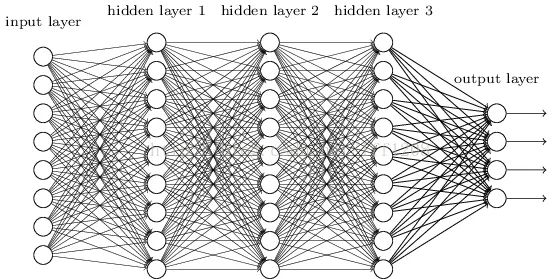
CNN形成
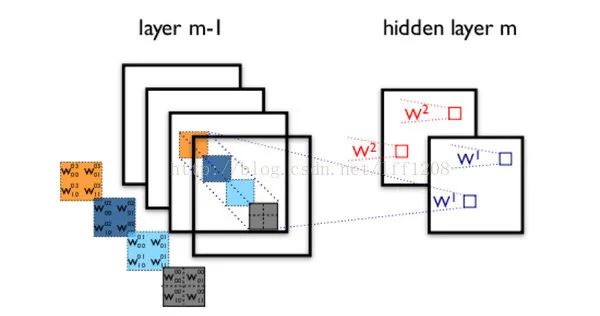
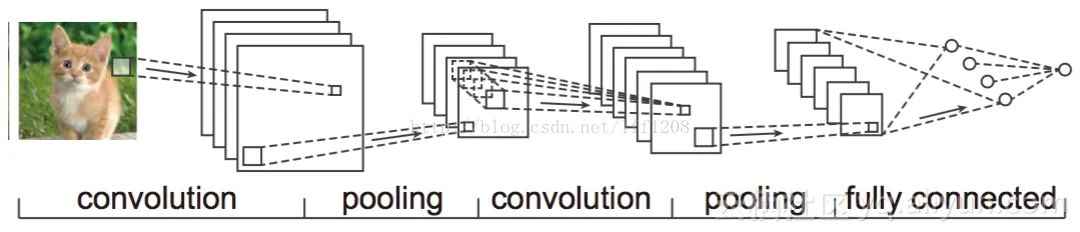
RNN形成
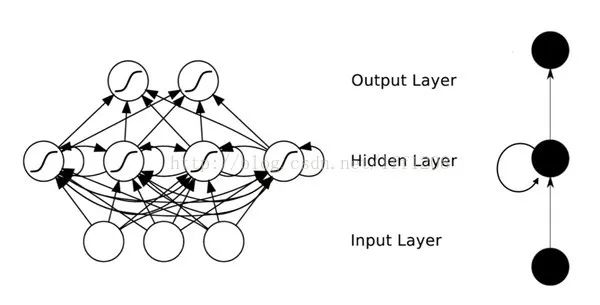
评论
