【C++简明教程】Python和C++指定元素排序比较
Python 中的排序
在 Python 中,常用的排序就是 sorted ,对于列表这种数据结构来说,还有 sort 方法
列表的排序
使用 sort 方法进行排序,以第二个值进行升序排序,列表的 sort 方法是原地排序
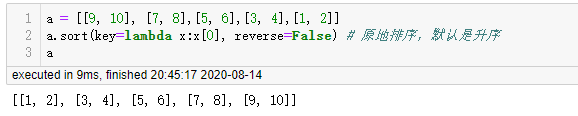 另外一种排序方法是
另外一种排序方法是 sorted ,此方法不是原地排序,以第一个值进行排序,同样也是默认升序排序
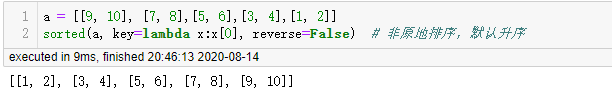
字典排序
有时候我们也需要对字典进行排序,也是使用 sorted 函数,不过对字典排序后返回的是列表,列表中是元组(tuple)
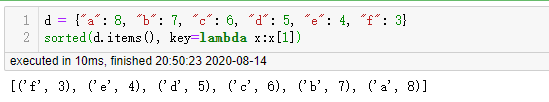
C++ 中的排序
对 vector 排序
要对 vector 容器中的元素排序,可以使用 algorithm 算法库中的 sort 函数
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<int> a;
cout << "sort before" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i <10; i++){
a.push_back(10-i);
cout << a[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "sort after" << endl;
sort(a.begin(), a.end()); //
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
cout << a[i] << " " ;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
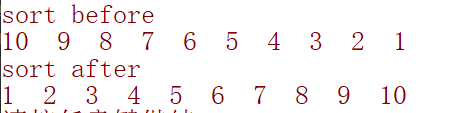
对 2 维vector 排序
类似于 Python ,我们也可以指定根据哪个元素进行排序
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
# 根据第二个元素进行排序
bool sort_by_second_val(vector<int> v1, vector<int> v2) {
return v1[1] > v2[1];
}
int main() {
// 模拟一个输入
vector < vector<int>> arr;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i+=2)
{
vector<int> temp;
temp.push_back(i);
temp.push_back(i+1);
arr.push_back(temp);
}
// 排序前:arr = [[0, 1], [2, 3], [4, 5], [6, 7],[8, 9]]
sort(arr.begin(), arr.end(), sort_by_second_val);
// 排序后:arr = [[8, 9], [6, 7], [4, 5], [2, 3],[0, 1]]
return 0;
}
对结构体进行排序
模拟一个学生管理系统,依次创建学生信息,然后加入到 vector 中,接着对学生的年龄进行排序
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
struct Studen{
string name;
int age;
};
bool sort_by_age(Studen s1, Studen s2) {
return s1.age< s2.age;
}
int main() {
vector studens; // 用来存储所有学生的信息
Studen s1, s2, s3; // 创建 3 个学生
s1.name = "xx";
s1.age = 20;
studens.push_back(s1);
s2.name = "yy";
s2.age = 18;
studens.push_back(s2);
s3.name = "zz";
s3.age = 10;
studens.push_back(s3);
sort(studens.begin(), studens.end(), sort_by_age);
return 0;
}
排序前
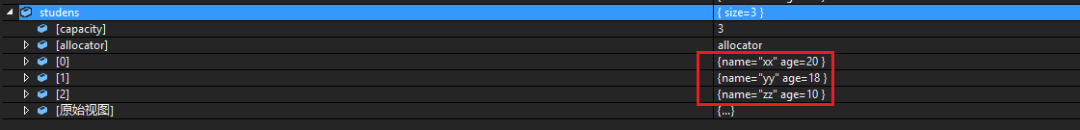
排序后
往期精彩回顾
获取一折本站知识星球优惠券,复制链接直接打开:
https://t.zsxq.com/662nyZF
本站qq群1003271085。
加入微信群请扫码进群(如果是博士或者准备读博士请说明):
评论
