【43期】盘点那些必问的数据结构算法题之二叉树基础
程序员的成长之路
共 8496字,需浏览 17分钟
·
2020-09-21 17:11
阅读本文大概需要 7 分钟。
来自:juejin.im/post/5ba3bb52e51d450e942f3031
0 概述
若任意结点的左子树不空,则左子树上所有节点的值均小于它的根节点的值;
若任意结点的右子树不空,则右子树上所有节点的值均大于或等于它的根节点的值;(有些书里面定义为BST不能有相同值结点,本文将相同值结点插入到右子树)
任意结点的左、右子树也分别为二叉查找树;
1 定义
typedef struct BTNode {
int value;
struct BTNode *left;
struct BTNode *right;
} BTNode;
2 基本操作
1) 创建结点
/**
* 创建BTNode
*/
BTNode *newNode(int value)
{
BTNode *node = (BTNode *)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
node->value = value;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
2) BST 插入结点
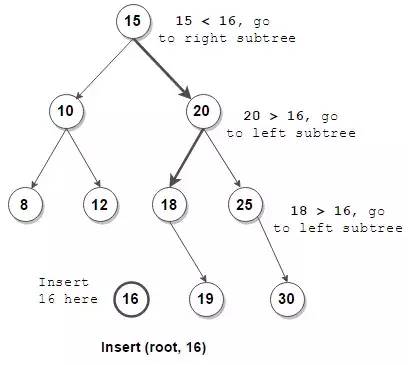
/**
* BST中插入值,递归方法
*/
/**
* BST中插入结点,递归方法
*/
BTNode *bstInsert(BTNode *root, int value)
{
if (!root)
return newNode(value);
if (root->value > value) {
root->left = bstInsert(root->left, value);
} else {
root->right = bstInsert(root->right, value);
}
return root;
}
/**
* BST中插入结点,非递归方法
*/
BTNode *bstInsertIter(BTNode *root, int value)
{
BTNode *node = newNode(value);
if (!root)
return node;
BTNode *current = root, *parent = NULL;
while (current) {
parent = current;
if (current->value > value)
current = current->left;
else
current = current->right;
}
if (parent->value >= value)
parent->left = node;
else
parent->right = node;
return root;
}
3) BST 删除结点
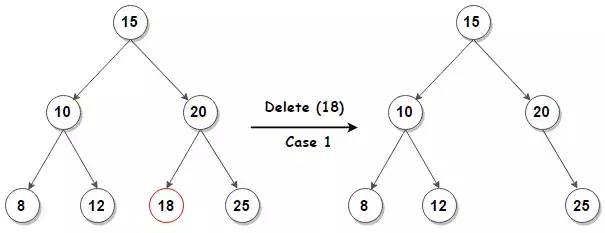
/**
* BST中删除结点
*/
BTNode *bstDelete(BTNode *root, int value)
{
BTNode *parent = NULL, *current = root;
BTNode *node = bstSearchIter(root, &parent, value);
if (!node) {
printf("Value not found\n");
return root;
}
if (!node->left && !node->right) {
// 情况1:待删除结点是叶子结点
if (node != root) {
if (parent->left == node) {
parent->left = NULL;
} else {
parent->right = NULL;
}
} else {
root = NULL;
}
free(node);
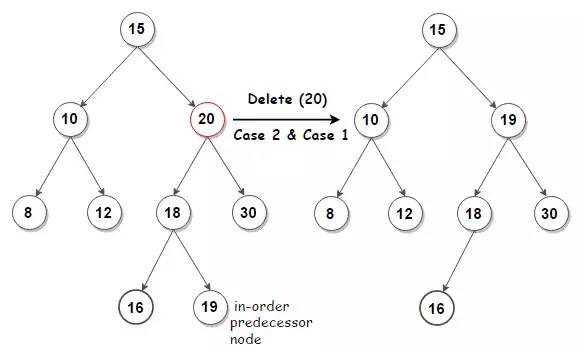
} else if (node->left && node->right) {
// 情况2:待删除结点有两个子结点
BTNode *predecessor = bstMax(node->left);
bstDelete(root, predecessor->value);
node->value = predecessor->value;
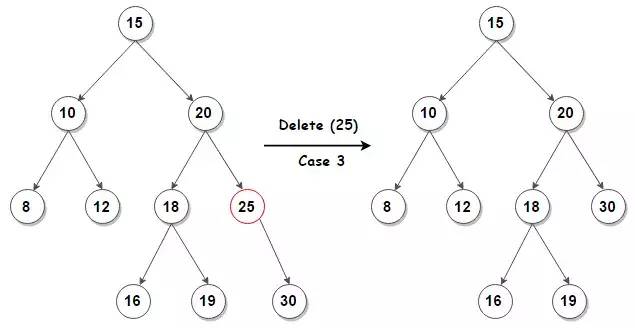
} else {
// 情况3:待删除结点只有一个子结点
BTNode *child = (node->left) ? node->left : node->right;
if (node != root) {
if (node == parent->left)
parent->left = child;
else
parent->right = child;
} else {
root = child;
}
free(node);
}
return root;
}
4) BST 查找结点
