『每周译Go』手把手教你用 Go 实现一个 mTLS
想知道什么是 mTLS(双向 TLS)?来吧,让我们用 Golang 和 OpenSSL 实现一个 mTLS。
介绍
TLS(安全传输层协议简称)为网络通信的应用程序提供必要的加密。HTTPS (超文本安全协议) 是 HTTP 的一种扩展,利用 TLS 实现安全性。TLS 技术要求 CA (证书颁发机构) 向服务颁发 X.509 数字证书,然后将该数字证书移交给服务的消费者,由其使用 CA 本身进行验证。mTLS 将同样的思想扩展到应用程序中,例如,在微服务中,提供者和消费者都需要向对方生成自己的证书。这些证书由双方使用各自的 CA 进行验证。一旦经过验证,服务器/客户端或提供者/使用者之间的通信就会安全地进行。
实现
第一步 - 构建一个简单的 HTTP 服务端和客户端
让我们先 在server.go 里创建一个简单的 HTTP 服务,当访问 8080 端口,请求 /hello 资源时回复 Hello, world!
package main
import (
"io"
"log"
"net/http"
)
func helloHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// Write "Hello, world!" to the response body
io.WriteString(w, "Hello, world!\n")
}
func main() {
// Set up a /hello resource handler
http.HandleFunc("/hello", helloHandler)
// Listen to port 8080 and wait
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil))
}
客户端通过 8080 端口请求 /hello 资源,然后将响应体通过 stdout 打印。下面是 client.go 代码:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"log"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
// Request /hello over port 8080 via the GET method
r, err := http.Get("http://localhost:8080/hello")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// Read the response body
defer r.Body.Close()
body, err := ioutil.ReadAll(r.Body)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// Print the response body to stdout
fmt.Printf("%s\n", body)
}
打开一个终端并运行服务端:
go run -v server.go
打开另外一个终端运行客户端:
go run -v client.go
你可以从客户端看到以下输出:
Hello, world!
第二步 - 生成和使用服务端证书
使用以下命令生成证书。该命令将创建一个有效期为 10 年的 2048 位密钥证书。此外,CN=localhost 说明该证书对 localhost 域是有效的。
openssl req -newkey rsa:2048 \
-new -nodes -x509 \
-days 3650 \
-out cert.pem \
-keyout key.pem \
-subj "/C=US/ST=California/L=Mountain View/O=Your Organization/OU=Your Unit/CN=localhost"
你应该目录里面有 cert.pem 和 key.pem 证书了。
现在让我们启用服务器 HTTP 的 TLS,也就是 HTTPS。server.go 里面的 http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil) 调用替换成 http.ListenAndServeTLS(":8443", "cert.pem", "key.pem", nil) ,通过 8443 端口监听链接。同时提供前面生成的证书。
-// Listen to port 8080 and wait
-log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil))
+// Listen to HTTPS connections on port 8443 and wait
+log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServeTLS(":8443", "cert.pem", "key.pem", nil))
你可以通过运行并在浏览器输入 https://localhost:8443/hello 来验证服务器是否工作。
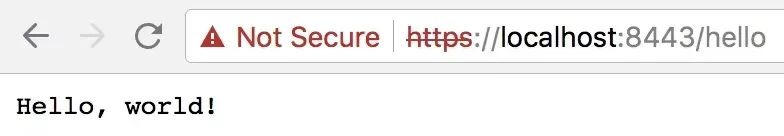
现在我们更新 client.go 代码来通过 HTTPS 连接服务端。
-// Request /hello over port 8080 via the GET method
-r, err := http.Get("http://localhost:8080/hello")
+// Request /hello over HTTPS port 8443 via the GET method
+r, err := http.Get("https://localhost:8443/hello")
由于我们客户端还不知道证书,直接运行服务器会显示下面的错误:
http: TLS handshake error from [::1]:59436: remote error: tls: bad certificate
在客户端,你需要注意以下几点:
x509: certificate is not valid for any names, but wanted to match localhost
第三步- 向客户端提供证书
更新 client.go 代码读取之前生成的证书,代码如下:
-// Request /hello over HTTPS port 8443 via the GET method
-r, err := http.Get("https://localhost:8443/hello")
+// Create a CA certificate pool and add cert.pem to it
+caCert, err := ioutil.ReadFile("cert.pem")
+if err != nil {
+log.Fatal(err)
+}
+caCertPool := x509.NewCertPool()
+caCertPool.AppendCertsFromPEM(caCert)
+
+// Create a HTTPS client and supply the created CA pool
+client := &http.Client{
+Transport: &http.Transport{
+TLSClientConfig: &tls.Config{
+RootCAs: caCertPool,
+},
+},
+}
+
+// Request /hello via the created HTTPS client over port 8443 via GET
+r, err := client.Get("https://localhost:8443/hello")
这里,我们读取 cert.pem 文件并在创建客户端时提供根 CA 。运行客户端现在应该可以成功显示以下内容:
Hello, world!
