Python数学建模系列(三):规划问题之非线性规划
非线性规划
非线性规划可以简单分两种,目标函数为凸函数or非凸函数
凸函数的非线性规划,比如,有很多常用库完成,比如cvxpy
非凸函数的非线性规划(求极值),可以尝试以下方法:
纯数学方法,求导求极值 神经网络、深度学习(反向传播算法中链式求导过程) scipy. optimize. minimize
scipy.optimize.minimize(fun,x0,args=(),method=None,jac=None,hess=None,hessp=None,bounds= None,constaints=() , tol= None,Callback= None, options=None)
fun:求最小值的目标函数
args:常数值
constraints :约束条件
method:求极值方法,一 般默认。
xO:变量的初始猜测值,注意minimize是局部最优
例题 - 1
计算1/x + x 的最小值
from scipy.optimize import minimize
import numpy as np
def fun(args):
a = args
v = lambda x:a/x[0] + x[0]
return v
args = (1)
x0 = np.asarray((2))
res = minimize(fun(args), x0, method='SLSQP')
res
运行结果
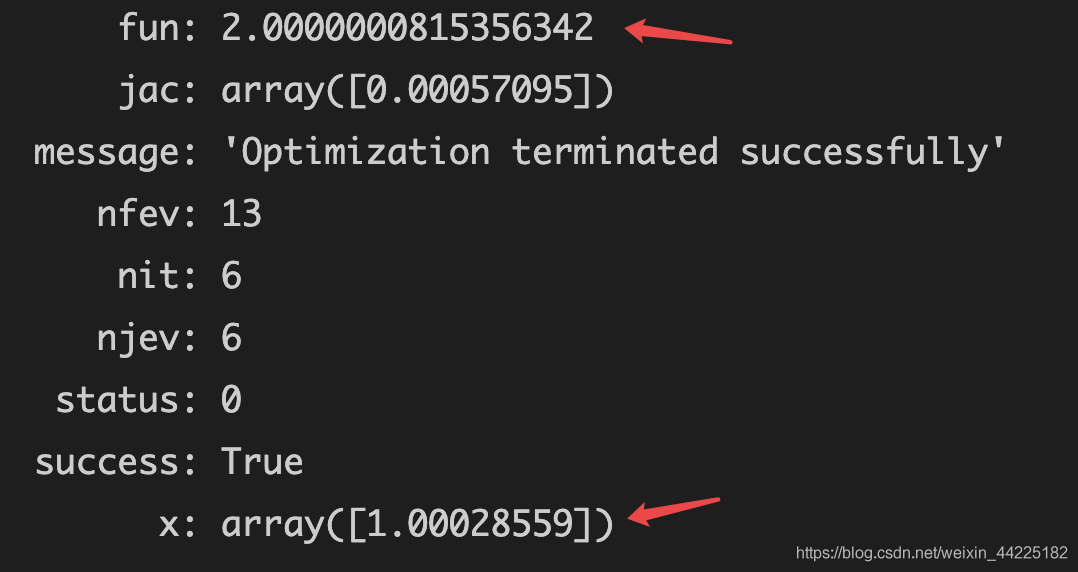
例题 - 2
计算的最小值,其中范围在0.1 到 0.9 之间
# 运行环境 Vs Code
from scipy.optimize import minimize
import numpy as np
def fun(args):
a,b,c,d = args
v = lambda x: (a + x[0]) / (b + x[1]) - c * x[0] + d * x[2]
return v
def con(args):
x1min,x1max,x2min,x2max,x3min,x3max = args
cons = ({'type':'ineq','fun':lambda x : x[0] - x1min},\
{'type':'ineq','fun':lambda x:-x[0] + x1max},\
{'type':'ineq','fun':lambda x:x[1] - x2min},\
{'type':'ineq','fun':lambda x:-x[1] + x2max},\
{'type':'ineq','fun':lambda x:x[2] - x3min},\
{'type':'ineq','fun':lambda x:-x[2] + x3max})
return cons
args = (2,1,3,4)
args1 = (0.1, 0.9,0.1, 0.9,0.1, 0.9)
cons = con(args1)
x0 = np.asarray((0.5,0.5,0.5))
res = minimize(fun(args), x0, method='SLSQP',constraints=cons)
res.fun,res.success,res.x,res.status
# 结果
(-0.773684210526435, True, array([0.9, 0.9, 0.1]), 0)
结语
学习来源:B站及其课堂PPT,对其中代码进行了复现
链接:
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV12h411d7Dm?from=search&seid=5685064698782810720
文章仅作为学习笔记,记录从0到1的一个过程
希望对您有所帮助,如有错误欢迎小伙伴指正~
评论