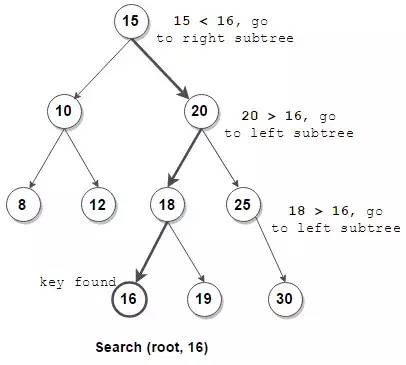
/**
* BST查找结点-递归
*/
BTNode *bstSearch(BTNode *root, int value)
{
if (!root) return NULL;
if (root->value == value) {
return root;
} else if (root->value > value) {
return bstSearch(root->left, value);
} else {
return bstSearch(root->left, value);
}
}
/**
* BST查找结点-非递归
*/
BTNode *bstSearchIter(BTNode *root, BTNode **parent, int value)
{
if (!root) return NULL;
BTNode *current = root;
while (current && current->value != value) {
*parent = current;
if (current->value > value)
current = current->left;
else
current = current->right;
}
return current;
}
5)BST 最小值结点和最大值结点
/**
* BST最小值结点
*/
BTNode *bstMin(BTNode *root)
{
if (!root->left)
return root;
return bstMin(root->left);
}
/**
* BST最大值结点
*/
BTNode *bstMax(BTNode *root)
{
if (!root->right)
return root;
return bstMax(root->right);
}
6)二叉树结点数目和高度
/**
* 二叉树结点数目
*/
int btSize(BTNode *root)
{
if (!root) return 0;
return btSize(root->left) + btSize(root->right) + 1;
}
/**
* 二叉树高度
*/
int btHeight(BTNode *root)
{
if (!root) return 0;
int leftHeight = btHeight(root->left);
int rightHeight = btHeight(root->right);
int maxHeight = leftHeight > rightHeight ? leftHeight+1 : rightHeight+1;
return maxHeight;
}
3 二叉树遍历
递归遍历-先序、中序、后序、层序
/**
* 二叉树先序遍历
*/
void preOrder(BTNode *root)
{
if (!root) return;
printf("%d ", root->value);
preOrder(root->left);
preOrder(root->right);
}
/**
* 二叉树中序遍历
*/
void inOrder(BTNode *root)
{
if (!root) return;
inOrder(root->left);
printf("%d ", root->value);
inOrder(root->right);
}
/**
* 二叉树后序遍历
*/
void postOrder(BTNode *root)
{
if (!root) return;
postOrder(root->left);
postOrder(root->right);
printf("%d ", root->value);
}
/**
* 二叉树层序遍历
*/
void levelOrder(BTNode *root)
{
int btHeight = height(root);
int level;
for (level = 1; level <= btHeight; level++) {
levelOrderInLevel(root, level);
}
}
/**
* 二叉树层序遍历辅助函数-打印第level层的结点
*/
void levelOrderInLevel(BTNode *root, int level)
{
if (!root) return;
if (level == 1) {
printf("%d ", root->value);
return;
}
levelOrderInLevel(root->left, level-1);
levelOrderInLevel(root->right, level-1);
}
非递归遍历-先序、中序、后序、层序
非递归遍历里面先序遍历最简单,使用一个栈来保存结点,先访问根结点,然后将右孩子和左孩子依次压栈,然后循环这个过程。中序遍历稍微复杂一点,需要先遍历完左子树,然后才是根结点,最后才是右子树。
后序遍历使用一个栈的方法postOrderIter()会有点绕,也易错。所以在面试时推荐用两个栈的版本postOrderIterWith2Stack(),容易理解,也比较好写。