最后一步 - 启用 mTLS
在客户端,读取并提供密钥对作为客户端证书。
+// Read the key pair to create certificate
+cert, err := tls.LoadX509KeyPair("cert.pem", "key.pem")
+if err != nil {
+log.Fatal(err)
+}
...
-// Create a HTTPS client and supply the created CA pool
+// Create a HTTPS client and supply the created CA pool and certificate
client := &http.Client{
Transport: &http.Transport{
TLSClientConfig: &tls.Config{
RootCAs: caCertPool,
+Certificates: []tls.Certificate{cert},
},
},
}
在服务端,我们创建一个类似于 CA 池 ,并将其提供给 TLS 配置,来作为验证客户端证书的权威。我们还对服务器证书使用相同的密钥对。
-// Listen to HTTPS connections on port 8443 and wait
-log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServeTLS(":8443", "cert.pem", "key.pem", nil))
+// Create a CA certificate pool and add cert.pem to it
+caCert, err := ioutil.ReadFile("cert.pem")
+if err != nil {
+log.Fatal(err)
+}
+caCertPool := x509.NewCertPool()
+caCertPool.AppendCertsFromPEM(caCert)
+
+// Create the TLS Config with the CA pool and enable Client certificate validation
+tlsConfig := &tls.Config{
+ClientCAs: caCertPool,
+ClientAuth: tls.RequireAndVerifyClientCert,
+}
+tlsConfig.BuildNameToCertificate()
+
+// Create a Server instance to listen on port 8443 with the TLS config
+server := &http.Server{
+Addr: ":8443",
+TLSConfig: tlsConfig,
+}
+
+// Listen to HTTPS connections with the server certificate and wait
+log.Fatal(server.ListenAndServeTLS("cert.pem", "key.pem"))
先 运行 server.go 然后运行 client.go,然后你可以在客户端上看到如下一条成功的消息:
Hello, world!
完整代码
最终, server.go 代码如下:
package main
import (
"crypto/tls"
"crypto/x509"
"io"
"io/ioutil"
"log"
"net/http"
)
func helloHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// Write "Hello, world!" to the response body
io.WriteString(w, "Hello, world!\n")
}
func main() {
// Set up a /hello resource handler
http.HandleFunc("/hello", helloHandler)
// Create a CA certificate pool and add cert.pem to it
caCert, err := ioutil.ReadFile("cert.pem")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
caCertPool := x509.NewCertPool()
caCertPool.AppendCertsFromPEM(caCert)
// Create the TLS Config with the CA pool and enable Client certificate validation
tlsConfig := &tls.Config{
ClientCAs: caCertPool,
ClientAuth: tls.RequireAndVerifyClientCert,
}
tlsConfig.BuildNameToCertificate()
// Create a Server instance to listen on port 8443 with the TLS config
server := &http.Server{
Addr: ":8443",
TLSConfig: tlsConfig,
}
// Listen to HTTPS connections with the server certificate and wait
log.Fatal(server.ListenAndServeTLS("cert.pem", "key.pem"))
}
client.go 代码如下:
package main
import (
"crypto/tls"
"crypto/x509"
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"log"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
// Read the key pair to create certificate
cert, err := tls.LoadX509KeyPair("cert.pem", "key.pem")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// Create a CA certificate pool and add cert.pem to it
caCert, err := ioutil.ReadFile("cert.pem")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
caCertPool := x509.NewCertPool()
caCertPool.AppendCertsFromPEM(caCert)
// Create a HTTPS client and supply the created CA pool and certificate
client := &http.Client{
Transport: &http.Transport{
TLSClientConfig: &tls.Config{
RootCAs: caCertPool,
Certificates: []tls.Certificate{cert},
},
},
}
// Request /hello via the created HTTPS client over port 8443 via GET
r, err := client.Get("https://localhost:8443/hello")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// Read the response body
defer r.Body.Close()
body, err := ioutil.ReadAll(r.Body)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// Print the response body to stdout
fmt.Printf("%s\n", body)
}
结论
Golang 让实现 mTLS 变得非常容易,而且不到 100 行代码。
我很想听听你的意见。
原文信息
原文地址:https://venilnoronha.io/a-step-by-step-guide-to-mtls-in-go
原文作者:Venil Noronha
本文永久链接:https://github.com/gocn/translator/blob/master/2021/w44_A_step_by_step_guide_to_mTLS_in_Go.md
译者:朱亚光
校对:
想要了解关于 Go 的更多资讯,还可以通过扫描的方式,进群一起探讨哦~