层序遍历用了队列来辅助存储结点,还算简单。
/*********************/
/** 二叉树遍历-非递归 **/
/*********************/
/**
* 先序遍历-非递归
*/
void preOrderIter(BTNode *root)
{
if (!root) return;
int size = btSize(root);
BTNodeStack *stack = stackNew(size);
push(stack, root);
while (!IS_EMPTY(stack)) {
BTNode *node = pop(stack);
printf("%d ", node->value);
if (node->right)
push(stack, node->right);
if (node->left)
push(stack, node->left);
}
free(stack);
}
/**
* 中序遍历-非递归
*/
void inOrderIter(BTNode *root)
{
if (!root) return;
BTNodeStack *stack = stackNew(btSize(root));
BTNode *current = root;
while (current || !IS_EMPTY(stack)) {
if (current) {
push(stack, current);
current = current->left;
} else {
BTNode *node = pop(stack);
printf("%d ", node->value);
current = node->right;
}
}
free(stack);
}
/**
* 后续遍历-使用一个栈非递归
*/
void postOrderIter(BTNode *root)
{
BTNodeStack *stack = stackNew(btSize(root));
BTNode *current = root;
do {
// 移动至最左边结点
while (current) {
// 将该结点右孩子和自己入栈
if (current->right)
push(stack, current->right);
push(stack, current);
// 往左子树遍历
current = current->left;
}
current = pop(stack);
if (current->right && peek(stack) == current->right) {
pop(stack);
push(stack, current);
current = current->right;
} else {
printf("%d ", current->value);
current = NULL;
}
} while (!IS_EMPTY(stack));
}
/**
* 后续遍历-使用两个栈,更好理解一点。
*/
void postOrderIterWith2Stack(BTNode *root)
{
if (!root) return;
BTNodeStack *stack = stackNew(btSize(root));
BTNodeStack *output = stackNew(btSize(root));
push(stack, root);
BTNode *node;
while (!IS_EMPTY(stack)) {
node = pop(stack);
push(output, node);
if (node->left)
push(stack, node->left);
if (node->right)
push(stack, node->right);
}
while (!IS_EMPTY(output)) {
node = pop(output);
printf("%d ", node->value);
}
}
/**
* 层序遍历-非递归
*/
void levelOrderIter(BTNode *root)
{
if (!root) return;
BTNodeQueue *queue = queueNew(btSize(root));
enqueue(queue, root);
while (1) {
int nodeCount = QUEUE_SIZE(queue);
if (nodeCount == 0)
break;
btHeight
while (nodeCount > 0) {
BTNode *node = dequeue(queue);
printf("%d ", node->value);
if (node->left)
enqueue(queue, node->left);
if (node->right)
enqueue(queue, node->right);
nodeCount--;
}
printf("\n");
}
}
推荐阅读:
微信扫描二维码,关注我的公众号
朕已阅 
评论

